Skeletal, Muscular and Immune Systems Review
advertisement

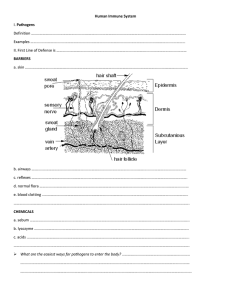
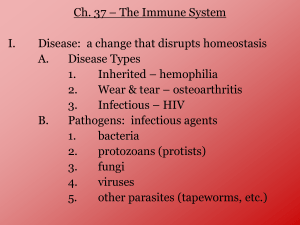
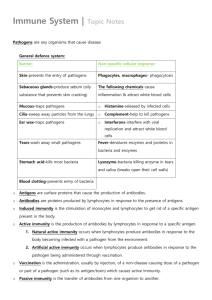
Skeletal, Muscular and Immune Systems Review The process in which provides the movement of the body or body parts from 1 place to another is know as Locomotion _________________. Describe some functions of the skeletal system. Movement Protects organs and tissues Produces blood cells Gives body shape and support Stores calcium and phosphorus Identify the two types of bone marrow and the function of each type. • Yellow marrow and red marrow. • Yellow marrow is made up of fat cells and red marrow produces blood cells. Identify the type of muscle observed in each picture. Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Identify the muscle type described. 1. Attached to bones. Skeletal 2. Involuntary and striated. Cardiac 3. Lines the digestive tract and blood vessels. Smooth 4. Voluntary. Skeletal 5. Only found in the heart. Cardiac 6. Not striated and involuntary. Smooth 7. Branched fibers. Cardiac Identify each structure in the diagram and describe its function. . A – Skeletal muscle •Attach to bone to aid in movement B - Ligament •Connect bone to bone C - Tendon •Connect muscle to bone The tissue that cushions the vertebrae and provides flexibility to joints is known as cartilage _______. Which statement describes ligaments? 1. They are made of cartilage and cushion the vertebrae. 2. They are made of tough, elastic tissue and join bones. 3. They are made of tough, inelastic tissue and connect muscles. 4. They are striped and controlled by the nervous system. Which of the following actions requires the muscular and skeletal systems to work together? 1. breaking down food into usable pieces 2. division of cells 3. eliminating waste 4. running from a predator What is a function of bones? 1. It serves as a site for the synthesis of hormones. 2. It supports and protects body structures. 3. It contracts to aid in locomotion. 4. It provides vitamins during periods of physical stress. 1. Identify the labeled structures in the diagram. 2. Identify the bones that protect the spinal cord. D vertebrae vertebrae 3. Identify the bones that protect the brain. cranium 4. Identify the bones that protect the heart and lungs. rib cage 5. Where is cartilage found? In rib cage, tip of nose, ears, between bones (joints), between vertebrae A cranium rib cage B C humerus E pelvis F femur Locomotion Review 1. Thick, smooth layer of tissue that covers the ends of bones. CARTILAGE TENDONS 2. Thick bands of tissue that attach muscles to bones. 3. Any place where two bones meet. JOINTS 4. Tough bands of tissue that hold bones together. LIGAMENTS 5. A tissue that relaxes and contracts. MUSCLE 6. Involuntary muscles in the digestive system. SMOOTH 7. Part of the bone that produces blood cells. BONE MARROW 8. Involuntary muscle found only in the heart. CARDIAC 9. Gland that regulates calcium metabolism. PARATHYROID 10. Gives the body shape. SKELETON 11. Bones that protect the spinal cord. VERTEBRAE 12. Part of the bone that stores fat. YELLOW MARROW 13. Also known as voluntary muscles. SKELETAL 14. The gland that stimulates the elongation of bones.PITUIARY 15. One of the minerals that keep bones strong. CALCIUM 16. Bones that protect the brain. CRANIUM 17. Bones that protect the lungs. RIB CAGE 18. One of the strongest bones in the body. Also known as the thigh bone. FEMUR 19. Bones that make up your fingers and toes. PHALANGES 20. Type of tissue that makes up your bones, muscles, ligaments and tendons. CONNECTIVE 1. Why is passive immunity short term? You are not making antibodies. You receive them. 2. Why is active immunity long term? You produce your own antibodies. 3. Identify the two ways you can get active immunity to a disease. Getting the disease. Getting a vaccine. 7. Contrast infectious and noninfectious diseases. Infectious diseases can be transmitted. Noninfectious diseases cannot be. Infectious diseases are caused by pathogens. Noninfectious diseases are not caused by pathogens. Explain how wbc’s can protect the body against disease. Wbc’s produce antibodies when a pathogen (antigen) enter the body. Give an example of a process that brings about active immunity. Person can come into contact with the pathogen (get sick). A person can get a vaccine. What substances are formed by the human body in response to foreign proteins entering the body? Antibodies An individual who has had chicken pox rarely gets this disease again. What type of immunity is represented? Active Immunity Identify the contents of