WESTERN SOCIETY AND EASTERN EUROPE IN THE DECADES OF THE COLD WAR:
advertisement

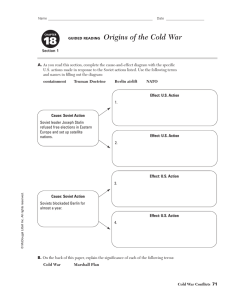
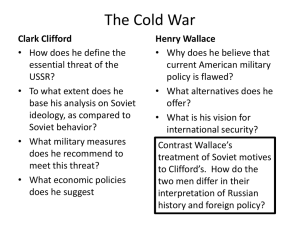
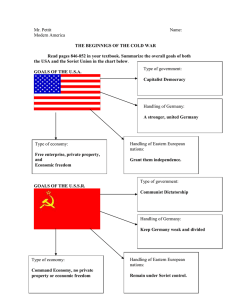
WESTERN SOCIETY AND EASTERN EUROPE IN THE DECADES OF THE COLD WAR: 1945 - 1991 THE COLD WAR The origins of the cold war (1947-1990) Postwar settlement established at Yalta and Potsdam Perception of world divided between so-called free and enslaved peoples Interventionist policy, dedicated to "containment" of communism The Marshall Plan, 1948: U.S. aid for the recovery of Europe Soviets took east Germany, while United States, Britain, and France took west Germany Berlin also divided four ways; by 1950 division seemed permanent Churchill spoke of an "iron curtain" across Europe, separating east and west Similar division in Korea: Soviets occupied north and United States the south Truman doctrine, 1947: USA would support "free peoples resisting subjugation" Each Allied power to occupy and control territories liberated by its armed forces Stalin agreed to support United States against Japan Stalin's plans prevailed; Poland and east Europe became communist allies President Truman took hard line at Potsdam, widened differences Postwar territorial divisions reflected growing schism between USA, USSR Unlikely alliance between Britain, USSR, USA held up for duration of war Not without tensions: Soviet resented U.S.-British delays in European invasion Soviet Union and United States vied for nonaligned nations Idea to rebuild European economies and strengthen capitalism Soviet response: Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (COMECON) for its satellites NATO and the Warsaw Pact: militarization of the cold war 1949, United States created NATO, a regional military alliance against Soviet aggression 1955, Soviets formed the Warsaw Pact in response Two global superpowers protecting hegemony with alliances United Nations, established 1945 to maintain international peace and security CAN YOU IDENTIFY THESE ITEMS? COLD WAR IN EUROPE Postwar Europe Divided into competing blocs Western Europe Dominated by Soviet Union, Red Army, secret police Communist governments modeled after USSR dominate countries Germany divided east and west in 1949 Soviets refused to withdraw from eastern Germany after World War II Allied sectors reunited 1947-1948, Berlin remained divided as well Berlin blockade and airlift, 1948-1949 Soviet closed roads, trains, tried to strangle West Berlin into submission Britain and United States kept city supplied with round-the-clock airlift Soviets backed down and ended blockade The Berlin Wall, 1961 U.S. allies supported by permanent presence of American army Parliamentary governments, capitalist economies Eastern Europe NATO, European Economic Communities Warsaw Pact, COMECON Neutral: European Free Trade Association; Yugoslavia 1949-1961, refugees from East to West Germany, East to West Berlin Soviet solution: a wall of barbed wire through the city fortified the border Former Allied nations objected but did not risk a full conflict over the wall Nuclear arms race Terrifying proliferation of nuclear weapons by both sides NATO and Warsaw Treaty Organization amassed huge weapons stockpiles By 1960s USSR reached military parity with United States By 1970 both superpowers acquired MAD, "mutually assured destruction" ECONOMIC EUROPE DURING THE COLD WAR RESURGENCE OF WESTERN EUROPE New State Structures Liberal Democracy The Welfare State Minorities clamored for inclusion, to be heard, anti-establishment Students, youth, women heavily involved in these movements Environmental movements in Europe (Green Movement) Civil Rights, Gay Rights, Women’s Rights in the US Cooperation European cooperation critical for future Economic cooperation led to European Economic Communities European politics shifted left Governments run by technocrats – experts in their fields Embraced idea of state support of all elements in society Included education, health care, state planning, social insurance Government active in housing New Challenges to Political Stability West had rejected authoritarianism, embraced inclusive democracy Embraced both Social Democracy, Christian Socialism Began as a Coal and Steel customs union Led to broad economic common market of France, Italy, Benelux, Germany Expanded to include most of Western, Central, Southern Europe Led to