A Safe Landing for the Climate (Chapter 2)
advertisement

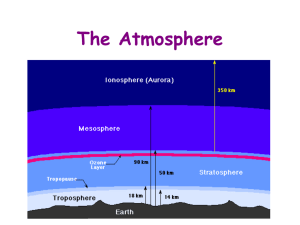
A Safe Landing for the Climate (Chapter 2) Green House Gases • Greenhouse gases are gases in an atmosphere that absorb and emit radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. Common greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere include water vapor, CO², methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone. • Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is a scientific intergovernmental body tasked to evaluate the risk of cliamte change caused by human activity. The panel was established in 1988 by the World Meterological Organization WMO) and the United Nations Environment Program (UNEP. • The IPCC does not carry out research, nor does it monitor climate or related phenomena. A main activity of the IPCC is publishing special reports on topics relevant to the implementation of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). Tipping Point Defined as the levels at which the momentum for change becomes unstoppable. It is also defined as the moment of critical mass, the threshold, the boiling point. • Parliamentarian: Defined as a person who is expert in the formal rules and procedures of deliberative assemblies and other formal organizations. • Preindustrial: It is an adjective relating to, or being a society or an economic system that is not or has not yet become industrialized. • • • • • • Radiative forcing: The warming effect of changed concentrations in GHGs and aerosols, gaseous suspensions of fine solid or liquid particles that are associated with most CO2 emission on the energy balance of the lower atmosphere. Inertia : - When no one wants to do anything to change a situation. Technically ,it means the force that keeps an object in the same position on keeps it moving until it is moved or stopped by another force. It could also mean a lack of energy and a feeling that you do not want to do anything. Carbon cycle: The change from carbon dioxide to living matter and back to carbon dioxide. Montreal protocol: (on the substances that depletes the ozone layer ) Is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of a number of substances believed to be responsible for ozone depletion. • Stringent : Very strict and must be obeyed. (short-term reductions in greenhouse gas emissions) • Feasibility of … : A plan, idea, or method that is possible and likely to work. • Substantial : Something which is considerable. • Sustainability consequences: Able to continue without causing damage to the environment. • Deforestation: The cutting or burning down of all the trees in an area. • Ecosystems : The totality of interactions among organisms and the environment in the area of consideration • LPJ : Lund Potsdam Jena • Unmitigated-Not diminished or moderated in intensity or severity; unrelieved. • Without qualification or exception; absolute. • Science is looking for a way to discover the answer to how to create a pathway for emission levels to decrease through controlling climate temperature, and much like a jet aircraft carrying people aboard • Must safely land, they are trying to find the safest and healthiest way to avoid unmitigated problems in the foreseeable future on the planet. • Tropospheric Ozone• Tropospheric ozone is a greenhouse gas and initiates the chemical removal of methane and other hydrocarbons from the atmosphere. Thus, its concentration affects how long these compounds remain in the air. • The troposphere is the lowest portion of Earth's atmosphere. It contains approximately 75 percent of the atmosphere's mass and 99 percent of its water vapor and aerosols.