JAVA Database Connectivity (JDBC) update it using SQL.
advertisement

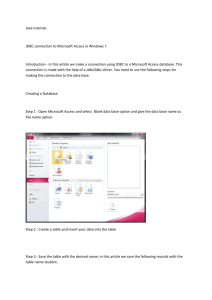
JAVA Database Connectivity (JDBC)
JDBC lets Java programmers connect to a database, query it or
update it using SQL.
Java and JDBC have an essential advantage over other database
programming environments since the programs developed with
this technology are platform-independent and vendorindependent.
Because of its universality Java and JDBC could eventually
replace proprietary database languages.
The Design of JDBC
JavaSoft's JDBC consists of two layers: the JDBC API and the
JDBC Driver Manager API.
The JDBC API is the top layer and is the programming interface in
Java to structured query language (SQL) which is the standard for
accessing relational databases.
The JDBC API communicates with the JDBC Driver Manager
API, sending it various SQL statements. The manager
communicates (transparent to the programmer) with the various
third party drivers (provided by Database vendors like Oracle) that
actually connect to the database and return the information from
the query.
Java Application
JDBC Driver Manager
JDBC/
ODBC
Bridge
Vendorsupplied
JDBC
driver
ODBC
driver
Database
Database
JDBC to Database communication path
Notes:
Some database vendors already have JDBC drivers (e.g.
Oracle).
For those databases that do not have a JDBC driver, you need to
install the database's ODBC driver (available for most
databases) and the JDBC to ODBC bridge supplied by JavaSoft.
The JDBC to ODBC bridge has the advantage of letting people
use JDBC immediately. It has the disadvantage of requiring yet
another layer between the database and the JDBC, although in
most cases the performance is acceptable.
Basic JDBC Programming Concepts
Example shown below opens a database connection, executes a
query, and iterates through the results.
import java.net.*;
import java.sql.*; //needed for JDBC
import java.io.*;
class MakeDB {
public static void main (String args[]) {
try {
//load the driver needed by the application
Class.forName("specialdb.Driver");
//Construct the database address
String dbaseURL = "jdbc:mysubprotocol://dbasehost/dbasename";
//Make the database connection
Connection dbConnection =
DriverManager.getConnection(dbaseURL, "dbaseuser", "dbasepasswd");
//Create a statement and execute the SQL query
Statement query = dbConnection.getStatement();
ResultSet results =
query.executeQuery("SELECT first_name, last_name from user_table);
//Iterate through the results and print them to standard output
while(results.next()) {
String fname = results.getString("first_name);
String lname = results.getString("last_name");
System.out.println("Found user " + fname + " " + lname);
}
catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("SQLException: " + e.);
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("ClassNotFoundException: " + e);
}
}
}