CH Inspiring Women in FELS Session
advertisement

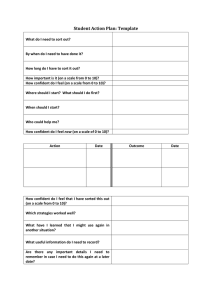
Lessons from Sport Psychology: How to be confident and achieve your goals! Dr. Caroline Heaney These slides are available to download from www.open.ac.uk/blogs/OU-sport Session overview What is confidence? Where does confidence come from? Performance profiling activity Goal setting What is self-confidence? What is confidence? What does confidence mean to you? Self-belief / belief that you can achieve your goals Positive attitude Definition: Self-efficacy is “the belief that a person has in their capability of performing a particular task”(Bandura, 1986) I.e. Situation or task specific self-confidence How do you know when someone is confident (or lacking confidence)? Think of an example of an extremely confident person – what signals do they give off? Actions, behaviours, body language E.g. walking tall, calm and focussed appearance, eye contact Interesting video: http://www.ted.com/talks/amy_cuddy_your_body_language_shapes_who_you_are How can you use this to improve your self-confidence? Fake it until you make it! Sources of self-efficacy According to Bandura’s theory self-efficacy comes from a range of sources, including: PERFORMANCE ACCOMPLISHMENTS – Previous mastery experiences (“Last time I was successful”) VICARIOUS EXPERIENCE – Information derived from seeing others perform the task/activity (role models – “if she can do it so can I”!) VERBAL PERSUASION – The persuasive techniques used by self or others (“I can do this!”) EMOTIONAL AROUSAL – The performers appraisal of their emotional arousal e.g. their cognitive interpretation of their physiological arousal (“My nerves are a sign of readiness!”) How can you use these to boost your confidence? Performance profiling activity Strategy to improve confidence and aid goal-setting PROCESS: Identify the qualities of the ‘perfect’ performer in your role (could be skill, attitude, psychological, physical, technical etc related) Give yourself a score out of 10 on each of these Identify your strengths & areas for development Variations: (a) can ask a colleague or line manger to score you as well (b) can identify a target score TASK: Working with people who do a similar job to you identify at least 8 qualities and then rate yourself against each of these (out of ten). QUALITY CURRENT RATING Make a list of your strengths (be proud!) If you have time set yourself some goals for development IDEAL RATING Goal setting A few notes on effective goal-setting: Types of goals Outcome goals = Outcome of a particular event e.g. to win a race (externally referenced, less control) Performance goals = Internally referenced end product of performance e.g. to run a race in a particular time Process goals = The processes to be engaged in e.g. to drive low out of the starting blocks Set both short term and long term goals (stepping stones to ultimate goal) What are your short term and long term career aspirations? What do you need to do to achieve these? SMART / SMARTER goals That’s all from me… Thanks for listening! These slides and supporting resources will be available on the Sport and Fitness team blog: www.open.ac.uk/blogs/OU-sport