Week 9 Notes
advertisement

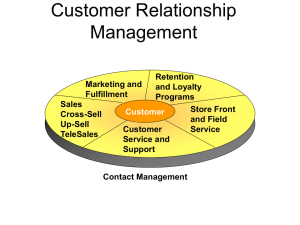
MIS Notes April 1 2015 Managing Internal Firm Processes (ERP) Branching out into supply chain and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Upstream Supply Chain Management Just In Time productions Benefits of well oiled supply chains Synergies Process Innovations Just-in-Time production Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)s Potential problems with bad supply chains Distorted info Excessive inventories Inaccurate capacity plans Missed product schedules Just0in-Time Production Keeping inventory is costly, storages, taxes, capital tied up that could be else where, etc Either wasteful, or wasteful for not meeting demand JIT Optimizes ordering quantities Insures that materials are there when needed Either smaller inputs more often. APPROACH PIONEERED BY Toyota Six Sigma- if something that occurs that is two SD away from the mean, that is significant, so you want a process that is so specific, you are right %99.99999 of the time. We don’t want over or under inventory Computer manufactures capitalize on this the most because they need to be extra careful about inventory, as electronics are quickly outdated. Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) Business model in which suppliers manage the manufacturers inventory levels based on pre-established service levels. Suppliers monitor’s stock levels and sales data You give the supplier access to your sales and projections, and the supplier decides what to get to you to make sure order is filled. Requires retailer to share real time data Benefits Cost savings Minimized stock out situations Accurate forecasts Reduced errors a Prioritized goods shipments Great example at AMAZON- Can go right from supplier to customer, mitigating just in time problem by serving as a brokerage. Buyer can see if it is in stock, and supplier ships it directly Optimize coordination of planning s Supply Chain Management (SCM) see page 19 of PowerPoint Safety Stock- Assign optimal extra stock SCM helps with ERP- Limits the ability of a human to screw up ERP systems are primarily used to optimize business processes within the org SCM is used to improve business processes that span organizational boundaries Supply Chain Visibility – The ability to track products as they move through the supply chain and foresee external events Supply Chain Analytics- the use of key performance indicators to monitor performance of the entire supply chain, including sourcing, planning, production and distribution. RFID- Radio Frequency Identification Counts and tracks every item/pallet/box through radio waves Bullwhip effect in Supply Chain Unexpected occurrences have a ripple effect and this ripple gets larger as it moves up the supply chain Downstream has incentive to exaggerate demand True for hot items In fear of out of stock, retailers exaggerate demand to get more quota Apple I phone- orders are 3 times demand Promotions Distort the natural demand from consumers Information not shared through the supply chain Consequences Higher production and transportation costs because we are over producing Creates more inventory in the supply chain, hurts bc there is now inefficiency, excess Bullwhip effect Solutions to Bullwhip problem Share info across supply chain But not everyone wants to do this Can lose bargaining position by sharing info Porters 5 forces- whoever is at the weaker end will want to share info Make it possible for those that want to share info to do so Basic Principles Maximize Profit How Does IT help?? Increases competitive advantage, but IT is just another part required to further the objective of the firm What do you think about when it comes to attracting and retaining customers? Exploit customer at maximum point they are willing to pay, we need to dissect the market to find this info, and minimize competition Sales- Art or Science Answer-Both Data allows us to resolve issues of speculations so the firm can deploy the assets to correct area (sales people to correct market) CRM- Management of all aspects of the relationship between the firm and its customers. Objective Increase Loyalty, retention, and overall, profitability--- Willingness to pay What this enables Identify customer types, customization of marketing, comprehension of buying behaviors CRM You are trying to emotionally lock in your customer, making it more difficult for them to switch We do this through CRM We have info on the customer, and can analyze each on Think amazon, it knows what you bought, and what to display because it can guess what you will buy next Developing a CRM strategy MARs- no CRM More than just software purchase and installation Enterprise wide changes Policy changes Need to reflect goals- customer or profit centric? Business values? Collect data on all customer Architecture of CRM Operational CRM Sales force Automation Analytical CRM Collaborative CRM Operational CRM 1) Salesforce Automation Get customer to do the work so you don’t have to Enables direct interaction with customers Access to complete info about consumer Sales force Automation 2)Customer service and Support Dissect customers concerns so that issues can be routed to correct person Better efficiency, better service, and hopefully customers can answer their own questions 3) Enterprise Marketing Management (EMM) Improve management of promotional campaigns Make sure right messages are sent to the right people through the right channels Customer lists need to be managed carefully Individualized attention to each potential customer Analytical CRM Looking for customer behavior and perceptions Customized marketing Upselling-cross selling Key technologies used to create predictive models Data mining Decision support systems Continuous data collection and analysis is necessary Analytical CRM also helps coordinate when people have multiple online identities Facebook, yahoo, google, multi devices, firm needs to track all these to understand each customer Collaborative CRM Refers to systems providing effective and efficient communication with the customer from the entire organization Collaborative CRM enhances communication Greater customer focus Lower communication barriers Example – Threadless- a Company that Sells shirts online, runs competition where customers design the shirts, all they do is print and ship, no need to create product, customer does it for them and chooses what they want Info integration Critical Thinking Why don’t focus group methods work People dont know what they want People don’t tell the truth Expressed vs actual belief