powerpoint all sides
advertisement

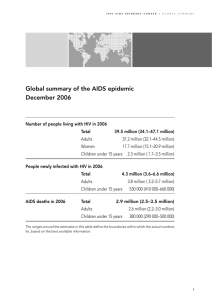
Global summary of the AIDS epidemic December 2008 Number of people living with HIV in 2008 Total Adults Women Children under 15 years 33.4 million [31.1 – 35.8 million] 31.3 million [29.2 – 33.7 million] 15.7 million [14.2 – 17.2 million] 2.1 million [1.2 – 2.9 million] People newly infected with HIV in 2008 Total Adults Children under 15 years 2.7 million [2.4 – 3.0 million] 2.3 million [2.0 – 2.5 million] 430 000 [240 000 – 610 000] AIDS-related deaths in 2008 Total Adults Children under 15 years 2.0 million [1.7 – 2.4 million] 1.7 million [1.4 – 2.1 million] 280 000 [150 000 – 410 000] The ranges around the estimates in this table define the boundaries within which the actual numbers lie, based on the best available information. 2009 AIDS epidemic update Global estimates 1990–2008 Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) Number (millions) Number of people living with HIV 40 1.2 30 0.9 20 % 10 0.3 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1990 Number of people newly infected with HIV 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Number of adult and child deaths due to AIDS 5 5 4 4 Number (millions) Number (millions) 0.6 3 2 1 3 2 1 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure I 1999 2002 2005 2008 Regional HIV and AIDS statistics 2008 and 2001 (First of 2 parts) Adults & children living with HIV 2008 Sub–Saharan Africa Middle East & North Africa South and South–East Asia East Asia Latin America Caribbean Eastern Europe & Central Asia Western & Central Europe 2001 Adults & children newly infected with HIV 2008 2001 22.4 million 19.7 million 1.9 million 2.3 million [20.8 – 24.1 million] [18.3 – 21.2 million] [1.6 – 2.2 million] [2.0 – 2.5 million] 310 000 200 000 35 000 30 000 [250 000 – 380 000] [150 000 – 250 000] [24 000 – 46 000] [23 000 – 40 000] 3.8 million 4.0 million 280 000 310 000 [3.4 – 4.3 million] [3.5 – 4.5 million] [240 000 – 320 000 [270 000 – 350 000] 850 000 560 000 75 000 99 000 [700 000 – 1.0 million] [480 000 – 650 000] [58 000 – 88 000] [75 000 – 120 000] 2.0 million 1.6 million 170 000 150 000 [1.8 – 2.2 million] [1.2 – 1.6 million] [150 000 – 200 000] [140 000 – 170 000] 240 000 220 000 20 000 21 000 [220 000 – 260 000] [200 000 – 240 000] [16 000 – 24 000] [17 000 – 24 000] 1.5 million 900 000 110 000 280 000 [1.4 – 1.7 million] [800 000 – 1.1 million] [100 000 – 130 000] [240 000 – 320 000] 850 000 660 000 30 000 40 000 [710 000 – 970 000] [580 000 – 760 000] [23 000 – 35 000] [31 000 – 47 000] North America 1.4 million 1.2 million 55 000 52 000 [1.2 – 1.6 million] [1.1 – 1.4 million] [36 000 – 61 000] [42 000 – 60 000] Oceania 59 000 36 000 3900 5900 [51 000 – 68 000] [29 000 – 45 000] [ 2900 – 5100] [ 4800 – 7300] TOTAL 33.4 million 29.0 million 2.7 million 3.2 million [31.1 – 35.8 million] [27.0 – 31.0 million] [2.4 – 3.0 million] [2.9 – 3.6 million] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Regional HIV and AIDS statistics 2008 and 2001 (Last of 2 parts) Adult prevalence (%) 2008 Sub–Saharan Africa Middle East & North Africa South and South–East Asia East Asia Adult & child deaths due to AIDS 2001 2008 2001 5.2% 5.8% 1.4 million 1.4 million [4.9% – 5.4%] [5.5% – 6.0%] [1.1 – 1.7 million] [1.2 – 1.7 million] 0.2% 0.2% 20 000 11 000 [<0.2% – 0.3%] [0.1% – 0.2%] [15 000 – 25 000] [7800 – 14 000] 0.3% 0.3% 270 000 260 000 [0.2% – 0.3%] [<0.3% – 0.4%] [220 000 – 310 00] [210 000 – 320 000] 0.1% <0.1% 59 000 22 000 [<0.1%] [<0.1%] [46 000 – 71 000] [18 000 – 27 000] Latin America 0.6% 0.5% 77 000 66 000 [0.5% – 0.6%] [<0.5% – 0.6%] [66 000 – 89 000] [56 000 – 77 000] Caribbean 1.0% 1.1% 12 000 20 000 [0.9% – 1.1%] [1.0% – 1.2%] [9300 – 14 000] [17 000 – 23 000] Eastern Europe & Central Asia 