the European Union including a Parliament, currency union Economic Expansion Marshall Plan helped create an economic boom Agriculture flourished, growth in industrial base, productivity Heavy expansion of technical sectors, service industries, external trade Supported heavy immigration within Union and from outside Mediterranean nations Rise of consumer economy WESTERN EUROPE AFTER 1945 France From 4th to 5th Republic 5th Charles de Gaulle wanted Europe free from superpower domination French government refused to ban nuclear tests in 1963, tested bomb in 1964 Increasingly a welfare, graying state with heavy problems due to immigration Slow recovery from the war and decolonization Labor Party comes to power and gradually built welfare state and mild socialism Never fully able to recover from loss of colonies, heavy migration to UK by colonials Margaret Thatcher 1979 – 1992 tried to relax welfare state West Germany Republic strengthened role of president, lessened power of legislature United Kingdom Immediately after war, France tried to hold on to its colonies This led to several colonial struggles in Vietnam, Algeria, collapse of 4th Republic Under US, French, UK pressure, integrated into Europe to avoid future wars Strong economic recovery after 1949 called Economic Miracle Rose to become one of the strongest economic nations in the world Under Brandt (SDU), initiated Ost-Politik to bridge relations with USSR Builds a social market economy of mixed capitalism, welfare socialism European Union Began as European Steel/Coal Community: Germany, Italy, France, Benelux Grew into European Economic Community and European Communities Goal was to synchronize economic, trade policies This grew into a desire for a political union By 1989 included UK, Ireland, Spain, Portugal, Greece In 2005 had common parliament, passport, trade policies, currency, central bank A NEW EUROPE? USA, AUSTRALIA, NEW ZEALAND, & CANADA Changes in Europe paralleled abroad All avoided destruction of World War II Innovation consequently was less severe Former Dominions All became liberal democracies, welfare states All aligned to the USA Canada Joined US, Mexico in NAFTA Internal issues with Catholic Quebec, Inuit devolution Australia UK declined as great power, increasingly Euro-centric Australia and New Zealand because of WW II Canada because of decline of UK, rise of US markets A strong US ally Internally adopted a whites-only immigration policy The US Century From 1914 onward, US dominated world stage US military second to none; US expenditures on defense high Economic, military, political, cultural influence predominant US’ Truman Doctrine, Marshall Plan, military alliances critical US saw expansion of defense industries, governmental apparatus Sought to contain the USSR, communism Led to the US involvement in many wars of national liberation CULTURE AND SOCIETY IN THE WEST Social Structures Expansion of consumer culture, society Increasing prosperity to all classes Social conflicts eased Social lines blurred, increased social mobility Increased participation in political process Society not without troubles but… Dramatic changes in gender relations After WW II, women had vote AND entered politics WWII saw women enter all aspects of society Family life transformed by work, technology Women delayed marriage, children to work Birth control, abortion increase, divorce increased New Feminism Working women increased: reaches 44% in 1970s; women’s access to education increased But women paid less, much discrimination Gender equality lacking but women acquired legal rights 2nd Sex by Simone de Beauvoir Feminine Mystique by Betty Friedan Women agitated for more rights, literal and legal equality Western Culture Great political stability expected Expanded access to education including universities Massive application of technology, science to all aspects of life Expression in arts and cultures to challenge traditional approaches Extremely active popular, counter culture among youth, young Sexual experimentation increasing leads to sex for pleasure Secularization of most aspects of life Decline in mainline churches, church attendance EASTERN EUROPE AFTER 1945 USSR as Superpower Emerged from WWII with largest army in world One of the two great victors of WW II along with US Enormous industrial foundation based on armaments Had expanded its borders Actively involved in diplomacy, UN