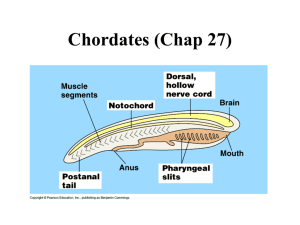
INVERTEBRATES p.1
advertisement

INVERTEBRATES p.1 ORGANISM Common name Scientific name examples SPONGE (Porifera) “Pore-filled” CNIDARIA (Cnidaria) “Stinging Cell” Hydra or Jelly FLATWORM (Platyhelminthes) Planaria NERVOUS BODY PLAN Symmetry, Tissue layers Coelom? ? ____________, ______ tissues, ___body cavity. Nerve net. Allows for coordinated motion in one direction. _____?______ symmetry ?_tissue layers, _?_ body cavity, polyp and medusa = (bell) Nerve _____, Planaria have eye_____, nerve clusters in head. ROUNDWORM (Nematoda) Ascaris _____ ladder, nerve clusters in _______. SEGMENTED WORMS (Annelida) Earthworm, leech Brain, ventral nerve cord, cluster of nerves in each segment. LOCOMOTION/ Skeletal Sessile/ Spongin, Spicules REPRODUCTIVE Sexual: egg and sperm, common release of gametes into water. “Baby” sponges freeswimming until settled, then sessile. EXCRETORY Food-getting, DIGESTIVE CIRCULATORY GAS EXCHANGE _____cytosis _________feeders or ______ feeders, _________cytes or collar cells trap food, _______cytosis _______cytes ? Carnivores use nematocysts ( ? = poison harpoon) and ________ to subdue and push prey into ________. _________. cavity ____-filled layer between tissue layers have scattered _________. ? Simple________ tissue/ _____skeleton Asexual by________, Sexual: common release of _________into water. Waste exits through_______, ____-way digestive system. ___________ symmetry, ___body cavity. ____ for forward motion, _______ to twist and turn. Hermaphroditic: Each individual has ______ ____________________ but impregnates another planarian. Reproductive organs take up nearly entire interior of parasitic flatworms. Repeated units break off with mature eggs. Planaria: ___way system, mouth serves as anus. Parasitic absorb what is needed. No need for excretion. Planaria: Two-way, ________________ cavity branches for distribution, _____-tube projects from mid-ventral. _________ & ____________ are parasitic with suckers & hooks: scolex, no mouth. ? diffusion ? ? ? L____________ muscle contraction creates _______ motion / ______________ acts as a hydroskeleton C. elegans adult has only_____ cells. Development followed by researchers. How _____ control development. _____-way: mouth to anus, allows for specialization, increased efficiency of digestive tract. Parasitic: have cuticle to protect from ________ ____ of host. _________ intestine secretes and mixes with enzymes. Posterior ___?____. Absorption of nutrients by pseudocoelo m distributes ? ? ? ? segmented body. Longitudinal + ______ muscles work against coelomic fluid: ______skeleton. Bristles. H____________: mate with another. Easier to locate “another” than 1 in every two worms. M________-secreting organ. Excretory organs called________, in each segment, eliminate fluid waste. Solid waste called _____________. M__________, C__________, G__________, I___________, (continuous, not segmented) ___________ System Blood remains enclosed in vessels. __________ across epidermis. C_________ system assists diffusion. INVERTEBRATES p.2 ORGANISM MOLLUSC (Mollusca) NERVOUS BODY PLAN X Classes: Gastropod: snail Bivalve: clam “two folding doors” Cephalopod: “head/foot”: squid ARTHROPOD (Arthropoda) “Jointed foot” Head with _______ on tentacles Crustacea Arachnida (chilicerates) ECHINODERM (Echinodermata) “Spiney Skin” Sea Star, Sea Urchin ? Muscular foot, M_______: “soft body” most have hard shell secreted by the ___________. Single, spiral _____, retreat. Slugs & sea slugs have _____________. ? Nerve cords _______ eyes _____-part shell Muscular ____. ______ brain, sense organs, _______ eyes _________-jet propulsion, Directional _____ & tentacles ?, ?, ?. Eyes, jointed mouth parts Classes: Insecta ? LOCOMOTION / Skeletal Antennae? Antennae? Antennae? No brain, Sea star has _________ at the tip of each ray. Embryonic Arthropods all have head, thorax, abdomen. All have _______ appendages, ___skeleton, which must _____ for growth. REPRODUCTIVE EXCRETORY Food-getting, DIGESTIVE Gills in ___________ _________. R_______ = scrapes food like algae Lack _______, mantle lining is lung-like. Complete ___________ ___________ is called a trochophore _____________ Separate sexes _____________ with specialization along length. Separate sexes Internal fertilization, Lay eggs Complete digestive systems System Gills _____-like jaw, radula. _______ Complete digestive systems X Complete and _____________ metamorphosis, both include molting X X Adult has: __________ __________. ___ pairs legs X X X X Many spiders make webs, scorpions hunt at night and use a poison barb to ____________ prey. Anus on dorsal?/ventral? side of sea star Uses __________ to open shells. Mouth on ________ side of sea star, turns stomach_________, digestive enzymes, absorbs jelly mass. Larva:_________ symmetry; Adults ______, _______ tissue layers, _______ coelom ____ feet, water vascular system, / ____skeleton. spiny protrusions from endoskeleton give rough skin X Separate sexes. Can ___________ some body parts, not asexual reproduction. _______ S________ feeders. Gills absorb food too Mucus + cilia ___ pairs legs, most have ____, ___ pairs legs, most have ____, GAS EXCHANGE X Adult has: Head, ______ __________. Adult has: Head, ______ __________. CIRCULAT ORY Open circulatory system, short arteries with spaces surrounding organs Spiracles + tracheae, gills Book lung Diffusion from __________ __________ ___________ from pyloric cecum