Honors Chemistry: Periodicity & Bonding Review
advertisement

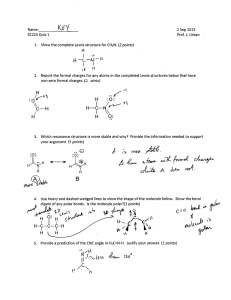
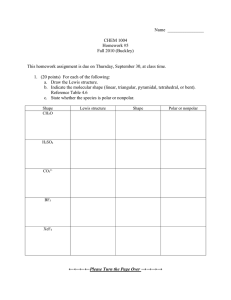
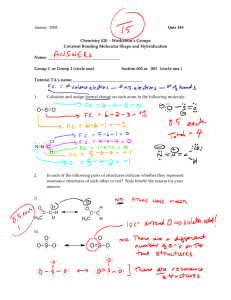
Name Date Pd Honors Chemistry – Unit 7 Review Periodicity and Bonding 1. Rank the following elements in order of increasing (a) ionization energy: S, F, P and increasing (b) atomic radius: Sr, Sn, Na. 2. Explain your choices above using what you know about atomic structure. 3. Predict the formulas of (a) Ca and S (b) K and O (c) Al and Cl. 4. Rank the following elements in order of increasing reactivity and explain your choices using ionization energy and atomic radius. (a) Ca, Zn, K (b) Cl, F, P 5. Which pairs of elements will form covalent bonds? Explain. (a) N and Cl (b) Al and N (c) Na and Ne (d) Cl and F 6. Sketch Lewis structures of the compounds in the pairs of elements in #5 will form. 7. Determine whether the following molecules are polar or nonpolar. Sketch the Lewis structure of each. Name the electron geometry and shape for each molecule. (a) NH3 (b) HCN (c) CF2Cl2 (d) SO2 (e) CH4 8. What determines a solute’s solubility in a given solvent? 9. Water is a polar solvent. Which compounds from #7 will dissolve in water? 10. Explain how you can use electronegativity values to classify a bond as nonpolar covalent or polar covalent. 11. What is meant by the term polar bond? How does this affect the behavior of a collection of molecules? 12. It is possible to have a molecule that does not have polar bonds but it is a polar molecule. Explain this statement using NCl3 as an example. 13. Not every molecule with polar bonds is a polar molecule. Explain this statement using CCl4 as an example. 14. Draw the Lewis dot structures for HCl and H2O. Identify polar covalent bonds by sketching dipoles and assigning slightly positive (+) and slightly negative (-) symbols to the appropriate atoms. 15. When salt (NaCl) dissolves in water the ions become solvated. Explain why the water molecules orient themselves differently around the anions and cations. Use a diagram to support your explanation.