KEY Note Taking Guide Topic # 3041
advertisement

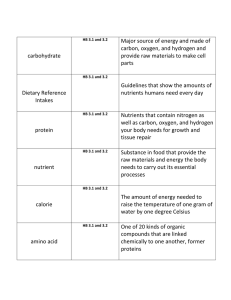
KEY Note Taking Guide Topic # 3041 Basics of Nutrients and Nutrient Requirements Anna Blight Nutrients are: Any feed component that functions in the support of life. There are 20 chemical elements in nutrients. These 20 elements and their chemical symbols are: calcium (Ca) carbon (C) chlorine (Cl) cobalt (Co) copper (Cu) fluorine (F) hydrogen (H) iodine (I) iron (Fe) magnesium (Mg) manganese (Mn) molybdenum (Mo) Nitrogen (N) oxygen (O). phosphorus (P) potassium (K) selenium (Se) sodium (Na) sulfur (S) zinc (Zn) The six basic classes of nutrients are: water carbohydrates fats proteins vitamins minerals Feeds are made up of: concentrates roughages Concentrates consists of: cereal grains oil meals molasses dried milk products. Roughages include: legume hays, grass hays, and straws Other forms of roughage are: silage stovers soilage grazed forages Concentrates are: high in energy low in fiber highly digestible Concentrates include: corn wheat barley oats milo soybean meal, linseed meal, and cottonseed meal. Roughages are: less digestible bulkier, courser feed Water is: most important nutrient contains hydrogen and oxygen transports other nutrients helps maintain normal body temperature Carbohydrates: major energy source containds carbon, hydrogen and oxygen found in grains and hays Fats: primary energy source 2.25 more energy/pound than carbohydrates contains carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Protein: only nutrient class that contains nitrogen protein in feeds contain average of 16% nitrogen building blocks of the body proteins compose most of the muscle mass Minerals: elements other than carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen macrominerals are required in larger amounts microminerals in smaller amounts necessary for healthy body functions Vitamins: organic nutrients – contain carbon provide for very specific body functions required in very small amounts 16 known vitamins in animal nutrition A, C, D, E, K, choline and the B-complex vitamins Energy - two basic functions are run by energy: maintenance an reproduction supplied by nutrients containing carbon carbohydrates, fats and proteins all supply energy Energy evaluation of feeds is measured by: total digestible nutrients digestible energy energy for metabolism net energy