0.7% 0.5% 87 000 26 000 [0.6% – 0.8%] [0.4% – 0.5%] [72 000 – 110 000] [22 000 – 30 000] Western & Central Europe 0.3% 0.2% 13 000 7900 [0.2% – 0.3%] [<0.2% – 0.3%] [10 000 – 15 000] [6500 – 9700] North America 0.6% 0.6% 25 000 19 000 [0.5% – 0.7%] [0.5% – 0.7%] [20 000 – 31 000] [16 000 – 23 000] Oceania 0.3% 0.2% 2000 <1000 [<0.3% – 0.4%] [<0.2% – 0.3%] [1100 – 3100] [<500 – 1200] TOTAL 0.8% 0.8% 2.0 million 1.9 million [<0.8% – 0.8%] [<0.8% – 0.8%] [1.7 – 2.4 million] [1.6 – 2.2 million] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Estimate of the annual number of infant infections averted through the provision of antiretroviral prophylaxis to HIV-positive pregnant women, globally, 1996–2008 70 000 Infant infections averted 60 000 50 000 40 000 30 000 20 000 10 000 0 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure II 2005 2006 2007 2008 Estimated number of new child infections at current levels of antiretroviral prophylaxis and without antiretroviral prophylaxis , globally, 1996–2008 600 000 500 000 400 000 300 000 200 000 100 000 0 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 No prevention of mother-to-child transmission At current levels of antiretroviral prophylaxis 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure III 2007 2008 Regional estimates of the number of infant infections at current levels of antiretroviral prophylaxis and without antiretroviral prophylaxis Latin America 6 50 8 5 40 30 20 (thousands) 10 6 4 2 10 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 1996 2008 Caribbean 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 (thousands) 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 5 500 4 400 3 2 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2006 2008 300 200 100 0 0 1998 Sub-Saharan Africa 1 0.5 1998 1996 Middle East and North Africa 3.5 3.0 1996 2 0 2008 (thousands) 1996 4 3 1 0 0 (thousands) Eastern Europe and Central Asia 60 (thousands) (thousands) Asia 0 1996 1998 No prevention of mother-to-child transmission 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 1996 1998 2000 2002 At current levels of antiretroviral prophylaxis 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure IV 2004 Estimated number of AIDS-related deaths with and without antiretroviral therapy, globally, 1996–2008 3.0 Number (millions) 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Year No antiretroviral therapy At current levels of antiretroviral therapy 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure V 2007 2008 Estimated number of AIDS-related deaths with and without antiretroviral therapy, by region, 1996–2008 Caribbean 120 400 20 100 300 200 (thousands) 25 100 15 10 5 0 2000 2002 2004 2006 Latin America 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 (thousands) 120 80 40 0 25 2.0 20 1.6 15 1.2 10 2002 2004 2006 2008 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 2006 2008 0.8 0.4 0 2000 1998 Sub-Saharan Africa 5 1998 1996 Middle East and North Africa 160 1996 40 0 1996 2008 (millions) 1998 80 60 20 0 1996 (thousands) Eastern Europe and Central Asia 500 (thousands) (thousands) Asia 0 1996 No antiretroviral therapy 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 2008 1996 1998 At current levels of antiretroviral therapy 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure VI 2000 2002 2004 Estimated number of Life-years added due to antiretroviral therapy, by region, 1996–2008 8 7.2 million 7 (millions) 6 5 4 3 2.3 million 2 1.4 million 1 590 000 73 000 40 000 49 000 Eastern Europe and Central Asia Caribbean Oceania 7500 0 Western Europe and North America SubSaharan Africa Latin America Asia 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure VII Middle East and North Africa Adult (aged 15–49) HIV prevalence in (sub-) national population-based