Heat Of Fusion
advertisement

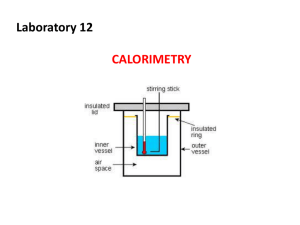
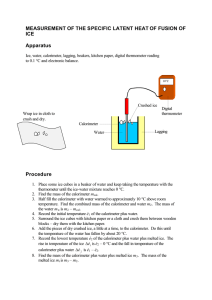
Mr. O Lab 18 Calorimetry Name: Heat of fusion of ice Pre-Lab Discussion: Calorimeter is an insulated container made up of two chambers. The outer chamber contains a known water mass. The inner chamber, the experimenter places the materials that are to lose or gain heat while undergoing physical or chemical change. The transfer of heat between the two chambers allows the experimenter to take a direct temperature reading. Using the following formula the individual can calculate heat gained or lost. Heat = mass of water x specific heat of water x change in temperature (q=mC T) Equipment: 250 beaker, graduated cylinder, Styrofoam cup, thermometer, burner, ring stand, iron gauze, tongs, and safety goggles. Materials: water and ice Observation and Data V1=___________ V2=____________ T1=___________ T2=__________ Calculations: 1. Using the known density of water, find the mass(m1) of the original volume of water. 2. Find the volume of water resulting from the melted ice. (V=V2 – V1) 3. Find the mass (m2) of the volume of water. 4. Find the change in temperature of the water. T=T1 – T2) 5. Find the heat lost by the original mass of the water. ( q = m1 x C x T) 6. Find the heat of fusion of ice. ( q/m2) 7. Find your percent error. (true value of fusion 334 J/g) Conclusion and Questions: 1. List the possible sources of error. How might the use of a calorimeter reduce error? 2. One source of error is the flow of heat between the water in the cup and the surroundings. Explain how this error is reduced by starting with water at about 50 degrees Celsius? 3. In what way does calorimetry make the use of the law of conservation of energy? 4. Define: exothermic, endothermic, heat of fusion, and specific heat capacity. 5. Is the process of melting exothermic or endothermic? Explain? 6. What is the difference between heat and temperature?