FALL SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW

FALL SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW
Answer the following on a separate sheet of paper.
UNIT 1: U.S. Geography
1.
Locate the following U.S. physical features: Appalachian Mountains, Mississippi River, Rocky
Mountains, Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, Gulf of Mexico, Great Lakes. Use map to locate these
features.
UNIT 2: Colonization
2. Why are 1607 and 1620 important dates in American history?
1607 – founding of Jamestown, first permanent English settlement in North America
1620 – Plymouth, MA founded by Pilgrims fleeing England for religious freedom
3. Explain the different reasons why Europeans colonized North America, especially from England.
Gold – seeking economic opportunity and profits for king and country
Glory – military leaders and governors made reputations in England
God – seeking religious freedom (Puritans, Pilgrims) or missionary work
4. How did the Magna Carta, Mayflower Compact, Fundamental Orders of Connecticut, and
English Bill of Rights each influence English colonial governments?
Magna Carta (1215) – established precedent of limited government
Mayflower Compact (1620) – stated intent for self-government of colony
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut (1639) – written constitution with separation of church and state
English Bill of Rights (1689) – listed rights of citizens, influenced Bill of Rights
5. Describe the differences between the three colonial regions in economy, culture, and religion.
New England – Cold with rocky soil; timber, fishing, shipbuilding, trade; strict Puritan religion, small farms, little diversity
Middle Colonies – moderate weather, good soil; grain farms (Breadbasket), iron works, large cities; diverse culture and religious tolerance – English, Swedish, Dutch, German, Irish,
Quakers
Southern Colonies – warm weather, good soil; large plantations, cash crops, few large cities, slave labor; Anglican church, wealthy lived like English nobles
6. Summarize the ideas of Enlightenment Thinkers: John Locke, Baron de Montesquieu, William
Blackstone
John Locke - natural rights of “life, liberty, and property”; government by people’s consent
Baron de Montesquieu - separate branches with divided powers
William Blackstone- British legal scholar: influence U.S. law and the Constitution
7. Explain the meaning of the 3 G’s of exploration. See #3
UNIT 3: Revolutionary Era
8. Define “mercantilism” and explain how Britain used the colonies for economic gain.
Economic philosophy that national power comes from favorable trade. Britain established colonies for:
Natural resources – gold, metals, or agricultural products
Markets – sold manufactured goods to colonists
Limited trade – forced colonies to trade only with Britain
Taxes – passed taxes on colonies to pay for French & Indian War debts
9. How did the Proclamation of 1763 lead to conflict between Britain and the colonies?
After gaining western territories from French, British established forts to prevent war between Natives and colonists. Costs for these were passed to colonies through tax bills
(Sugar Act, Stamp Act, Townshend Acts).
10. Why did the colonists reject British taxes such as the Stamp Act and Townshend Acts?
The colonies had no voting members in Parliament. Colonists rejected taxes passed on them without representation (James Otis: “Taxation without representation is tyranny!”).
11. What was the importance of the pamphlet Common Sense in American independence?
Paine used plain language and logic to persuade colonists undecided about independence to support the patriot side.
12. Why is the year 1776 an important date in American history?
Thomas Jefferson wrote and Congress ratified the Declaration of Independence on July 4.
13. Define “unalienable rights” and summarize why Jefferson wrote the Declaration of
Independence.
Unalienable rights – natural rights given all persons at birth; Jefferson listed “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness”
3 goals of the Declaration:
Define America’s right to self-government
List grievances against King George
Announce America’s independence to the world
14. Explain the importance of the following events in the American Revolution: Battle of
Lexington & Concord, Battle of Saratoga, winter at Valley Forge, Battle of Yorktown, and Treaty of
Paris.
Lexington & Concord – first battle between British and colonial militia, war begins
Saratoga – American victory convinced France and Spain to ally with Americans
Valley Forge – hardships and harsh winter costs ¼ of Continental Army
Yorktown – Cornwallis trapped and forced to surrender, last battle of the Revolution
Treaty of Paris – Britain recognizes U.S. independence, U.S. extends to Mississippi River
15. Explain the importance of foreign allies to the American fight for independence.
After Saratoga, France and Spain provided military and financial aid to American side. French navy and army helped trap Cornwallis at Yorktown. Von Steuben brought his experience in
German military to train Washington’s troops at Valley Forge, and LaFayette served under
Washington and provided aid from France. Spanish governor Bernardo de Galvez attacked
British shipping and ports along the Gulf of Mexico.
16. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of each side in the Revolutionary War
Continental Army Advantages:
● motivation to fight for independence
● fighting on home ground
● strong leader in Gen. Washington
● foreign aid after 1778
Continental Army Disadvantages:
❖ not enough troops
❖ lack of training and experience
❖ low on money
❖ no regular navy - mostly privateers
British Army Advantages
❏
Large army and navy
❏
Well trained, experienced
❏
Plenty of money
❏
Aided by loyalists
British Army Disadvantages:
➔
Great distance from home
➔
“Away team” - not familiar with land
➔
Lack of aggressive leaders
➔
Lost support of British people
17. Explain the contributions of people such as Abigail Adams, Ben Franklin, Crispus Attucks,
Bernardo de Galvez, Haym Salomon, James Armistead, King George III, and Wentworth
Cheswell.
Abigail Adams - wife of patriot leader John Adams; asked to “remember the ladies” in
creating the U.S. government
Ben Franklin - patriot leader; Continental Congress’ ambassador to France who helped win
French aid
Crispus Attucks - African-American killed in Boston Massacre; first to die in Revolution
Bernardo de Galvez - see #15
Haym Salomon - Jewish businessman who helped fund Continental Army
James Armistead - African-American slave who spied on British for Washington
King George III - monarch of England; angered colonies with his policies
Wentworth Cheswell - African-American patriot, businessman, and political leader
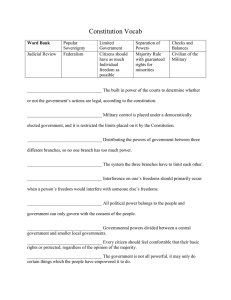
24. Define the 7 Principles of the Constitution - popular sovereignty, republicanism, limited government, separation of powers, checks and balances, federalism, individual rights - and understand how they are applied to our system of government.
Popular sovereignty – political power comes from the people
Republicanism – government of elected representatives
Limited government – government by rule of law
Separation of powers-power divided among 3 branches: Legislative, executive, judicial
Checks and balances-branches have powers (checks) over others to balance branches
Federalism-shared power between national (federal) and state governments
Individual Rights- personal rights and
UNIT 4: Confederation to Constitution
18. What was the main goal for the 1785 Land Ordinance and the 1787 Northwest Ordinance?
To settle the Northwest Territory and organize it politically into states.
19. Describe the weaknesses of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Why was the government set up this way?
Articles created a weak national government that depended on the states for financial support. No powers to tax, create courts, control trade or currency. After years of British tyranny, they wanted to leave most powers with the states.
20. How did Shays’ Rebellion affect the Articles of Confederation government?
Shays’ Rebellion exposed the weakness of the Confederation to manage and protect the country, resulting in the Constitutional Convention in 1787 to revise the articles that instead created the current federal republic.
21. Explain the Great Compromise and the issue it attempted to solve.
The Great Compromise addressed how to represent states with different populations fairly.
House of Representatives based on population, while all states have equal representation in the Senate.
22. Why was compromise necessary in writing the Constitution?
The states all had different economies, populations, and geographic factors, so they had different interests and needs from the government. Compromises over representation, slavery, and taxes were necessary to get enough delegates to support the Constitution.
23. Summarize the arguments of the Anti-Federalists in opposing the Constitution as written.
● President would become a dictator, wouldn’t willingly give up power
● Congress should be most powerful branch
● States should maintain most important powers – national government can’t represent everyone fairly
● Needs a Bill of Rights to protect individual freedoms
Separation of powers – power divided among 3 branches: legislative, executive, judicial
Checks and balances – branches have powers (checks) over others to balance branches
Federalism – shared powers between national (federal) and state governments
Individual rights – personal rights and freedoms
25. Summarize the rights guaranteed in the Bill of Rights.
1st – RAPPS (see #4)
2 nd – right to bear arms (guns)
3 rd – no forced quartering of soldiers in peacetime
4 th – no unreasonable search and seizure
5 th – indictment, right to silence, no double jeopardy, private property
6 th – speedy trial by jury of peers, right to counsel
7 th – jury trial in civil cases
8 th – no excessive fines or cruel punishment
9 th – people have rights not listed in Constitution
10 th – states’ rights
26. What is due process? What are the due process amendments in the Bill of Rights?
Rights and protections of the accused – must follow or case can be dismissed. 4 th , 5 th , 6 th , 7 th , and 8 th Amendments.
27. Describe the 5 Freedoms found in the 1 st Amendment.
Religion – free exercise and no established state religion
Assembly – right to gather and assemble
Press – freedom to read and write news without censorship
Petition – right to express opinions to leaders
Speech – freedom to say what we think (within certain limits)
28. What are some of the rights and responsibilities of U.S. citizenship?
Rights – voting, education, participation in public affairs
Responsibilities – taxes, jury duty, obey laws, be informed before voting
29. Describe the steps to amend the Constitution.
Step 1: Proposal (suggesting)- requires ⅔ vote of Congress or ⅔ of states in convention
Step 2: Ratification (approving) - requires ¾ of state legislatures or states in convention