surveys which include HIV testing, 2001–2008 Country Sub–Saharan Africa Benin Botswana Burkina Faso Burundi Cameroon Central African Republic Chad Congo Côte d'Ivoire DR Congo Djibouti Equatorial Guinea Ethiopia Ghana Guinea Kenya Lesotho Liberia Malawi Mali Niger HIV prevalence (%) (Year) 1.2 25.0 25.2 1.8 3.0 3.6 5.5 6.2 3.3 3.2 4.7 1.3 2.9 3.2 1.4 2.2 1.5 7.8 6.7 23.4 1.6 12.7 1.3 1.8 0.7 0.9 (2006) (2008) (2004) (2003) (2007) (2002) (2004) (2006) (2005) (2009) (2005) (2007) (2002) (2004) (2005) (2003) (2005) (2008) (2003) (2004) (2007) (2004) (2006) (2001) (2006) (2002) Country Nigeria Rwanda Senegal Sierra Leone South Africa Swaziland Uganda UR Tanzania Zambia Zimbabwe Asia Cambodia India Papua province (Indonesia) Hai Phong province (Viet Nam) Caribbean Dominican Republic Haiti 2009 AIDS epidemic update HIV prevalence (%) (Year) 3.6 3.0 0.7 1.5 1.5 16.9 16.2 15.6 25.9 6.4 5.7 7.0 14.3 15.6 18.1 (2007) (2005) (2005) (2008) (2005) (2008) (2005) (2002) (2006–07) (2004–05) (2007) (2004) (2007) (2001–02) (2005–06) 0.6 0.3 2.4 0.5 (2005) (2005–06) (2006) (2005) 0.8 1.0 2.2 (2007) (2002) (2005–06) Sub-Saharan Africa Number of people living with HIV 2008 22.4 million [20.8 million–24.1 million] 2001 19.7 million [18.3 million–21.2 million] 2008 Number of new infections 1.9 million [1.6 million–2.2 million] 2001 2.3 million [2.0 million–2.5 million] Number of children newly infected 2008 390 000 [210 000–570 000] 2001 460 000 [260 000–640 000] Number of AIDS-related deaths 2008 1.4 million [1.1 million–1.7 million] 2001 1.4 million [1.2 million–1.7 million] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Sub-Saharan Africa estimates 1990–2008 Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) Number (millions) Number of people living with HIV 25 10 20 8 15 6 % 10 4 5 2 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1990 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Number of adult and child deaths due to AIDS 4 3 3 2 2 1 (millions) 4 Number Number (millions) Number of people newly infected with HIV 1993 0 1 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 1 1999 2002 2005 2008 HIV prevalence by marital status and gender in the general populations of nine West African countries 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 Burkina Faso 6.3 2.2 1.6 0.8 Single too few cases 2.8 Divorced/ separated/ widowed Married/ cohabiting Ghana 6.7 6.2 2.9 1.1 3.3 2.3 too few cases 0.3 Single Married/ cohabiting Divorced/ separated Widowed Niger 6.4 3.6 0.4 0.4 Single 0.5 0.9 Married/ cohabiting Divorced/ separated 3.9 too few cases Widowed 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 Benin 10.6 7.2 0.5 1.3 0.2 Single Married/ cohabiting too few cases 2.3 1.2 Divorced/ separated Guinea Widowed 14.8 3.9 1.2 1.6 0.6 Single 1.3 Married/ cohabiting too few cases 0.0 Divorced/ separated Widowed Senegal 3.8 0.3 0.0 Single 0.9 0.9 Married/ cohabiting 2.2 Divorced/ separated/ widowed Source: Lowndes et al. (2008). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 2 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 16 14 12 10 % 8 6 4 2 0 Côte d’Ivoire 14.9 11.0 6.1 4.6 3.6 1.3 Single Divorced/ separated/ widowed Married/ cohabiting Mali 8.2 0.4 0.6 Single 1.4 0.9 Married/ cohabiting 1.8 too few cases 2.2 Divorced/ separated Widowed Sierra Leone 5.3 1.8 0.9 Single 1.4 1.8 Married/ cohabiting 3.1 Divorced/ separated 2.2 too few cases Widowed Female Male Distribution of new infections by mode of exposure in Ghana and Swaziland, 2008 100 No risk Medical injections 80 Blood transfusions Injecting drug use (IDU) Partners IDU 60 Sex workers % Clients Partners of Clients 40 Men who have sex with men (MSM) Female partners of MSM Engaged in casual sex (CS) 20 Partners of CS Low-risk heterosexual 0 Ghana Swaziland 1 Swaziland 2 Note: sensitivity analysis for Swaziland used different data sources. Sources: Bosu et al. (2009) and Mngadi et al. (2009). