The Heart
advertisement
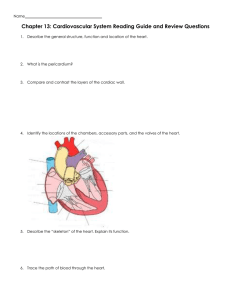
The Heart LEARNING ITS STRUCTURE AND HOW IT WORKS The Heart Organ that supplies blood and oxygen to the body. •Located slightly to the left of your breast bone (sternum) • Protected by a fluid filled sac called the pericardium • Receives blood from the vena cavae and pulmonary veins and sends blood out through the pulmonary arteries and aorta. Non-oxygenated blood travels to the heart through the superior and inferior vena cavae into the Right Atrium Allowed into the Right Ventricle through the Tricuspid Valve Sent through the Pulmonary Valve into the Pulmonary Artery, which feed blood to the capillaries surrounding the lungs How the Heart Works Oxygenated blood travels back to the heart through the Pulmonary Veins into the Left Atrium Allowed into the Left Ventricle through the Mitral Valve Sent through the Aortic Valve into the Aorta Blood sent through the Aorta is sent through all areas of the body to feed oxygen and nutrients to muscles, organs, and tissues. Cardiac Conduction The sinoatrial (SA) node contracts generating nerve impulses throughout the heart wall. 1. 1. Both Atria contract 2. The atrioventricular (AV) node is delays the impulse from the SA node 1. Allows contents of Atria to empty 3. AV Bundle Impulse Conduction 1. Impulse travels through atrioventricular bundle to left and right ventricles 4. Purkinje Fibers 1. Triggers ventricles to contract Cardiac Conduction SA Node (pacemaker of the heart) AV node AV bundles Purkinje Fibers Types of Cardiac Conditions Arrhythmia A change in the normal sequence of the heart rate Irregular Heartbeat Atrial Fibrillation – upper chambers contract irregularly Bradycardia – slow heart rate Premature Contraction Tachycardia – fast heart rate Ventricular Fibrillation – lower chambers contract irregularly Atherosclerosis A buildup of plaque on the artery walls Types of Cardiac Conditions Congenital Heart Defects Structural problems present from birth Could range from valve to structural to arterial defects Myocardial Infarction Heart attack Occurs when the supply of nutrient-rich and oxygenated blood is cut off from the heart - ischemia Atherosclerosis occurring in the coronary arteries leads to ischemia, which leads to the heart attack Heart muscle tissue dies as a result of the stoppage of oxygen and nutrients How a Heart Attack Occurs Types of Cardiac Conditions Cardiac Arrest NOT a heart attack Caused when the electrical system malfunctions Arrhythmia can lead to cardiac arrest Ventricular fibrillation is most common during cardiac arrest Cardiac Arrest Types of Cardiac Conditions Hypertension High Blood Pressure Heart is working too hard to push blood through the body Can be caused by smoking, obesity, high salt intake, lack of physical activity, stress, genetics, excessive alcohol consumption Hypotension Low Blood Pressure Heart isn’t pumping enough blood to the organs and tissues Pregnancy, hormonal imbalances, diabetes, low blood sugar, medications, or heart diseases can cause this Serious injury, dehydration, low or high body temperature can cause sudden hypotension Types of Cardiac Conditions Stroke Blood flow to the brain is interrupted Results from a blockage of oxygen and nutrient rich blood to the brain Deadly if not treated immediately Severe headache Dizziness Numbness on one side of body Confusion Trouble walking Trouble seeing out of one or both eyes Cardiovascular System Responsible for transporting and providing nutrients and oxygen, carries away wastes, and helps fight disease Blood – comprised of plasma (55%), red blood cells (40%), white blood cells and platelets (together ~5%) Heart – pumps blood Arteries – transport blood away from heart Veins – transport blood to the heart Capillaries – tiny blood vessels that allow nutrients and oxygen to pass through to organs and skin and waste to enter the blood stream to be carried away