4. Digestive System WEB
advertisement
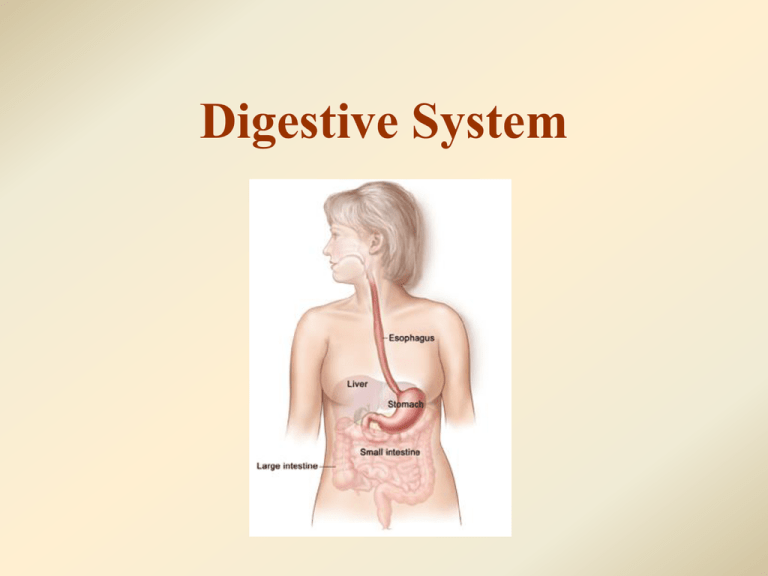
Digestive System DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Main function: • Breaks down food into nutrients that can be absorbed by body cells • Peristalsis = contraction & relaxation of the smooth muscle in digestive tract; helps to move the food down (said ‘peri stahl sis’) • Mouth = teeth ↑ surface area of food ; salivary glands produce enzyme amylase which begins to break down carbohydrates • Uvula = prevents food from entering the nasal cavity • Epiglottis = prevents food from entering the trachea (chewing while talking or with mouth open allows the epiglottis to remain open and therefore increases your likelihood of choking or having your food/drink ‘go down the wrong pip’ • Esophagus = takes the swallowed food into the stomach • Stomach = continues to break down carbohydrates and digestion of proteins begins (contains HCl & enzyme pepsin) (HCl is hydrochloric acid) • Small intestine = – digestion of carbohydrates & proteins continues and ends – digestion of fats begins & ends – uses bile and many digestive enzymes – broken down nutrients pass through the intestinal walls into the bloodstream Small Intestine Cont. • 7 m long (1 meter is about the width of a doorway) • 1st part = duodenum, receives bile from gallbladder & digestive enzymes from pancreas (25 cm) • 2nd part = jejunum (2.5 m) • 3rd part = ilium (3.5 m) Small Intestine Cont. • Large surface area due to the presence of villi • Villi – one cell thick; ↑ surface area for diffusion • Next to each villus are blood vessels which carry nutrients to other cells of the body • Liver = secretes bile needed for digestion of fats • Gallbladder = stores bile & releases it into small intestine • Pancreas = releases digestive enzymes into small intestine • Large intestine (colon) = water is removed from the undigested food • Rectum = last 8 inches of the large intestine; pass the undigested food out of the body through anus Action of Bile • Emulsifies (breaks down) fats (↑ surface area to help enzyme action) • Bile also neutralizes any excess stomach acid (C.H.O.) carbohydrase Glucose and simple sugars WATER PROTEINS CARBOHYDRATES FATS + OILS (C.H.O.) lipase Glycerol and fatty acids (C.H.O.N.) protease Amino acids VITAMINS + SALTS (H2O) (various elements) Keeping the body in good health excess Many uses in the body Excess broken down in liver Excess stored in liver as glycogen Energy produced in cell respiration Stored under the skin Form proteins in the body urea glucose Passed to the kidneys by blood for removal as urine Some out in sweat How much do we remember? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What enzyme is in saliva? What does this enzyme help break down? What type of food is broken down in the stomach? What happens to food that can’t be digested? What is the function of bile? Talk about the questions and answers with a friend.










