Kingdoms
advertisement

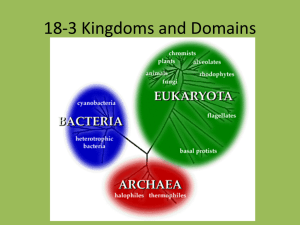
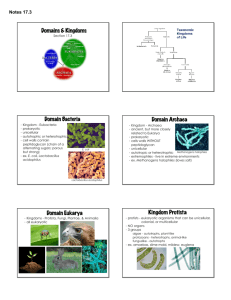
Topic: Classification Aim: Describe characteristics of each of the six kingdoms. Do Now: 1.Take out your Kingdoms Recall Notes 2.Take out the Bacteria ISA. 3. Identify the TAXON that contains organisms that are VERY SIMILAR. How similar are they??? HW: Kingdoms Review Entry Card Castle Learning Microscope Review – Due Tuesday, January 5th. Identify the 7 levels of classification. Describe what occurs to the number of organisms in each level as you move down the levels. Describe what occurs to the similarity between organisms in each level as you move down the levels. Before Linnaeus developed his naming system, plants and animals were named by a series of Latin words that described the physical appearance of the organism. This was very confusing. For example, let’s look at the first name of the honey bee. Apis pubescens, thorace subgriseo, abdomine fusco, pedibus posticis glabris utrinque margine ciliatus. This means “fuzzy bee, light gray middle, brown body, smooth hind legs that have a small bag edged with tiny hairs.” Linnaeus named it Apis mellifera which means “honey-bearing bee.” Is their a taxon that is LARGER than a KINGDOM???? Domain Bacteria is familiar to most people when associated with human or animal disease. However, there are many bacterial species do not (and cannot) cause disease. Many species even play beneficial roles by producing antibiotics and food. The soil teems with free-living bacteria that perform many essential functions in the biosphere, e.g. nitrogen fixation. Domain Eukaryota include protists and the cells that make up fungi, plants, animals. Domain Archaea wasn't recognized as a major domain of life until quite recently. Scientists were studying different prokaryotes and found that there were 2 different groups: those that lived at high temperatures or produced methane clustered together as a group. Because of their difference in genetic makeup, scientists proposed that life be divided into 3 domains. • Unicellular Archea • Prokaryotic • Autotrophic or heterotrophic • Found in extreme environments – oxygen-free – hot acidic waters of sulfur springs – bodies of concentrated salt water Hot Springs Hydrothermal vents The hot springs of Yellowstone National Park, USA, were among the first places Archaebacteria were discovered. • Unicellular Eubacteria • Prokaryotic • Autotrophic or heterotrophic Yogurt contains lactobacteria, intestine-friendly bacterial cultures that foster a healthy colon, and even lower the risk of colon cancer. Lactobacteria, especially acidophilus, promotes the growth of healthy bacteria in the colon. The more of these intestine-friendly bacteria that are present in your colon, the lower the chance of colon diseases. Basically, the friendly bacteria in yogurt seems to deactivate harmful substances before they can become carcinogenic. • Found everywhere – most are helpful (produce vitamins) – some cause disease (Ex: Strep throat) Streptococci pyogenes Salmonella enteriditis Strep throat Salmonella poisoning Fun Fact: There are more bacteria in one person's mouth than there are people in the world. Protists • Unicellular • Eukaryotic • Animal-like heterotrophic – Protozoa Ex: Amoeba, paramecium • Plant-like autotrophic –Algae Fungi Fungi • Multicellular • Unicellular yeast • Eukaryotic cells • Heterotrophic – Decomposers absorb nutrients of dead organisms • Mushrooms •Mold • Multicellular Plants • Eukaryotic cells • Autotrophic • Ex: Trees, grasses… • Multicellular Animals • Eukaryotic cells • Heterotrophic • Examples: Humans, jellyfish, insects, dogs, fish… Let’s summarize… 1. Identify the six kingdoms. Archaea, Eubacteria, Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals 1. Identify the kingdom described: a. Unicellular and eukaryotic Protists b. Multicellular and autotrophic Plants c. Unicellular, prokaryotic and live in extreme environments Archaea Fungi and d. Multicellular and heterotrophic Animals e. Unicellular, prokaryotic, and are very common Eubacteria 3. Identify the protists that are autotrophic. Algae 4. Why are fungi called decomposers? They absorb nutrients of dead organisms. 