Flowers and Pollintaion
advertisement

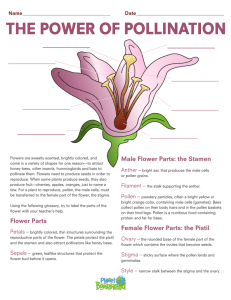
Topic: Reproduction http://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/ks2/science/living_things/plant_life_cycles/read/2/ Aim: Use textual evidence to describe the structure of a flower and pollination. Directions: Read the passage below. Use textural evidence from the reading and the diagrams to answer questions 1 – 24. Not all plants produce flowers. These are called non-flowering plants. Ferns and mosses are examples of plants, which do not produce flowers. They grow from spores instead of seeds. Non-flowering plants as well as flowering plants make their own food through photosynthesis. Petals are often very brightly colored. This is because their main job is to attract insects, such as bees or butterflies, into the flower. The insects pick up pollen from the flower, and carry it to the next flower they visit. This is how most flowers are pollinated. Not all flowers have brightly colored petals. Some grasses, for example, have small, dull, off-white flowers. This is because they are not pollinated by insects or other animals, but use the wind to blow their pollen grains to other plants. Sepals are special types of leaves that form a ring around the petals. Their job is to protect the flower while it is still a bud. After the flower has opened, the sepals can still be seen behind the petals. Sepals are usually green or brown, although in some plants they are the same color as the petals. Stamens are the male parts of the flower. Their job is to make pollen. Pollen is a fine yellow powder that is needed to make a new plant. Each stamen has two parts: an anther and a filament. The anther contains the pollen and the filament holds up the anther. The pistil is the female part of the flower, where the seeds are made. The pistil has three parts: the stigma, the style, and the ovary. The stigma is covered in a sticky substance. Its job is to "catch" the grains of pollen (which usually come from another flower). The style is the stalk that holds up the stigma. The ovary contains the ovules (or "eggs"). When the flower is pollinated, the pollen sticks to the stigma. A pollen tube forms down the style from pollen grains to allow pollen to travel down the style to the ovary. In the ovary, the pollen joins with the ovules, and the ovules become seeds. After fertilization, the ovary turns into the fruit. The pollen is carried to the stigma of another flower and fertilizes it, and new seeds are made. Sometimes pollen from a flower gets onto the stigma in the same flower, and it fertilizes itself. Questions: 1. How do non-flowering plants reproduce? (3) _________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Why are petals brightly colored?________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Label the petals in the diagram below and color the petals PURPLE. 4. Identify two ways flowers can be pollinated. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Identify the structures that protect the flower when it is still a bud. _____________________________________________ 6. Describe the appearance of sepals. _______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Label the sepals in the diagram, and color the sepals GREEN. 8. Identify the male parts of a flower and the two parts that it consists of. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Identify the part of the male reproductive structure that produces and contains pollen. _______________________________ 10. Label this structure in the diagram below and color it DARK BLUE. 11. Identify the part of the male reproductive structure that holds up the anther. _______________________________________ 12. Label this structure in the diagram below and color it LIGHT BLUE. 13. Identify the female part of the flower and the three parts it consists of. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. Identify the part of the female reproductive structure that pollen grains stick to. ___________________________________ 15. Label this structure in the diagram below and color it YELLOW. 16. Identify the part of the female reproductive structure that holds up the stigma. ____________________________________ 17. Label this structure in the diagram below and color it ORANGE. 18. Identify the part of the female reproductive structure that contains the ovules. _____________________________________ 19. Label this structure in the diagram below and color it PINK. 20. Identify what is found in ovules. _______________________________________ 21. Label this structure in the diagram below. 22. Describe what occurs during pollination. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Describe what happens after pollination occurs. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ 24. Describe the two events that occur after fertilization takes place in the ovary. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________