Global imbalances and exchange rates Jomo Kwame Sundaram 26 January 2010
advertisement

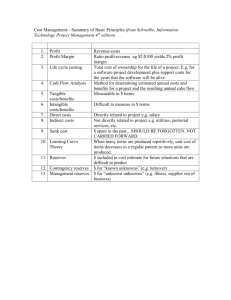
Global imbalances and exchange rates Jomo Kwame Sundaram 26 January 2010 Global imbalances grow USD bn 1000 Latin America Other industrialised 800 Other Asia China 600 Japan 400 Oil exporters 200 0 . -200 -400 United States -600 -800 Euro Area Central and Eastern -1000 2 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 Europe World trade collapse 12 10.9 9.2 7.7 Annual percentage change 8 6.6 4.1 4 2.4 0.5 0 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 -4 -8 -12 -11.1 3 South exports fall more (volume index, 1998 = 100) 280 Developing and other non-OECD country exports 260 240 220 World trade 200 180 160 OECD country exports 140 120 20 06 M 20 1 06 M 20 3 06 M 20 5 06 M 20 7 06 M 00 9 6M 20 11 07 M 20 1 07 M 20 3 07 M 20 5 07 M 20 7 07 M 00 9 7M 20 11 08 M 20 1 08 M 20 3 08 M 20 5 08 M 20 7 08 M 00 9 8M 20 11 09 M 1 100 Source: CPB Mineral prices fell more Imbalances narrow 600 United States 400 Japan Billion US$ 200 0 European Union -200 -400 -600 Developing countries (excl China) and EiT -800 China 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 6 ST real interest rates Short-term real interest rates of major economies (%) 4 3 2 Japan U.S. Euro 1 Negative 0 Area Rates -1 2008M7 2008M1 2007M7 2007M1 2006M7 2006M1 2005M7 2005M1 2004M7 2004M1 2003M7 2003M1 2002M7 2002M1 2001M7 2001M1 2000M7 2000M1 -2 7 US Fed LT rates Yields of U.S. T-Bonds and Corporate Bonds %(1978-2007) persistenly 20 18 falling long-term 16 rates 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1/31/1978 6/30/1982 11/30/1986 4/30/1991 9/30/1995 2/29/2000 7/31/2004 BAA corporate bond AAA corproate bond 8 10-year T-bond (%) Easy liquidity Measurement of Traditional Liquidity Indicator in Major Economies (as a percentage of total GDP of U.S., Japan and Euro Area) Base Money 2008Q1 2007Q3 2007Q1 2006Q3 Reserve 2006Q1 2005Q3 2005Q1 9 Base Money+Reserve 2004Q3 2004Q1 2003Q3 2003Q1 2002Q3 2002Q1 2001Q3 2001Q1 2000Q3 2000Q1 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 Net transfer of financial resources from South to North 200 Billions of US dollars 0 -200 -400 -600 -800 -1000 Developing economies Africa Eastern and Southern Asia Western Asia Source: UN World Economic Situation and Prospects 2008 (forthcoming) Latin America Net capital importers Capital Importers Turkey 3% Others 20% Greece 3% Italy 3% Australia 3% U.K. 9% Spain 9% U.S. 50% 11 Capital inflows contract $ Billions 750 500 250 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009* Bretton Woods vs Keynes • • • • • • • • • Dollar-gold parity ($35/oz.) Permanent US current account deficit possible Seigneurage income Vietnam Run on Eurodollars 1971 End of BW system ‘Non-system’: IMF Interim Committee Rise of Japan Plaza 2 endaka Drucker: X border flows; K acct liberalization Rise of China exchange rates, SWF EA miracle + X rates • EP con EP: ISI + EOI; scale economies • Undervalued X rates since postwar Japan • SEA mid-80s devaluations + endaka • Unlike NEA, SEA FDI-dependent • Finance dominant, oppose $ appreciation post-1995 end of endaka 1997-98 crisis China boom + X rates • • • • • • • • • 1994 RMB ‘devaluation’ Contract manufacturing: learning by doing End of TVEs boom scale economies Productivity gains + Lewisian L market consumer price deflation + high growth China super-competitive Big overall trade surplus reserves accumulation from mid-2000s $3trn USD assets, including >$1trn US T bonds China cannot afford massive $ depreciation Japanese endaka end of Japanese miracle Self-protection • 1990s’ LA, EA crises accumulate reserves - no lender of last resort - onerous IMF conditionalities • No insurance element Crisis + reserves Financial positions stronger than during Asian + LA crises (more foreign reserves, ‘better’ fiscal balances) But reserves rapidly evaporated with export collapse; fiscal space also diminished • IMF late ‘09 paper (Blanchard, et al.): Reserve accumulation did not help in crisis 17 Thank you Please visit IDEAs www.networkideas.org UN-DESA esa.un.org and G24 www.g24.org websites •Research papers •Policy briefs •Other documents 18