Phase Changes

Topic : Chemistry
Aim : Explain the different types of phase changes and the energy changes involved.
Do Now : Write the aim on today’s notes sheet.
Tape today’s notes sheet on the back of yesterday’s notes.
HW: Properties Reading due Monday!
SOLID LIQUID GAS
Let ’ s summarize … Identify the phase being described (solid, liquid or gas):
1. No definite shape or volume.
Gas
2. Takes the shape of the container it is in and has a definite volume.
Liquid
3. Made up of high energy atoms.
Gas
4. Atoms are tightly packed together.
Solid
5. Molecules are cohesive.
Liquid
6. Has a definite shape and volume.
Solid
7. Takes the shape of a closed container. Gas
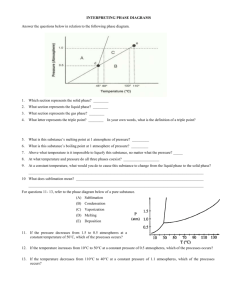
Observe the phase change diagram.
Identify the events that can occur to cause a phase change.
HEAT IS
RELEASED
OR
HEAT IS
ABSORBED
Melting
Substance absorbs heat energy
Substance
GAINS energy
Melting
• S L
• Solid ABSORBS heat energy
Substance absorbs heat energy
Melting points of different substances
• Iron : 1536ºC
• Gold : 1063ºC
• Glucose : 150ºC
• Urea: 132134ºC
Identify the phase change represented in the photographs below.
LIQUID
Substance loses heat energy
SOLID
Freezing
• L S
• Liquid RELEASES heat energy
Substance loses heat energy
Identify the process occurring in the animation.
LIQUID
Substance
ABSORBS energy
GAS
Vaporization
• L G
• Liquid ABSORBS heat energy
• Evaporation: occurs on surface of liquid
GAS
Liquid absorbs heat energy
LIQUID
Boiling points of different substances
• Alcohol (Ethanol): 79ºC
• Iodine : 184.3ºC
• Mercury : 356.9ºC
• Olive oil : 300ºC
• Jet fuel : 163ºC
Identify the phase change represented in the photograph.
GAS
Substance loses heat energy
LIQUID
Condensation
• G L
• Gas RELEASES heat energy
GAS
Gas loses heat energy
LIQUID
Identify the phase change represented in the photograph.
SOLID
Substance
ABSORBS energy
GAS
Sublimation
• Solid Gas
• Solid ABSORBS energy
GAS
Solid absorbs heat energy
Solid
Mt. Everest loses some snow cover due to common windstorms.
Snow is also constantly lost, invisibly, due to sublimation
Moth balls are used when storing clothing and other articles susceptible to damage from mold or moth larvae. Moth balls commonly undergo the process of sublimation. Sublimation is the process in which a solid changes directly to its gaseous phase, skipping the liquid phase.
Humid air to condenses into frost patterns, for example in singlelayer window glasses and windshields.
Deposition
GAS
Substance
LOSES energy
SOLID
Deposition
• G S
• Gas RELEASES energy https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ft2KgtlP8Lk
Solid
GAS
Solid releases heat energy
Let ’s summarize …
1. List the different types of phase changes.
2. Explain what happens to heat energy in each phase change.
5
A
1
3
B
2
4
C
When a liquid becomes a solid, energy
1. does not change
2. is released
3. is absorbed
4. is first absorbed, then released
_______ is the process in which liquid changes to gas below the boiling point.
1. Sublimation
2. Condensation
3. Evaporation
4. Combustion
On a hot day, the outside of a glass containing a cold drink becomes frosty.
When touching the glass, it feels
1. water that has passed through the glass
2. water that has condensed from a gas in the air
3. water that has solidified
4. water that has absorbed energy
The change of a liquid to a solid is called
1. freezing
2. melting
3. sublimation
4. vaporization
When substances go directly from the solid phase to the gas phase, the phase change is called
1. sublimation
2. condensation
3. evaporation
4. vaporization
• Mass number :
137
• Atomic #:
56
• # of neutrons:
137-56
81 neutrons
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XaDxwe8l3us&feature=related