1. Cells PPT
advertisement

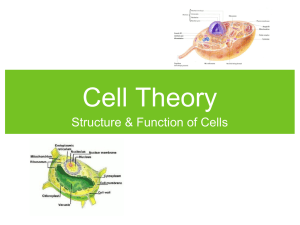
The Cellular Level of Organization Cell Diversity • Lots of shapes and sizes; we have about 200 different types of specialized cells Typical Cell Fig. 3.1 What discipline studies cells? Cell biology (Cytology) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tkx14B7WFcM What is around our cells? Our cells are surrounded by extracellular fluid frequently called interstitial fluid Cell Organization The cell includes three basic parts: 1. Plasma membrane (outer covering of cell) 2. Cytoplasm (cytosol & organelles) 3. Nucleus Plasma Membrane Functions Outer boundary; functions in: 1. Physical isolation 2. Regulates what comes in and out 3. Anchors cytoskeleton (think of this as scaffolding) Cell Membrane Structures The cell membrane contains: 1. Two layers of phospholipids (isolate the cell from extracellular fluid) 2. Proteins (may attach cell membrane to other structures, recognize invaders, speed up chemical reactions, bind & transport certain substances) 3. Cholesterol (↑ stability of cell membrane) Cell Membrane Selective Permeability = not all material can enter the cell Transport processes found in cells: • PASSIVE: simple diffusion & facilitated diffusion • ACTIVE: active transport & transport in vesicles Active = requires E; from low to high concentration Passive = does not require E; from high to low concentration Osmosis – simple diffusion of water Fig. 3.8 Facilitated diffusion or Active transport - Fig. 3.10 – 3.11 Vesicular Transport (endocytosis & exocytosis) Fig. 3.12 – 3.14 Cytoplasm 2 parts: 1. Cytosol = fluid portion, also called intracellular fluid; contains dissolved nutrients, ions, proteins, and waste products 2. Organelles = cell “organs” or functional parts Cytoskeleton • Gives the cytoplasm strength & flexibility Microfilaments Microvilli • ↑ the surface area for absorption of material Centrioles • Direct the movement of chromosomes during cell division Cilia & Flagella • Cilia beat rhythmically to move fluids across cell surface • Flagella move cells Ribosomes • Sites of protein synthesis • Attached to ER or free in the cytosol Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 1. Rough – contains ribosomes; chemically modifies newly made proteins and ships them to the Golgi apparatus 2. Smooth – no ribosomes; synthesis of lipids, detoxifies certain drugs Golgi Apparatus •Involved in packaging of proteins and production of lysosomes Lysosomes, Peroxisomes & Proteasomes • Vesicles filled with digestive enzymes • Lysosomes recycle worn out cell structures • Peroxisomes neutralize toxins such as alcohol and hydrogen peroxide (abundant in liver) • Proteasomes destroy unneeded and damaged proteins Lysosomes & Peroxisomes Blue arrows = peroxisomes Red arrow = lysosome Mitochondria • Produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) = our energy currency Nucleus • Control center of cell • Contains DNA needed for synthesis of 100,000 different proteins Red blood cells of humans do not have a nucleus; Skeletal muscle cells have multiple nuclei