Federalism Federalism: government where a written
advertisement

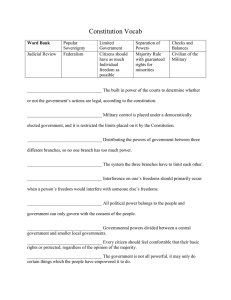
Federalism Federalism: a system of government where a written constitution divides the powers of government Federalism Division of Powers: separate powers for national government and the states –Spelled out in the 10th Amendment Federalism Delegated Powers: powers granted to the national government by the Constitution • Expressed Powers: spelled out specifically in the Constitution – Article 1 Sec. 8 – gives 27 specific powers to Congress Federalism Implied Powers: powers not expressly stated in the Constitution but are reasonably implied. implied powers are an expressed power! Confused yet? Federalism Article 1 sec. 8 clause 18 gives Congress the “necessary and proper” power to do what is necessary and proper to carry out its duties Federalism Inherent Powers: Powers given to the national government because it is the national government. – i.e. regulate immigration, deport aliens, acquire territory, etc… Powers Denied to the National Government (expressed) – Levy duties on exports – Deny freedom of religion, speech, press, or assembly – Conduct illegal search and seizures – Deny people a speedy, public trial by jury Powers Denied to the National Government (silence of the Constitution) - Public school system - Enact uniform marriage or divorce laws - Set up units of local governments Powers Denied to the National Government (threat to the federal system) - Cannot tax a state. Alternate Intelligence What can you break with only one word? Silence. What can you give away and still keep? A cold. What cannot be seen but only heard, and will not speak unless it is spoken to? An echo. What can't you see that is always before you? The future. What comes from a tree and fights cavities? A toothpick. Reserved Powers - Reserved Powers are powers held by states in the federal system. - Powers not given to National Government, and not denied to the states. - i.e. drinking laws, marriage laws, driving laws, etc. Powers denied to the States - Enter in to a treaty or alliance - Coin money - Deprive due process - Cannot threaten the federal system – i.e. Tax the National Government Local Governments - A federal system only calls for the national government, and the state governments - There are more than 80,000 local governments - Local governments are subunits of the state - Local governments only have the powers that the states give them. Exclusive Powers - Powers that can be only exercised by the National Government - i.e. Coin money, make treaties Concurrent Powers - Powers that both the National Government and the States posses and exercise - i.e. Collect taxes, define crimes, set punishment - Concurrent powers are held and exercised separately and simultaneously Supremacy Clause - Article VI Section 2: The Constitution is the supreme law of the land - McCulloch v. Maryland 1819 Massachusetts placed a tax on a national bank.