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 3 HIV prevalence among antenatal clinic clients in Swaziland, 1992–2008 50 HIV prevalence (%) 40 30 20 10 0 1992 1994 1996 1998 2000 2002 Source: Ministry of Health and Social Welfare (2009). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 4 2004 2006 2008 Age at first sexual intercourse by education status in Swaziland, 2007 100 No education Lower primary 80 Higher primary Secondary High School 60 Tertiary % 40 20 0 Women < 15 yrs Women < 18 yrs Men < 15 yrs Sources: Central Statistical Office & Macro International (2008). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 5 Men < 18 yrs HIV prevalence among men who have sex with men in countries in sub-Saharan Africa, 2002–2008 50 HIV prevalence (%) 40 30 20 10 0 Botswana Malawi Namibia South Africa 1 South Africa 2 Zambia Kenya 1 Southern Africa Kenya 2 East Africa Source: Smith et al. (2009), Baral et al. (2009), and Sanders et al. (2007) 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 6 UR Tanzania Nigeria Senegal West Africa Asia Number of people living with HIV 2008 4.7 million [3.8 million–5.5 million] 2001 4.5 million [3.8 million–5.2 million] 2008 Number of new infections 350 000 [270 000–410 000] 2001 400 000 [310 000–480 000] Number of children newly infected 2008 21 000 [13 000–29 000] 2001 33 000 [18 000–49 000] Number of AIDS-related deaths 2008 330 000 [260 000–400 000] 2001 280 000 [230 000–340 000] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Asia estimates 1990–2008 Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) Number (millions) Number of people living with HIV 8 0.4 6 0.3 4 % 2 0.1 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1990 Number of people newly infected with HIV 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Number of adult and child deaths due to AIDS 1.0 1.0 0.8 0.8 Number (million) Number (million) 0.2 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.6 0.4 0.2 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 7 1999 2002 2005 2008 Age-adjusted HIV prevalence among antenatal attendees aged 15–24 from 2000 to 2007 in high-prevalence southern states (Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu) and northern states of India 2.5 Age-adjusted HIV prevalence (%) Southern states 2.0 Northern states 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Logarithmic trend line; test for trend by logistic regression, with age adjustment to the entire study population, n = 202 254 for the south, n = 221 588 for the north. Source: Arora et al. (2008). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 8 2007 Vulnerability to sexual HIV transmission in commercial sex in Karachi and Lahore, Pakistan 28 Female sex workers (FSWs) 60 82 20 Male clients of FSWs 45 61 42 Male sex workers 57 63 31 51 Hijras 55 0 20 40 60 80 Per cent Has never heard of HIV/AIDS Does not know that condoms can prevent transmission of HIV No perceived HIV risk Source: Bokhari et al. (2007). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 9 100 Saturating prevention coverage through complementary programming. Avahan has achieved a high coverage of target populations (routine programme monitoring data) Injecting drug users Manipur 62% 35 000 est. Nagaland 53% 28 000 est. Karnataka Andhra Pradesh Maharashtra Tamil Nadu* High Risk – Men who have sex with men 26 000 est. Andhra Pradesh 46 000 est. 61% 26% 70% 19% 14% 76% 64% 27 000 est. 21 000 est. 36% 15% Maharashtra Tamil Nadu* 11% 74% 38% 84 000 est. Karnataka 20% 26% 72 000 est. 22% 58% 29% 115 000 est. 12% 26% 22% 89 000 est. Female sex workers 26% 24% 5% 36% 49% 26% Percent of Mapped Urban Key Population covered** Government of India and Others Avahan Percentages indicate intended coverage through establishment of services in specific geographic areas. * Includes districts with no intended coverage. ** Mapping and size estimation quality varies by state. Does not include rural areas Source: Avahan and State AIDS Control Society programme data (2008). