Understanding Inheritance Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Part 1
advertisement

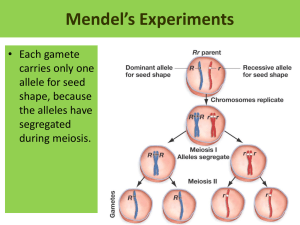
Understanding Inheritance Chapter 5 Lesson 2 Part 1 Understanding Inheritance • What determines the expression of traits? • How can inheritance be modeled? • How do some patterns of inheritance differ from Mendel’s model? What controls traits Mendel concluded that two factors—one from each parent—control each trait. Mendel’s “factors” are part of chromosomes which exist as pairs—one chromosome from each parent. Each cell in an offspring organism contains chromosomes from both parents. What controls traits A gene is a section on a chromosome that has genetic information for one trait. The different forms of a gene are called alleles. Each chromosome has one allele for every gene on it. The two chromosomes in an offspring cell may have the same or different alleles. Important Genetic Terms An allele is one member of a pair or series of different forms of a gene (the different forms of a trait that a gene may have) What controls traits An example is the gene for blossom color in many species of flower — a single gene controls the color of the petals, but there may be several different versions (or alleles) of the gene. One version might result in red petals, while another might result in white petals. The resulting color of an individual flower will depend on which two alleles it possesses for the gene and how the two interact. Important Genetic Terms Geneticists call how a trait appears, or is expressed, the trait’s phenotype. • The two alleles that control the phenotype of a trait are called the trait’s genotype. Important Genetic Terms Genotype - genetic makeup or allele combinations when writing a genotype, the dominant trait is always listed first Scientists use uppercase and lowercase letters as symbols to represent the alleles in a genotype. RR or Rr Important Genetic Terms Phenotype - the physical traits of the organism (its physical appearance or visible traits) Red Rose Genotypes: GG Gg GG Phenotypes: purple-grained white-grained Important Genetic Terms When the two alleles of a gene are the same, the genotype is homozygous. • If the two alleles of a gene are different, the genotype is heterozygous. Homozygous (purebred) an organism usually the result of many generations of such breeding (both alleles the same) (having identical factors) Heterozygous (hybrid) an offspring that was given different genetic information for a trait from each parent (alleles different) (having factors that are different) (has two different alleles for a trait) a hybrid was the result of a cross between two different homozygous (purebred) organisms Important Genetic Terms cross – mating of organisms to test how they inherit traits Important Genetic Terms first filial generation (F1) - the 1st generation of offspring of a genetic cross The word filial comes from filia and filius, the Latin words for “daughter” and “son.”