The Cold War Begins Essential Question: Cold War?
advertisement

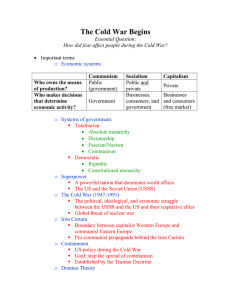
Topic: The Cold War Begins Essential Question: How did fear affect people during the Cold War? Important terms Economic systems: Karl Marx Adam Smith Important terms Economic systems: Important terms Economic systems: Communism Socialism Capitalism Important terms Economic systems: Communism Who owns the means of production? Socialism Capitalism Important terms Economic systems: Communism Who owns the means of production? Who makes decisions that determine economic activity? Socialism Capitalism Important terms Economic systems: Communism Who owns the means of production? Who makes decisions that determine economic activity? Socialism Capitalism Private Important terms Economic systems: Communism Who owns the Public means of (government) production? Who makes decisions that determine economic activity? Socialism Capitalism Private Important terms Economic systems: Communism Socialism Who owns the Public Public and means of (government) private production? Who makes decisions that determine economic activity? Capitalism Private Important terms Economic systems: Communism Socialism Capitalism Who owns the Public Public and means of (government) private production? Private Who makes decisions that determine economic activity? Businesses and consumers (free market) Important terms Economic systems: Communism Socialism Capitalism Who owns the Public Public and means of (government) private production? Private Who makes decisions that determine Government economic activity? Businesses and consumers (free market) Important terms Economic systems: Communism Socialism Capitalism Who owns the Public Public and means of (government) private production? Private Who makes decisions that determine Government economic activity? Businesses and consumers (free market) Businesses, consumers, and government Systems of government Totalitarian Absolute monarchy Dictatorship Fascism/Nazism Communism Fascism/Nazism Communism Democratic Republic Constitutional monarchy Republic Constitutional monarchy Superpower A powerful nation that dominates world affairs The US and the Soviet Union (USSR) A powerful nation that dominates world affairs The US and the Soviet Union (USSR) The Cold War (1947-1991) The political, ideological, and economic struggle between the USSR and the US and their respective allies Global threat of nuclear war The political, ideological, and economic struggle between the USSR and the US and their respective allies Global threat of nuclear war Iron Curtain Boundary between capitalist Western Europe and communist Eastern Europe 1946 Iron Curtain Boundary between capitalist Western Europe and communist Eastern Europe Pro-communist propaganda behind the Iron Curtain Boundary between capitalist Western Europe and communist Eastern Europe Pro-communist propaganda behind the Iron Curtain Containment US policy during the Cold War Goal: stop the spread of communism Established by the Truman Doctrine Goal: stop the spread of communism Established by the Truman Doctrine Domino Theory Belief that as one nation became communist, others would follow Influenced America’s decision to get involved in conflicts like Korea and Vietnam Influenced America’s decision to get involved in conflicts like Korea and Vietnam Discuss Economic systems Systems of government Superpower Cold War Iron Curtain Containment Domino Theory Write a sentence explaining why an “Iron Curtain” is a good metaphor for the divide between capitalism and communism in Europe. Belief that as one nation became communist, others would follow Influenced America’s decision to get involved in conflicts like Korea and Vietnam Marshall Plan (1948-1951) US program of economic aid for European countries after World War II Hamburg Marshall Plan (1948-1951) US program of economic aid for European countries after World War II Helped them rebuild Helped contain communism Helped them rebuild Helped contain communism Crisis in Berlin Germany’s capital was located within the Soviet-controlled zone Crisis in Berlin Germany’s capital was located within the Sovietcontrolled zone Berlin Blockade (1948-1949) First major crisis of the Cold War Soviets cut off supplies to West Berlin First major crisis of the Cold War Soviets cut off supplies to West Berlin Berlin Airlift Western Allies brought food and supplies by air daily Berlin Airlift Western Allies brought food and supplies by air daily Stalin ended the blockade after 11 months Lt. Gail Halvorsen – Operation Little Vittles Western Allies brought food and supplies by air daily Stalin ended the blockade after 11 months Alliances: NATO (1949) US, Canada, and their European allies NATO (1949) US, Canada, and their European allies Warsaw Pact (1955) Soviet response to NATO USSR and its allies Soviet response to NATO USSR and its allies Arms Race The US and the USSR competed for superior weapons Arms Race The US and the USSR competed for superior weapons The Soviets developed the atomic bomb in 1949 Nuclear weapons stockpiles The US and the USSR competed for superior weapons The Soviets developed the atomic bomb in 1949 Hydrogen bomb Developed by both the Americans and the Soviets during the 1950s 1952 Marshall Islands – Bikini Atoll 1955 Hydrogen bomb Developed by both the Americans and the Soviets during the 1950s 1000 times more powerful than WW2 atomic bombs Tsar Bomba, 1961 Developed by both the Americans and the Soviets during the 1950s 1000 times more powerful than WW2 atomic bombs “Duck and cover” drills 1000 times more powerful than WW2 atomic bombs “Duck and cover” drills Discuss Marshall Plan Crisis in Berlin Alliances Arms Race Write a sentence explaining why the Berlin Airlift was important. 1000 times more powerful than WW2 atomic bombs “Duck and cover” drills Space Race The US and the USSR competed in space exploration Space Race The US and the USSR competed in space exploration Soviets: Sputnik (1957) First man-made satellite (object that orbits the earth) Established the Soviets as the early leaders in Space First man-made satellite (object that orbits the earth) Established the Soviets as the early leaders in Space First manned space flight Yuri Gagarin: first human in space (1961) First manned space flight Yuri Gagarin: first human in space (1961) NASA (1958) JFK challenged the nation to reach the moon by the end of the decade (1961) NASA (1958) JFK challenged the nation to reach the moon by the end of the decade (1961) Apollo 11 (1969) First humans on the moon (July 20) Apollo 8 NASA (1958) JFK challenged the nation to reach the moon by the end of the decade (1961) Apollo 11 (1969) First humans on the moon (July 20) Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin First humans on the moon (July 20) Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin One of the greatest accomplishments in human history Established the Americans as the new leaders in Space One of the greatest accomplishments in human history Established the Americans as the new leaders in Space Red Scare (1947-1957) Fear of communist influence in society and government Red Scare (1947-1957) Fear of communist influence in society and government McCarthyism Senator Joseph McCarthy Fueled anti-communist fears Many people were accused and forced to testify before Congress Senator Joseph McCarthy Fueled anti-communist fears Many people were accused and forced to testify before Congress The term McCarthyism now means accusing someone without concern for evidence Many people were accused and forced to testify before Congress The term McCarthyism now means accusing someone without concern for evidence Discuss Sputnik Yuri Gagarin Apollo 11 McCarthyism Write a sentence explaining why Apollo 11 was important.