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 10 Uncovered Comparison of the incidence of syphilis in China reported from 26 sentinel sites and from the nationwide sexually transmitted disease surveillance system 35 Incidence (per 100 000) 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 Reported incidence of total syphilis from sentinel sites Reported incidence of total syphilis from the nationwide sexually transmitted disease surveillance system Source: Chen et al. (2007). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 11 2005 Trends in HIV, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and syphilis in men who have sex with men in Beijing in 2004, 2005 and 2006 14 12 Prevalence (%) 10 HIV Hepatitis B 8 Hepatitis C Syphilis 6 4 2 0 2004 2005 2006 Source: Ma et al. (2007). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 12 Eastern Europe and Central Asia Number of people living with HIV 2008 1.5 million [1.4 million–1.7 million] 2001 900 000 [800 000–1.1 million] 2008 Number of new infections 110 000 [100 000–130 000] 2001 280 000 [240 000–320 000] Number of children newly infected 2008 3700 [1700–6000] 2001 3000 [1600–4300] Number of AIDS-related deaths 2008 87 000 [72 000–110 000] 2001 26 000 [22 000–30 000] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Eastern Europe and Central Asia estimates 1990–2008 Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) Number (millions) Number of people living with HIV 2.0 1.0 1.6 0.8 1.2 0.6 % 0.8 0.4 0.4 0.2 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1990 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Number of adult and child deaths due to AIDS 400 400 300 300 Number (thousands) Number (thousands) Number of people newly infected with HIV 1993 200 100 200 100 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 13 1999 2002 2005 2008 HIV cases per million population in the WHO Eastern Europe region by year of notification, 2000–2007 180 HIV cases per million population 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 Note: Data from Russian Federation not included. Source: Van de Laar et al. (2008). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 14 2005 2006 2007 Caribbean Number of people living with HIV 2008 240 000 [220 000–260 000] 2001 220 000 [200 000–240 000] 2008 Number of new infections 20 000 16 000–24 000 2001 21 000 [17 000–24 000] Number of children newly infected 2008 2300 [1400–3400] 2001 2800 [1700–4000] Number of AIDS-related deaths 2008 12 000 [9300–14 000] 2001 20 000 [17 000–23 000] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Caribbean estimates 1990–2008 Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) Number (thousands) Number of people living with HIV 400 2.0 300 1.5 200 % 100 0.5 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1990 Number of people newly infected with HIV 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Number of adult and child deaths due to AIDS 80 80 60 60 Number (thousands) Number (thousands) 1.0 40 20 0 40 20 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 15 1999 2002 2005 2008 HIV prevalence trends among young people (aged 15–24) in the Dominican Republic, 1991–2007 2.5 Pregnant women at La Altagracia Hospital, Santo Domingo HIV prevalence (%) 2.0 Women in population-based survey Men in population-based survey 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Source: Halperin, et al (2009). