Questions
advertisement

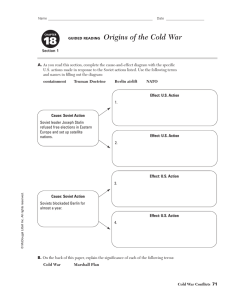
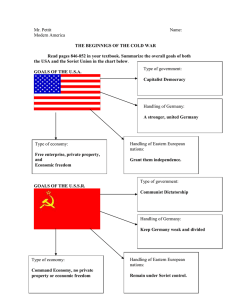
Questions • Why did the United States and Soviet Union become enemies after WWII? • How did the rivalry between the two nations affect Europe and Asia? • Why did Communism collapse in the Soviet Union? From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and, in many cases, increasing measure of control from Moscow. Winston Churchill- March 5, 1946 in Speech in Missouri The Cold War After the Second World War • Yalta, Feb. 1945 Arrangements made for occupied territories, including holding of elections – Soviet army ensured communist governments took power in E. Europe • Germany divided into 4 zones; Soviets controlled east. • United Nations established • Soviet Union obtained Abomb by 1949, U.S./European Security threatened Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin at Yalta A Bi-polar World • ‘Iron Curtain’ – USSR imposed communist govt’s. on E Europe • Truman Doctrine: U.S. would try to ‘contain’ communism – Support for govt. in Greece • 1948 Berlin Airlift • 1949 North Atlantic Treaty Organization created to stop Spread of Communism in Europe (NATO) • 1955 E. European nations and USSR sign Warsaw Pact The Berlin Airlift The Berlin Airlift is considered the first victory for the west in the Cold War. “IRON CURTAIN” Following WWII, E. Germany, Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria signed the Warsaw Pact with Russia. This created what was called the Eastern Block of the USSR. These countries were considered independent satellite states, although in reality they were under the control of the USSR. Cold War Europe After WWII the United States sought to relieve some of the suffering in Europe through economic aid called the Marshall Plan. This aid package included the rebuilding of Germany, which Stalin saw as a threat. MARSHALL PLAN NATO & Warsaw Pact Rising Tension The Berlin Wall • 1953 Stalin died – Nikita Khrushchev (18941971) eventually was named as his successor • 1956- Uprising in Hungary crushed by Soviet Tanks • 1957 Sputnik • 1961 The Berlin Wall was built • 1962 Cuban Missile Crisis • 1964 Khrushchev removed from power • 1968 Prague Spring- Czech reforms to gov., Soviets stomped it out with military. 1961 Berlin Wall Erected USSR built the Berlin Wall, 1960’s Stated purpose was to keep capitalists out, was really to keep people from leaving communist controlled area. Berlin Wall was centerpiece of Cold War and idea of Iron Curtain. E A S T W E S T “EAST LOOKING WEST” “SOME MADE IT.” 45000 40000 35000 30000 25000 US USSR 20000 15000 10000 5000 0 1945 1950 1955 1960 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 Total number of nuclear weapons, 1945-1990 Source: Norris and Arkin, Bulletin of Atomic Scientists 50 (1994), 58-9 The Cold War in Asia • 1949 Chinese Communists defeat Nationalists – Oct. 1, 1949 People’s Republic of China founded – Mao Zedong (1893-1976) • 1950-1953 Korean War North (Comm) v. South (Dem) China U.S. • Vietnam Conflict Mao Announces creation of the PRC – 1954 Dien Bien Phu – 1968 Tet Offensive – 1975 Communists unite Vietnam Domino Theory “THE COLD WAR TURNS HOT” THE KOREAN WAR MEMORIAL THE KOREAN WAR PARK The Collapse of Soviet Communism • Ronald Reagan and the end of Détente (Back to Brinksmanship) • 1980 Solidarity founded in Poland – Lech Walesa • 1981 Martial Law in Poland • 1985 Mikhail Gorbachev (1931-) became Premier – Glasnost ‘openness’ – Perestroika ‘restructuring’ • By Late 1980s Soviet Economy in state of near collapse Mikhail Gorbachev Why did the Soviet Union Fall so Quickly? Command Economy Fails Military Commitments Satellite Countries Want Out The government determines production and where the nation’s resources are going to go: Results in surpluses and shortages No motivation to work hard because everyone gets paid the same. “They pretend to pay us and we pretend to work.” The Soviet Union had to defend the all of its satellite communist countries. 50% of the country’s resources are going to the military, this destroys the economy. The End of the Cold War • Without strong hand in U.S.S.R., Eastern European governments collapse • 1989 Year of Change – Poland legalized Solidarity – Berlin Wall fell • 1990 Germany reunified • 1991 Hard-line coup against Gorbachev failed – Boris Yeltsin, President of the Russian Federation gains power, Soviet Union disintegrates The Fall of the Berlin Wall