a vaccine. Dead or weak PATHOGEN How does a measles vaccine protect a child entering school against the measles? Vaccine is injected. The body produces antibodies (and memory cells). Antibodies attach to antigens on the pathogen to help kill the pathogen. Which type of immunity is when your body makes the antibodies after recovering from a disease or getting a vaccination? Passive Immunity The immune system of humans may respond to chemicals on the surface of an invading organism. What are these chemicals on the surface called? Explain what will happen once these chemicals enter the body. Antigens The body will produce anibodies and memory cells. Which substances may form in the human body due to invaders entering the blood? Antibodies (and memory cells) Part of the body’s first line of defense against disease-causing organisms is a. the immune system b. the skin c. antibodies d. interferon Which substances may form in the human body due to invaders entering the blood? a. nutrients b. vaccines c. antibodies d. red blood cells Molecules that are foreign to your body are called a. antibodies b. white blood cells c. antigens d. histamines Which statement regarding antibodies is correct? a. Antibodies engulf the pathogen. b. Antibodies are found on the surface of pathogens. c. Antibodies attach to antigens that are on the surface of pathogens. d. Receiving antibodies provides active immunity. Once you have had the chicken pox, it is unlikely that you will ever get the disease again because your body has developed a(n) a. passive immunity. b. addiction. c. active immunity. d. antibiotic. Immunity that occurs when a body receives antibodies is called _________immunity. a. Passive b. Temporary c. Shortened d. Active An injection of a weakened virus that allows one to develop immunity against a disease is called a a. antibody b. vaccine c. epidemic d. pathogen Which statement best describes what happens when someone receives a vaccination? 1. The ability to fight disease will increase due to antibodies received from the pathogen. 2. The ability to fight disease caused by the pathogen will increase due to antibody production. 3. The ability to produce antibodies will decrease after the vaccination. 4. The ability to resist most types of diseases will increase. Which part of the human blood transports hormones, nutrients and antibodies? 1. plasma 2. platelets 3. red blood cells 4. white blood cells Which activity is not a function of white blood cells in response to a pathogen? 1. engulfing these bacteria 2. producing antibodies to act against this type of bacteria 3. preparing for future invasions of this type of bacteria 4. speeding transmissions of nerve impulses to detect these bacteria The immune system of humans may respond to chemicals on the surface of a pathogen by 1. releasing hormones that break down these chemicals 2. synthesizing antibodies that mark these organisms to be destroyed 3. secreting antibiotics that attach to these organisms 4. altering a DNA sequence in these organisms Vaccinations help prepare the body to fight invasions of a specific pathogen by 1. inhibiting antigen production 2. stimulating antibody production 3. inhibiting white blood cell production 4. stimulating red blood cell production Which statement best describes an immune response? 1. It always produces antibiotics. 2. It usually involves the recognition and destruction of pathogens. 3. It stimulates asexual reproduction and resistance in pathogens. 4. It releases red blood cells that destroy parasites. Which phrase does not describe a way the human body responds to fight disease? (1) destruction of infectious agents by white blood cells (2) production of antibodies by white blood cells (3) increased production of white blood cells (4) production of pathogens by white blood cells A Refer to the diagram below which represents a pathogen. Answer questions 1 - 4 on the loose-leaf below. 1. Identify structure A. ANTIGENS 2. Identify the substance produced that will bind to structure A. ANTIBODIES WILL ATTACH TO STRUCTURE A. A 3. Describe the body’s reaction when this pathogen enters the body in the space below. Be sure to use the following terms in your answer: pathogen, antigen, antibodies, shape. When a pathogen enters the body, antibodies will be produced. Antibodies attach to the antigens to help destroy the pathogen. The shape of the antibody and antigen must match perfectly. A 4. Identify the type of immunity that would be the end result of this pathogen entering the body and how it can be acquired. Active immunity Acquire active immunity by: - Getting the disease - Getting a vaccine