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 16 Latin America Number of people living with HIV 2008 2.0 million [1.8 million–2.2 million] 2001 1.6 million [1.5 million–1.8 million] 2008 Number of new infections 170 000 [150 000–200 000] 2001 150 000 [140 000–170 000] Number of children newly infected 2008 6900 [4200–9700] 2001 6200 [3800–9100] Number of AIDS-related deaths 2008 77 000 [66 000–89 000] 2001 66 000 [56 000–77 000] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Latin America estimates 1990–2008 Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) Number (millions) Number of people living with HIV 2.5 1.0 2.0 0.8 1.5 0.6 % 1.0 0.4 0.5 0.2 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1990 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Number of adult and child deaths due to AIDS 250 250 200 200 Number (thousands) Number (thousands) Number of people newly infected with HIV 1993 150 100 50 150 100 0 50 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 17 1999 2002 2005 2008 Distribution of HIV incidence by mode of exposure in Peru: estimate for 2010 Men who have sex with men 54.97% Risk groups Low-risk heterosexual Partners of clients of female sex workers 6.36% Casual heterosexual sex 6.30% Female partners of men who have sex with men 6.22% Partners (casual heterosexual sex) 5.54% Injecting drug users 1.98% Clients of female sex workers 1.33% Female sex workers 0.89% Medical injections 0.23% Partners (injecting drug users) 0.22% Blood transfusions 0.0% Without risk 0.0% 0 10 Source: Alarcón Villaverde (2009). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 18 20 30 % 40 50 60 Estimated HIV-1 seroprevalence and 95% confidence interval for HIV among men who have sex with men and female sex workers by country 25 Men who have sex with men Female sex workers HIV seroprevalence (%) 20 15.3 15 12.4 12.1 10 11.7 9.6 8.9 7.6 5 4.3 3.6 3.2 0 0.2 n: 281 484 El Salvador 157 511 Guatemala 267 493 Honduras 145 460 Nicaragua Source: Soto et al. (2007). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 19 0.2 235 418 Panama 1085 2366 All countries Condom use among female sex workers who attend VICITS (Vigilancia Centinela de ITS) in Tegucigalpa, San Pedro Sula and La Ceiba, Honduras, in 2008 100 96.7% 80 60 % 40.7% 40 20 10.6% 0 With clients With casual partners With regular partners Condom use (n= 463) Source: Secretaria de Salud Honduras (2008). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 20 North America and Western and Central Europe Number of people living with HIV 2008 2.3 million [1.9 million–2.6 million] 2001 1.9 million [1.7 million–2.1 million] 2008 Number of new infections 75 000 [49 000–97 000] 2001 93 000 [76 000–110 000] Number of children newly infected 2008 <500 [<200–<500] 2001 <500 [<200–<500] Number of AIDS-related deaths 2008 38 000 [27 000–61 000] 2001 27 000 [18 000–42 000] 2009 AIDS epidemic update North America and Western and Central Europe estimates 1990–2008 Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) Number (millions) Number of people living with HIV 3 0.6 2 0.4 % 1 0.2 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 21 1999 2002 2005 2008 Yearly number of new HIV and AIDS cases and related deaths in Switzerland, 1995–2008 1200 Number of people 1000 800 600 400 200 0 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 HIV Death with AIDS AIDS cases Death without AIDS Source: Federal Office of Public Health (2009). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 22 2006 2007 2008 Estimated new HIV infections by transmission category, extended back calculation model, 50 US states and the District of Columbia, 1977–2006 Infections 80 000 70 000 Men who have sex with men (MSM) Injecting drug use (IDU) 60 000 MSM / IDU Heterosexual 50 000 40 000 30 000 20 000 10 000 0 19771979 1980- 1982- 1984- 1986- 19881981 1983 1985 1987 1990 19911993 19941996 19971999 20002002 20032006 Period Tick marks denote the beginning and end of a year. The model specified periods within which the number of HIV infections was assumed to be approximately constant. Source: Hall et al. (2008a). