Flowers and Pollination
advertisement

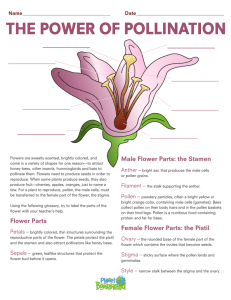
Topic: Reproduction Aim: Describe the structure of a flower and how it uses sexual reproduction. Do Now: Take out your HW. HW: Earth Day Poster due Friday! Castle Learning – Reproduction Due Tuesday, April 19th 1. 2. 3. 4. fertilization Identify the process that produces the zygote. Identify the structure after the zygote. morula mitosis What type of cell division occurs after the zygote? Identify the structure in the diagram that labeled “embryo.” gastrula differentiation 5. Identify the process that occurs after the “embryo.” 6. Where would the blastula go in the diagram? After the morula 1. How do nonflowering plants reproduce? • Grow from spores instead of seeds 2. Why are petals brightly colored? • To attract insects to pick up pollen from the flower and carry it to the next flower PETALS • By insects 4. Identify 2 • Wind ways flowers can be pollinated. 5. • Sepals Identify the structures that protect the flower when it is still a bud. 6. • Usually green or brown Describe the appearance (COLOR) of sepals. PETALS SEPALS 8. • Stamen Identify • Anther and filament the male parts of a flower and the two parts its consists of. 9. Identify • Anther the male • Pollen: male gamete reproductive structure that produces pollen. ANTHER PETALS SEPALS How many sperm nuclei are present in a pollen grain? 11. • Filament Identify the part of the male reproductive structure that holds up the anther. ANTHER PETALS FILAMENT SEPALS 13. • Pistil Identify the • Stigma, style and FEMALE ovary part of the flower and the THRER parts it consists of. 14. • Stigma Identify the female reproductive structure that pollen grains stick to. STIGMA ANTHER PETALS FILAMENT SEPALS 16. • Style Identify the female reproductive structure that holds up the stigma. STIGMA ANTHER PETALS STYLE FILAMENT SEPALS 18. • Ovary Identify the female reproductive structure that contains the OVULES. STIGMA ANTHER PETALS STYLE FILAMENT OVARY SEPALS • Eggs 20. Identify what is found in the ovules. STIGMA ANTHER PETALS STYLE FILAMENT OVARY SEPALS OVULES 22. • When the flower is Describe pollinated, the POLLEN what sticks to the STIGMA. occurs during pollination. • Pollen tubes form down the 23. style from pollen grains Describe – allow pollen to travel down what the style and into ovary happens once pollination occurs. A B C D F E Identify the labeled structures in the diagram. A – Pollen B – Stigma C – Pollen tube D – Style E – Ovary F - Egg • After fertilization 24. occurs, ovules become Describe the 2 SEEDS and the ovary events that turns into the FRUIT. occur once fertilization occurs. Cross pollination or self pollination? Let’s review: 1. Identify the male part of the flower. Stamen 2. Identify the female part of the flower. Pistil 3. Where is pollen produced? Anther 4. Where are eggs produced? Ovules 5. Identify the structure pollen stick to. Stigma 6. Identify the process in which pollen sticks to the stigma. Pollination 7. How are pollinators attracted to flowers? Petals 8. How else can a flower be pollinated? Wind 9. Identify the structure that forms in the style to bring pollen to the eggs. Pollen tube 10. What happens to the ovules and ovary once the eggs are fertilized? Ovary turns into the fruit. Ovules turns into the seeds. The part of the pistil which contains the pollen tube is the (1)stigma (2)style (3)ovary (4)ovule The transfer of pollen between the anther and the stigma in any flowering plant or plants is called (1)fertilization (2)pollination (3)photosynthesis (4)transpiration The sex cells in a flowering plant are located in the (1) sepals and petals (2) stigma and nectar (3) fruit and seed (4) stamens and pistil In order to reach an ovule, a ___________ grows through the style and into the ovary. (1)sepal (2) fruit (3) pollen tube (4) seed The egg cell of a flowering plant develops in the (1) pollen grain (2) ovule (3) stigma (4) fruit The sperm of flowering plants is contained in the (1) ovule (2) pollen grains (3) style (4) stigma The entire female reproductive organ in flowering plants is called the (1) pistil (2) stamen (3) stigma (4) sepals The sticky top of the pistil is called the (1) style (2)anther (3)stigma (4)filament Which statement below is true? (1) Nymphs after emerging from eggs look like adult insects. (2) Larva after emerging from eggs look like adult insects. (3) Nymphs will develop inside pupa before emerging as adults. At what stage of development is the insect encased in a protective cocoon? (1)Larva (2)Nymph (3)Pupa (4)Egg At what stage of development do insects appear work-like? (1)Larva (2)Nymph (3)Pupa (4)Egg Identify the process occurring in the diagram below. Support your answer. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VPHFzHRyZ1k