Document 15573406
advertisement

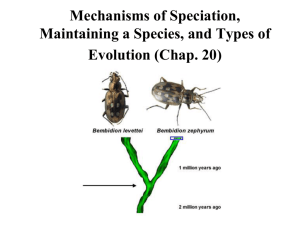
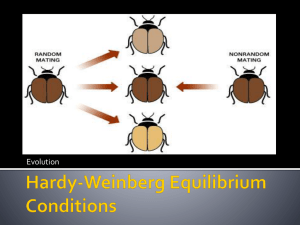
EVOLUTION & NATURAL SELECTION VOCABULARY • Evolution • Gradual change in the genetics of a species/population over time; how descendants differ from their ancestors. Types of Selection • Artificial Selection • Selection by humans for breeding of useful traits from the natural variation among different organisms, Ex. Dog Breeding Types of Selection • Natural Selection • Process by which individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce successfully How to Survive • Struggle for Existence • Competition among members of a species for food, living space, and the other necessities of life • Fitness • Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment • Adaptation • Inherited characteristic that increases an organism’s chance of survival Question: Do you think that there is a struggle for existence between humans? Example of natural selection, adaptations, fitness and the struggle for existence. Peppered Moth Peppered Moth Evolution Ancestry • Descent with Modification • Principle that each living species has descended, with changes, from other species over time • Common Descent • Principle that all living things have a common ancestor Evolution - "Stated Clearly" Ancestry • Homologous Structures • Structures that have different mature forms in different organisms but develop from the same embryonic tissues; common ancestor • Analogous Structures • Structures that appear the same but do not develop because of similar ancestry; same selective pressures • Vestigial Organs • A structure or organ that is useless today but an ancestor used Variation • Gene Pool • Combined genetic information of all the members of a particular population • Relative Frequency • Number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of times other alleles occur Question: Who is represented in the gene pool? Selection • Genetic Drift • Random change in allele frequencies that occurs in small populations • Founder Effect • Loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population • Genetic Equilibrium • Situation in which allele frequencies remain constant Founder Effect How do we get separate species? • Speciation • Formation of new species • Reproductive Isolation • Separation of a species or populations so that they cannot interbreed and produce fertile offspring • Behavioral Isolation • Form of reproductive isolation in which two populations have differences in courtship rituals or other types of behavior that prevent them from interbreeding. Ex. Albatross, Ex. Birds of Paradise How do we get separate species? • Geographic Isolation • Form of reproductive isolation in which two populations are separated physically by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or stretches of water • Temporal Isolation • Form of reproductive isolation in which two populations reproduce at different times CC - Big History "Evolution" What Darwin Never Knew - Part 1