THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 14 Lesson 1 part 2
advertisement

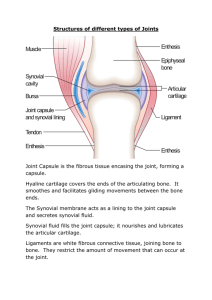
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 14 Lesson 1 part 2 joint a connection between two or more bones or between cartilage and bone Joints provide flexibility and enable the skeleton to move. Joints are designed for specific functions and are classified into two groups: • Movable Joints •Immovable Joints Movable Joints • ball and socket • hinge • pivot • gliding (condyloid) Ball and socket joint Hinge joint Pivot joint Gliding (condyloid) joint Immovable Joints sutures - the interlocking margins of skull bones Anatomy of a joint Tendon Bursa Femur Patella Bursa Synovial Cavity Ligament Tibia Bursa synovial membrane lines the inner surface of the joint cavity secretes a lubricating fluid called synovial fluid, which acts as a shock absorber between the bones ligaments connect the bones of a joint ligaments tendons connects muscle to bone; often extend across the joint and strengthens it bursas Bursa Bursa Bursa a fluid-filled sac; lined with synovial membrane bursas located between tendons, ligaments, & bones bursas Bursa Bursa Bursa serve as cushions and reduce friction Bone & Joint Diseases and Disorders • Arthritis • Rheumatism • Sprain • Double-jointed • Osteoporosis Arthritis a disease in which joints become irritated or inflamed, such as when cartilage in joints is damaged or wears away; usually accompanied by pain. Arthritis frequently results in changes in the joint structure, greatly hampering movement. Rheumatism a general term for various conditions that are characterized by soreness and stiffness of muscles and joints Sprain A stretch injury to the ligaments of a joint. In severe sprains, the ligaments may be torn. Double-jointed results from abnormally long ligaments, which allow a joint to be easily dislocated Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a common bone disease which causes bones to weaken and become brittle. Healthy Bones One of the best ways to keep bones healthy is to exercise. Without exercise, bones weaken and lose mass. Bones need a balanced diet that includes calcium and Vitamin D. The Skeletal System and Homeostasis Because bones supply calcium to your nerves, muscles, and heart, a healthy skeletal system is important in maintaining your body’s homeostasis. Working together with muscles, bones enable you to move away from unpleasant stimuli or danger.