Had active communist states, alliances around world New Soviet Empire in Eastern Europe After WWII, failed to hold open elections, withdraw Soviet Satellite Regimes Communists placed in power by rigged elections Any rivals for power eliminated, controlled by Red Army, Secret Police Agriculture collectivized, industry nationalized Tensions as elements resisted Soviet control Decided to create a buffer zone between USSR, West All states in region forcibly brought under USSR influence Hungary: 1956 East Germany: 1960s Berlin Wall Czechoslovakia, 1968 Poland, 1970s, 1980s and Solidarity Only Yugoslavia, Albania followed independent paths Domestic Realities Strong authoritarian control of society, regulation of all aspects of life Control of media, information by extensive bureaucracy Mechanization of agriculture Increased urbanization as peasants move to cities Industry heavily focused on military and not consumer goods SOVIET CULTURE, ECONOMY, SOCIETY Rapid Industrialization Significant Social Change State fostered, controlled from top down Gosplan, 5 Year Plans common Secularization of society, purging of religion Persecution of ethnic, religious minorities Tension increased with Western Culture Arts monitored to reflect Soviet culture Schools goal was to foster loyalty to state, science Attacked western styles of art, literature; heavy censorship Sovietized, Russified many aspects of culture Counter-Culture Arose Solzhenitysn’s Gulag Archipelago criticized Stalin, Stalinism Science, social studies, mathematics heavily favored Economy and Society Fully industrialized society by 1950s Horrible Damage to the Environment State control of virtually all aspects of economic sectors No individualized economic aspects allowed although a Black Market flourished Lagged in production of consumer goods, poorly funded But living standards improved Ecocide: Murder of the environment Soviets were not concerned with the environment only with production figures, development Agricultural sector was horribly inefficient Similarities with West Industrial life demeaning for both regions; state guaranteed vacations, sports, medical care Mitigation of class differences Similar responses with regard to women, family life, housing, childrearing DESTALINIZATION Stalin died in 1953 Rivals opposed his one man rule, cult of personality Khrushchev’s Rise Opened up society to innovation, some decentralization Regime less likely to execute opposition Released many prisoners from state camps, closed gulags Khrushchev pushes own industrial base to outdo west Soviet Space Program and Sputnik catches west by surprise Avoids Adventurism in Foreign Policy Enforces Soviet control in 1956 Hungary – De-Stalinization went to far But allows more independent roads to socialism by USSR’ Allies Cuba: nuclear flashpoint Fidel Castro establishes guerrilla force in mountains, 1953 Overthrew dictator Batista in 1959 Castro declared that his government would be socialist, angers USA Castro seized U.S. properties, killed, exiled political opponents United States cut off Cuban sugar imports, imposed export embargo Castro accepted Soviet economic aid and arms shipments Bay of Pigs fiasco, April 1961 CIA-sponsored invasion of Cuba failed Diminished U.S. prestige in Latin America Cuban missile crisis, October 1962 Rivals removed Stalin’s supporters, executed Beria (KGB) New Chairman attacked Stalinism for its excesses Khrushchev as Chairman of the USSR His reign had taught politicians to cooperate, avoid infighting His reign had also discouraged innovation, resistance Soviet deployed nuclear missiles in Cuba, aimed at USA; claimed Cuban defense Kennedy blockaded Cuba, demanded removal; two tense weeks Khrushchev backed down; Kennedy pledged not to overthrow Castro Brezhnev’s Years 1964 – 1982 Khrushchev became too difficult to control, removed in coup Brezhnev assumes control, maintains more stabile Soviet models Brezhnev Doctrine: USSR intervene in Czechoslovakia, 1968 to maintain Soviet control EASTERN EUROPE SINCE 1945 Warsaw Pact and COMECON Yugoslavia, Albania: independent communist states De-Stalinization led to pro-democracy movement in Hungary New government announced neutrality, withdrew from Warsaw Pact Soviet tanks crushed Hungarian uprising, 1956 Goulash Communism: a liberalization of communism in Hungary Prague Spring, Czechoslovakia, 1968 Marshall Tito (Josip Broz) resisted Soviet