5. What are heterotrophic protists called? Protozoa 6. Identify two heterotrophic protists. Ameba and Paramecia Identify the kingdom that is made up of unicellular organisms with no nucleus and can be found in hydrothermal vents. (1.) Eubacteria (2.) Fungi (3.) Archaebacteria (4.) Protists A scientist recently discovered a pond organism that is unicellular, contains chloroplasts and other membrane-bound organelles, and possesses a flagellum. In which kingdom is this organism classified? (1.) Eubacteria (2.) Fungi (3.) Protists (4.) Plant Mushrooms and molds belong to the kingdom (1.) Fungi (2.) Plants (3.) Protists (4.) Animals An organism that is unicellular, contains a nucleus and is autotrophic is classified as a (1.) Plant (2.) Protist (3.) Algae (4.) Fungi Multicellular organisms that absorb digested nutrients from the environment is classified as (1.) animals (2.) fungi (3.) protists (4.) paramecia Identify the kingdom consisting of multicellular and autotrophic organisms. (1.) Animals (2.) Fungi (3.) Protists (4.) Plant Identify the kingdom that is made up of unicellular prokaryotic organisms that are very common, (1.) Eubacteria (2.) Fungi (3.) Archaebacteria (4.) Protists Heterotrophic protists are known as (1.) algae (2.) bacteria (3.) protozoa (4.) yeast Endoplasmic reticulum Vacuole Cytoplasm Nucleus Chloroplasts Mitochondria Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Ribosomes Determine the length of each cell in um. 1000um Length of cell: 600um 500um Diameter = 2000um Determine the length of each cell in um. 6 cells 1000/6 = 100.7um Diameter = 1000um The diagram represents a cell being viewed with the low power objective. 1. Describe the field of view under low power compared to high power. It has a larger field of view 2. Identify the structure used to focus the image. coarse adjustment 3. In which direction should the slide be moved on the microscope stage to center the cell in the field of view? towards C A student sees the image to the left when observing the letter "f" with the low-power objective lens of a microscope. Which diagram below most closely resembles the image the student will see after switching to high power? The second part of an organism’s scientific name is its (1.) kingdom (2.) phylum (3.) genus (4.) species The branch of biology that is used for classifying and naming organisms is known as (1.) cytology (2.) taxonomy (3.) physiology (4.) genetics The system used to name organisms is called (1.) classification (2.) dichotomous keys (3.) binomial nomenclature (4.) punnett squares The name of the person who created binomial nomenclature is (1.) Carl Linnaeus (2.) Robert Hooke (3.) Robert Virchow (4.) Anton Van Leewenhoek The scientific name for a lion is Panthera Leo. The word Panthera tells us the lion’s (1.) kingdom (2.) phylum (3.) genus (4.) species Members of a population of gray squirrels, Sciurus carolinensis, are classified in the same species because they (1.) obtain their food in the same manner (2.) produce enzymes by synthesis (3.) can mate and produce fertile offspring (4.) live in the same area In today’s classification system, 2 organisms would be most closely related if they were classified in the same (1.) kingdom (2.) phylum (3.)genus (4.)species Which classification category contains the greatest number of different types of organisms? (1.) kingdom (2.) phylum (3.) genus (4.) species 1. Sodium is PUMPED out of a nerve cell. 2. A unicellular organism takes in a particle of food. 3. Water moves out of the fish’s body cells (98% water) and into the surrounding water (96% water) What were the three types of archaebacteria you read about? 1. Methanogens: 1. Prefix: methano2. Live in oxygen-free environments and produce methane 2. Extreme halophiles 1. Live in bodies of concentrated salt water 3. Thermoacidophiles 1. Prefix: thermo2. Live in hot, acidic waters of sulfur springs