Unit IV Anxiety Disorders and Crises Mental Health Nursing I NURS 1300

Mental Health Nursing I
NURS 1300
Unit IV
Anxiety Disorders and Crises
Objective 1
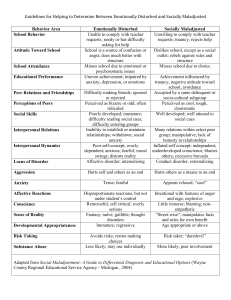
Define stress, stressors, and anxiety
Stress
a state of bodily or mental tension resulting from factors that tend to alter an existent equilibrium
necessary for growth and development
Stressor
anything that necessitates an adaptive response on the part of the individual
Objective 1 (cont’d)
Anxiety
a vague and sometimes intense sense of impending doom or apprehension that may appear to have no clearly identifiable cause
often an early response to illness
Objective 2
Describe the “fight-or-flight” syndrome
1 st stage of the general adaptation syndrome
Body’s response to perceived threat or danger
Hormones released to give body strength
increases heart rate
slows digestion
shunts blood flow to major muscle groups
Objective 3
Define the four levels of anxiety
Mild anxiety
client able to focus attention motivates learning and personal growth
Moderate anxiety
optimal level for learning client focused on immediate concerns
Severe anxiety
ability to think is clouded problem solving is impaired
Panic anxiety
inability to communicate or function effectively
misperceptions of surrounding events client may react impulsively by running or striking out
Objective 4
Describe various coping mechanisms used to deal with stress and anxiety
Imagery
Deep-breathing
Meditation
Yoga
Therapeutic touch
Music therapy
Biofeedback
Objective 5
Describe the major defense mechanisms
See Defense Mechanisms handout
Objective 6
Be able to discuss generalized anxiety, panic disorder, phobias, obsessivecompulsive disorder, and posttraumatic stress disorder
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Characterized by chronic anxiety and unrealistic, excessive worry and tension
Concurrent physical symptoms occur in the absence of organic conditions
fatigue headaches muscle aches and tension difficulty swallowing trembling and twitching irritability sweating and hot flashes
Panic Disorder
Characterized by recurrent panic attacks
episodes of intense apprehension of variable length
accompanied by feelings of impending doom often occur in familiar places, where there is seemingly nothing threatening to the individual
Concurrent physical symptoms include:
increased pulse
elevated blood pressure trembling diaphoresis shortness of breath chest pain nausea
Phobias
A phobia is an irrational, persistent fear of certain situations, objects, activities, or persons
The main symptom is the excessive, unreasonable desire to avoid the feared subject
Phobic fear interferes with daily life
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Obsessions = recurrent, unwanted thoughts
Compulsions = repetitive behaviors
often performed with the hope of preventing obsessive thoughts or making them go away hand washing, counting, checking, cleaning provides only temporary relief not performing rituals results in marked increase in anxiety
Time-consuming; causes distress or impairment
Client aware thoughts and behaviors are irrational, but feels powerless to stop
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
PTSD = a cluster of symptoms experienced following a distressing event
event is outside the range of normal experiences event produced intense fear, helplessness, and/or horror
Characteristic symptoms of PTSD include:
dissociative flashbacks
sustained high level of anxiety/arousal or a general numbing of responsiveness intrusive recollections or nightmares of the event
Objective 7
Be able to discuss somatoform disorders to include types, risk factors, signs and symptoms
Somatoform disorders = physical ailments for which no medical explanation has been found
Types of somatoform disorders
conversion disorder pain disorder hypochondriasis body dysmorphic disorder
Conversion Disorder
Disorder in which emotional distress or unconscious conflicts are expressed though physical symptoms
Sudden onset of symptoms following a stressful experience
Involves involuntary loss of one or more bodily functions in which diagnostic testing uncovers no physical cause
Risk factors
medical illness dissociative disorder
personality disorder
Pain Disorder
Persistent and chronic pain at one or more sites in which psychological factors are thought to play a role
Suffering is so severe that it impairs client’s ability to function
Risk factors
underlying medical condition
fibromyalgia
migraines
uncontrolled or inadequately managed pain depression and/or anxiety
Hypochondriasis
Excessive preoccupation or worry about having a serious illness
Characteristics include:
fears that minor bodily symptoms may indicate serious illness constant self-examination and self-diagnosis
preoccupation with one’s body
Fear is persistent and disabling in spite of reassurances that no organic pathology can be found
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Exaggerated belief that body is deformed or defective in some specific way
Most common complaints involve imagined or slight flaws of the face or head
Risk factors
chemical imbalance of the brain obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) eating disorder generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) higher socioeconomic status strict cultural standards
Objective 8
Describe the major types of crisis and what crisis intervention means
Major types of psychiatric crisis include:
1. Suicidal thinking or behaviors
2. Homicidal thinking or behaviors
3. Acute psychotic symptoms
4. Sudden change in mental status
5. Violence resulting from a mental disorder
Objective 8 (cont’d)
Crisis intervention = the provision of emergency psychological care to clients in order to restore their level of functioning and to prevent or decrease potential negative effects of the crisis
Intervention consists of:
preventing clients in crisis from harming themselves or others administering medications providing a supportive, therapeutic environment
Objective 9
Identify medical treatment and nursing interventions for the client with an anxiety or somatoform disorder
Medical treatment:
therapies
individual psychotherapy cognitive therapy behavior therapy group therapy medications
anxiolytics antidepressants
Nursing interventions:
anxiety R/T severe stress AEB patient’s selfreport/agitation/appearance
ineffective coping R/T severe stress AEB development of somatic symptoms disturbed body image R/T body dysmorphic disorder
AEB expression of repugnance with imagined defect or minor physical anomaly
Objective 10
Identify major drugs used, actions, side effects and nursing interventions for the client with an anxiety disorder or somatoform disorder
See Medications for Clients with
Anxiety/Somatoform Disorders handout