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 23 Middle East and North Africa Number of people living with HIV 2008 310 000 [250 000–380 000] 2001 200 000 [150 000–250 000] 2008 Number of new infections 35 000 24 000–46 000 2001 30 000 [23 000–40 000] Number of children newly infected 2008 4600 [2300–7500] 2001 3800 [1900–6400] Number of AIDS-related deaths 2008 20 000 [15 000–25 000] 2001 11 000 [7800–14 000] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Middle East and North Africa estimates 1990–2008 Number (thousands) Number of people living with HIV Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) 400 0.4 300 0.3 200 % 100 0.1 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1990 Number of people newly infected with HIV 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Number of adult and child deaths due to AIDS 50 50 40 40 Number (thousands) Number (thousands) 0.2 30 20 10 0 30 20 10 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 24 1999 2002 2005 2008 Percentage of condom use as reported by street children, male injecting drug users, female sex workers and men who have sex with men in Egypt 15 13.0% 12.0% 11.8% 9.2% 10 % 6.8% 5 0 Street boys Street girls Male injecting drug users At least once in 12 months prior to survey Source: Shawky et al. (2009). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 25 Female sex workers Men who have sex with men Last practice Oceania Number of people living with HIV 2008 59 000 [51 000–68 000] 2001 36 000 [29 000–45 000] 2008 Number of new infections 3900 2900–5100 2001 5900 [4800–7300] Number of children newly infected 2008 <500 [<500–<1000] 2001 <500 [<200–<500] Number of AIDS-related deaths 2008 2000 [1100–3100] 2001 <1000 [<5000–1200] 2009 AIDS epidemic update Oceania estimates 1990–2008 Number (thousands) Number of people living with HIV Adult (15–49) HIV prevalence (%) 80 0.4 60 0.3 40 % 20 0.1 0 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 1990 Number of people newly infected with HIV 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 2008 Number of adult and child deaths due to AIDS 8 8 6 6 Number (thousands) Number (thousands) 0.2 4 2 0 4 2 0 1990 1993 1996 1999 2002 2005 Estimate 2008 1990 1993 1996 High and low estimates Source: UNAIDS/WHO 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 26 1999 2002 2005 2008 Proportion of all HIV and AIDS cases in different Pacific island countries and territories, 1984–2007 New Caledonia 1.2% French Polynesia 1.1% Fiji 1.1% Guam 0.8% All others 0.8% Papua New Guinea 95.0% Sources: The Secretariat of the Pacific Community and the Papua New Guinea Department of Health. 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 27 Annual newly diagnosed HIV infections in Australia, 1999–2008 1200 Number of people 1000 800 600 400 200 0 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Source: National Centre in HIV Epidemiology and Clinical Research (2009). 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 28 2006 2007 2008 HIV infections detected in Papua New Guinea, by age, 1987–2006 3000 2500 Male Female Sex not Stated Number 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0-4 5-9 10-14 15-19 20-24 25-29 30-34 35-39 40-44 Age group Source: Papua New Guinea National AIDS Council and Department of Health. 2009 AIDS epidemic update Figure 29 45-49 50-54 55-59 Over 60 Unknown




![Talking Global Health [PPT 1.64MB]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015013625_1-6571182af875df13a85311f6a0fb019f-300x300.png)