Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Finz 2014
advertisement

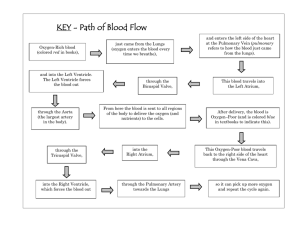
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Finz 2014 Function: transports nutrients and wastes through the body.maintains body temperature. Structure: • Blood which contains: red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma. Blood vessels • Veins - Returns blood to the heart • Arteries - Takes blood to the body. • Capillaries - Smallest, between arteries & veins. • Heart, the muscle that pumps the blood through the vessels. Human Circulation Key 1. superior vena cava 2. inferior vena cava 3. right atrium 4. tricuspid valve 5. right ventricle 6. semi lunar valve 7. pulmonary artery 8. pulmonary vein 9. left atrium 10. bicuspid valve 11. left ventricle 12. semi lunar valve (aortic) 13. aorta • • • • Valves: Flaps of connective tissue. Found in the heart and in the veins. Prevents blood from flowing backwards. Systemic Circulation: Circulation through the body. • Pulmonary Circulation: Circulation through the lungs. Structure of the heart and circulation of the blood. • Pulmonary Circulation: circulation from the body to the lungs. • Right atrium: receives blue blood from body through the vena cava and sends it through the tricuspid valve. • Tricuspid valve: leads to right ventricle. • Right ventricle: pumps blood through semi lunar valves into the pulmonary arteries. • Pulmonary arteries: transports blood to the lungs to get oxygen. • Lungs: carbon dioxide leaves blood and oxygen enters blood through the capillaries and alveoli. Systemic Circulation: circulation from the heart to the body. • Pulmonary veins: returns oxygenated blood to the heart. • Left atrium: receives red blood from pulmonary arteries and sends it through the bicuspid valve. • Bicuspid valve: leads to left ventricle. • Left ventricle: pumps blood through semi lunar valves into the aorta. • Aorta: largest artery that pumps blood out to the body's capillaries. • Capillaries: attached to body parts that exchange gases and nutrients/wastes with the body. The Respiratory System What is the function of the respiratory system? – The basic function of the human respiratory system is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the blood, the air, and tissues. The respiratory system consists of the: • • • • • • nose pharynx larynx trachea bronchi lungs Functioning: • Air entering the respiratory system must be warmed, moistened, and filtered. • Mucus moistens air and traps particles of dust or smoke. • Cilia sweep particles and mucus to the throat. • Mucus and particles are either swallowed or spit out. The Human Respiratory System Nose Pharynx Larynx Mouth Trachea Lungs Epiglottis Bronchus Bronchioles Diaphragm Nose • Air enters the nose or mouth and moves to the pharynx, or throat. • The pharynx serves as a passageway for both air and food. Pharynx • Air moves from Epiglottis the pharynx into the trachea, or windpipe. • The epiglottis covers the entrance to the trachea when you swallow. Trachea Larynx • At the top of the trachea is the larynx, which contains two elastic folds of tissue called vocal cords. • Air then passes through the trachea into two large passageways in the chest cavity called bronchi. • Each bronchus leads into one of the lungs. Lungs Bronchus • In each lung, the bronchus subdivides into smaller bronchi, and then into bronchioles. Bronchioles • Bronchioles subdivide into millions of tiny airBronchiole sacs called alveoli. Alveoli • Alveoli are grouped in clusters. • A network of capillaries surrounds each alveolus. Pulmonary artery Pulmonary vein Capillaries Gas Exchange • Gas Exchange O2 • Gas exchange takes place in the alveoli. • Oxygen diffuses into the blood. Capillary Gas Exchange • Carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses into the alveolus. O2 CO2 Capillary