SPM 100 Clinical Skills Lab 5 Pulse Oximetry and Cardiac Monitoring
advertisement
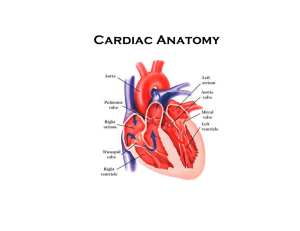
SPM 100 Clinical Skills Lab 5 Pulse Oximetry and Cardiac Monitoring Daryl P. Lofaso, M.Ed, RRT Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Normal Ranges pH 7.35-7.45 PaCO2 35-45 mmHg PaO2 80-100 mmHg Oxyhemoglobin Dissociation Curve Oxygen Transport Dissolved in plasma: (vol % = 0.0031 (ml O2 /100cm3/mmHg) x PaO2 Bond to Hemoglobin: 1.34 ml of O2/g of Hb x g of Hb x g of Hb/100 cm3 x % Saturated Cyanosis Approximately 5 g/dl of unoxygenated hemoglobin in the capillaries (> 5 gHb / 100ml of blood) Hypoxemia: Signs and Symptoms Tachycardia Tachypnea Mental Status Changes Changes in Oxygenation Altitude Hyperbaric Therapy Carbon Monoxide ECG Monitor Lead Placement Anatomy of Hearts Electrical System Basic ECG Confirmation of Asystole Check lead and cable Monitor power Monitor gain Change leads Cardiac Assessment Ref: Bates 8ed Heart Sounds S1: “ lub” occurs at the beginning of systole (mitral and tricuspid close) S2: “dub” marks the start of diastole, (aortic and pulmonic close) S3: (ventricular gallop) early signs of CHF S4: (atrial gallop) pulmonic stenosis, aortic stenosis, hypertension, MI & cardiomyopathy Professional Conduct Introduce yourself Explain the procedure / examination to the patient Ask the patient if they have any questions Cover the patient with a sheet. Only expose area examining while performing a procedure/examination