Anatomy and Physiology II Exam I
advertisement

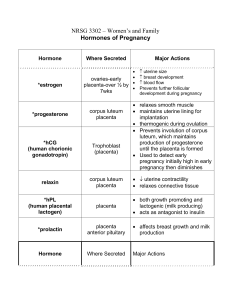
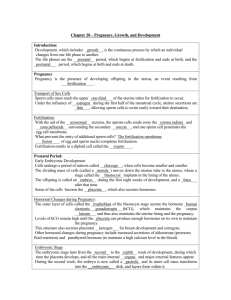
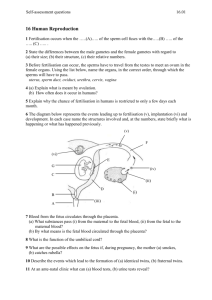
Anatomy and Physiology II Exam I What term refers to a cell's ability to become any other cell in the developing embryo? What do we call the liquid in the womb that surrounds the fetus and protects it from jarring movements of the mother? The period of development at the beginning, during which the contents of the zygote are divided initially into smaller and smaller cells, is called? The slender, tree-like projections that grow out from the base of the trophoblast/chorion into the uterine wall are called what? The umbilical artery transports oxygen ___________ blood, and the umbilical vein transports oxygen ___________ blood? What is each one of the Germ Layers responsible for forming? What term refers to the incubation period of a pregnancy? What term refers to the actual birthing process itself? What term refers to the production and secretion of milk by the mammary glands? Actual ejection and release of milk from the mammary glands, through the nipple, is known as? What term describes process of the enfolding of the endoderm to form the digestive tube? What do we call the first thin, watery fluid produced by the mammary glands and it is important because it contains what? What do we call the process where an egg and associated cells are released from an ovarian follicle? What do we call the structure that helps form the digestive tract and give rise to future sex cells? What two tissues technically compose the placenta? Identify, what is the normal site of fertilization? A fertilized egg is called what? How many sperm typically fertilize one egg? A solid ball of cells indicates what stage of development? During pregnancy, estrogen levels _________ and progesterone levels _________? Which of the hormones maintains the corpus luteum during pregnancy? Which structure will form the fetal portion of the placenta? During early pregnancy, the corpus luteum secretes what hormones? Which hormones will be inhibited during pregnancy? Identify, what is the initial site for the formation of fetal blood cells in a fetus? By what process does the exchange of oxygen occur between maternal and fetal circulation? In fetal circulation, what two things allow blood to bypass the lungs by flowing through the? Which structure shunts fetal blood from the right atrium directly to the left atrium? Which structure shunts blood from the pulmonary trunk to the aorta? What hormone stimulates milk production after the fetus is born, and what hormone stimulates milk release or letdown from the breast’s mammary glands? Which hormone promotes uterine smooth muscle contractions? What are the functions of estrogen and progesterone that are secreted from the placenta during pregnancy? The cells of the blastocyst that give rise to the body of the developing embryo constitute the? The corpus luteum, though considered a separate structure, is found inside what gland? Which structure will form the maternal portion of the placenta? Which of the following structures will eventually form the chorion? Which structure allows about half of the fetal umbilical blood supply to bypass the liver? Which hormone is produced by the corpus luteum to inhibit uterine smooth muscle contractions? Whenever an embryonic cell mass implants in tissues outside the uterus it is referred to as a? The stage of development where the solid ball of cells becomes a hollow ball of cells is called the? What are the functions of HCG? The pockets of maternal blood surrounding the chorionic villi are called what? The primary embryonic germ layers are derived from the initial? The amnion membrane is an outgrowth from what structure? The fetal stage of development begins at the end of the _______ week? Which of the following can be used to determine if a woman is pregnant? Does the implantation of the embryo get aided by digestive enzymes secreted by the trophoblast? How many veins and arteries does the umbilical cord contain? Does the amniotic fluid provide nourishment or absorb/remove wastes? About when does the placenta secrete estrogen? Which hormone are home pregnancy tests keyed to detect? Approximately how long is a normal gestational period? Does fetal blood have a higher or lower capacity to carry oxygen? Does maternal blood and fetal blood ever mix? Match the hormone with its function(s). A. Aldosterone B. Progesterone C. Estrogen D. Parathyroid hormone E. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin AB. Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin AC. Inhibin AD. Prostaglandins 1. Decreases uterine contractions and increases secretions by the uterine tubes and uterus, stimulates development of decidua cells. 2. Increases renal reabsorption of sodium leading to fluid retention. 3. Produced by the ovaries to aid in inhibiting FSH production 4. Increases the size of the uterus, breasts, and external genitalia. 5. Produced by cells to start labor, increase uterine contractions and control pain. 6. Only hormone produced while a woman is pregnant as a result of pregnancy. 7. Maintains higher calcium levels in maternal blood, prevents hypocalcaemia. 8. Actions similar to growth hormone, partial breast development, dropped maternal glucose levels, promotes release of fatty acids. Short Answer Place the following in chronological order: blastocyst (blastula), cleavage, embryo, morula, zygote, gastrula, and fetus. What would happen (include as many physiological effects as you can) if the corpus luteum was NOT maintained by HCG in the body?