control of Yugoslavia Stalin expelled Yugoslavia from Soviet bloc, 1948; Remained nonaligned throughout cold war Albania drawn into Chinese influence, denounces USSR Hungarian challenge, 1956 1955: USSR creates a military alliance to counter NATO – Warsaw Pact COMECON was attempt to rival EEC, EC States were originally satellites of USSR After 1964, increasing allowance for independent roads to socialism Liberal movement led by Dubcek sought "socialism with a human face" Soviet and east European forces crushed Prague liberal communism Brezhnev justified invasion by Doctrine of Limited Sovereignty Poland, 1970s – 1980s Remained strongly Catholic, strongly nationalist Polish communist party loyal to USSR but not always trusted Workers movements emerge which are for reform, pro-Catholic 1980s Strikes under Solidarity almost led to Soviet intervention Election of John Paul II as Pope only emboldened Poles DÉTENTE & DECLINE OF BIPOLAR WORLD Era of cooperation Demise of détente 1950s, USA committed to support noncommunist South Vietnam U.S. involvement escalated through 1960s U.S., allies unable to defeat North, South Vietnamese communists President Nixon pledged in 1968 to end war with Vietnam U.S. troops gradually withdrew; U.S. phase of war ended in 1973 North Vietnam continued war effort, unified the nation in 1976 Soviet setbacks in Afghanistan Full U.S.-China diplomatic relations in 1979 created U.S.-USSR strain U.S. weapons sale to China in 1981 undermined U.S.-Soviet cooperation 1980 Soviet intervention in Afghanistan prompted U.S. economic sanctions U.S. defeat in Vietnam Leaders of both superpowers agreed on policy of détente, late 1960s Exchanged visits and signed agreements calling for cooperation, 1972, 1974 Concluded Strategic Arms Limitations Talks (SALT), 1972, again 1979 Afghanistan had been a nonaligned nation until 1978, pro-Soviet coup Radical reforms in 1978 prompted backlash Islamic leaders objected to radical social change, led armed resistance 1979, rebels controlled much of Afghan countryside; USSR intervened United States, others supported Mujahedeen rebels; struggle lasted nine years 1989 cease-fire negotiation by UN led to full Soviet withdrawal Taliban forces captured Kabul and declared Afghanistan a strict Islamic state, 1996 Cold war countercultural protests in 1960s and 1970s Cultural criticism of cold war as seen in film Dr. Strangelove, 1964 European and U.S. students agitated for peace, end to arms race, Vietnam war Rock and roll music expressed student discontent END OF COLD WAR Revolution in east and central Europe Moscow's legacies Communism unable to satisfy nationalism in eastern and central Europe Soviet-backed governments lacked support, economies stagnant Soviet interventions in 1956 and 1968 dashed hopes of a humane socialism Mikhail Gorbachev, Soviet leader 1985-1991 1989, Gorbachev announced restructuring of USSR, withdrawal from cold war Satellites states informed that each was on its own, without Soviet support Rapid collapse of communist regimes across eastern and central Europe, 1989 In Poland, Solidarity leader Lech Walesa won election of 1990 Communism overthrown peacefully in Bulgaria and Hungary Czechoslovakia's "velvet revolution" in 1990, divided into Czech Republic, Slovakia Only violent revolution in Romania; ended with death of communist dictator East Germany opened Berlin Wall in 1989; two Germanys united in 1990 The collapse of the Soviet Union Gorbachev's reforms Hoped for economic liberalization within political communist system Centralized economy inefficient, military spending excessive Declining standard of living, food shortages, shoddy goods Perestroika: "restructuring" the economy Tried decentralizing economy, market system, profit motive Alienated those in positions of power, military leaders Glasnost: "openness" to public criticism, admitting past mistakes Opened door to widespread criticism of party and government Ethnic minorities, especially Baltic peoples, declared independence from USSR Russian Republic, led by Boris Yeltsin, also demanded independence Collapse of the Soviet Union, December 1991 In 1991, conservatives attempted coup; wished to restore communism With help of loyal Red Amy units, Boris Yeltsin crushed the coup Yeltsin dismantled Communist party, led market-oriented economic reforms Regions of ethnic groups became independent; Soviet Union ceased to exist