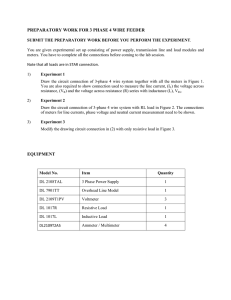
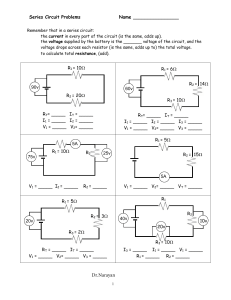
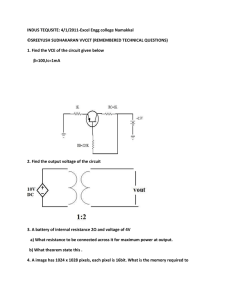
POS Circuits Tool Box (Conclusions for Series and Parallel Circuit Lab) Series
advertisement
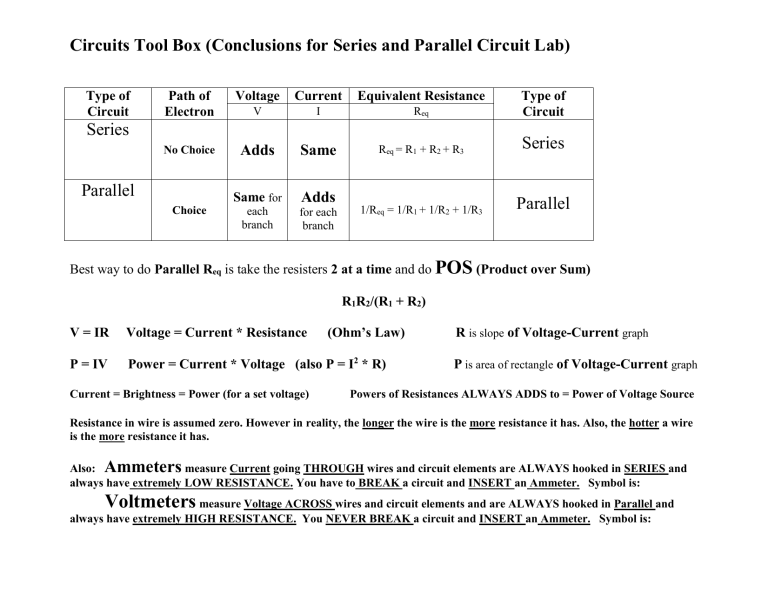
Circuits Tool Box (Conclusions for Series and Parallel Circuit Lab) Type of Circuit Path of Electron Voltage Current Equivalent Resistance V I Req Type of Circuit No Choice Adds Same Req = R1 + R2 + R3 Series 1/Req = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 Parallel Series Parallel Choice Same for Adds each branch for each branch Best way to do Parallel Req is take the resisters 2 at a time and do POS (Product over Sum) R1R2/(R1 + R2) (Ohm’s Law) V = IR Voltage = Current * Resistance P = IV Power = Current * Voltage (also P = I2 * R) Current = Brightness = Power (for a set voltage) R is slope of Voltage-Current graph P is area of rectangle of Voltage-Current graph Powers of Resistances ALWAYS ADDS to = Power of Voltage Source Resistance in wire is assumed zero. However in reality, the longer the wire is the more resistance it has. Also, the hotter a wire is the more resistance it has. Also: Ammeters measure Current going THROUGH wires and circuit elements are ALWAYS hooked in SERIES and always have extremely LOW RESISTANCE. You have to BREAK a circuit and INSERT an Ammeter. Symbol is: Voltmeters measure Voltage ACROSS wires and circuit elements and are ALWAYS hooked in Parallel and always have extremely HIGH RESISTANCE. You NEVER BREAK a circuit and INSERT an Ammeter. Symbol is: