1. Respiratory System WEB
advertisement
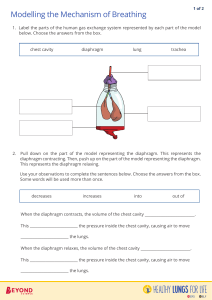
Respiratory System Chapter 23 Respiration Overview The Respiratory System • Provides a means of gas exchange between the environment and the body The Components of the Respiratory System 1. Upper Respiratory Passages: nose/mouth, pharynx (back of the mouth), larynx (voice box), trachea, bronchi & bronchioles • Filter, warm & moisten air • Trachea & bronchi are lined with cilia that move mucus towards throat 2. Lower Respiratory Passages: alveoli • Thin walled sacs where diffusion of O2 and CO2 takes place • Inhalation – ribcage expands, diaphragm contracts downward, space in chest cavity ↑, pressure in chest cavity ↓, and air from outside rushes in • Exhalation – ribs drop, diaphragm relaxes upward, space in chest cavity ↓ , pressure in chest cavity ↑, and air from inside rushes out Control of Respiration • Breathing is usually an involuntary process • Controlled by medulla oblongata • When levels of CO2 ↑, it sends nerve signals to contract the intercostals & diaphragm Common Disorders • Cystic Fibrosis – genetic disease, too much respiratory mucus is produced, breathing is difficult • Pneumonia – fluids leak into alveoli due to inflammation (typically from an infection), bronchioles swell and constrict • Emphysema – shortness of breath due to damage of alveoli, mainly due to smoking • Lung cancer – deadliest type of cancer