Chap 13C
advertisement

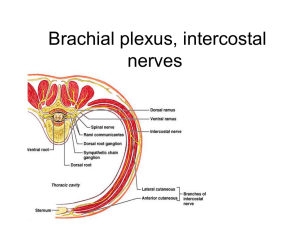
13 The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activity: Part C Spinal Nerves • 31 pairs of mixed nerves named according to their point of issue from the spinal cord • • • • • 8 cervical (C1–C8) 12 thoracic (T1–T12) 5 Lumbar (L1–L5) 5 Sacral (S1–S5) 1 Coccygeal (C0) Spinal Nerves: Roots • Each spinal nerve connects to the spinal cord via two roots • Ventral roots • Contain motor (efferent) fibers from the ventral horn motor neurons • Fibers innervate skeletal muscles) Spinal Nerves: Roots • Dorsal roots • Contain sensory (afferent) fibers from sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia • Conduct impulses from peripheral receptors • Dorsal and ventral roots unite to form spinal nerves, which then emerge from the vertebral column via the intervertebral foramina Spinal Nerves: Rami • Each spinal nerve branches into mixed rami • • • • Dorsal ramus Larger ventral ramus Meningeal branch Rami communicantes (autonomic pathways) join to the ventral rami in the thoracic region Spinal Nerves: Rami • All ventral rami except T2–T12 form interlacing nerve networks called plexuses (cervical, brachial, lumbar, and sacral) • The back is innervated by dorsal rami via several branches • Ventral rami of T2–T12 as intercostal nerves supply muscles of the ribs, anterolateral thorax, and abdominal wall Cervical Plexus • Formed by ventral rami of C1–C4 • Innervates skin and muscles of the neck, ear, back of head, and shoulders • Phrenic nerve • Major motor and sensory nerve of the diaphragm (receives fibers from C3–C5) Brachial Plexus • Formed by ventral rami of C5–C8 and T1 (and often C4 and T2) • It gives rise to the nerves that innervate the upper limb • Major branches of this plexus: • • • • Roots—five ventral rami (C5–T1) Trunks—upper, middle, and lower Divisions—anterior and posterior Cords—lateral, medial, and posterior Brachial Plexus: Nerves • Axillary—innervates the deltoid, teres minor, and skin and joint capsule of the shoulder • Musculocutaneous—innervates the biceps brachii and brachialis and skin of lateral forearm • Median—innervates the skin, most flexors and pronators in the forearm, and some intrinsic muscles of the hand • Ulnar—supplies the flexor carpi ulnaris, part of the flexor digitorum profundus, most intrinsic muscles of the hand, and skin of medial aspect of hand • Radial—innervates essentially all extensor muscles, supinators, and posterior skin of limb Lumbar Plexus • Arises from L1–L4 • Innervates the thigh, abdominal wall, and psoas muscle • Femoral nerve—innervates quadriceps and skin of anterior thigh and medial surface of leg • Obturator nerve—passes through obturator foramen to innervate adductor muscles Sacral Plexus • Arises from L4–S4 • Serves the buttock, lower limb, pelvic structures, and perineum • Sciatic nerve • Longest and thickest nerve of the body • Innervates the hamstring muscles, adductor magnus, and most muscles in the leg and foot • Composed of two nerves: tibial and common fibular Innervation of Skin • Dermatome: the area of skin innervated by the cutaneous branches of a single spinal nerve • All spinal nerves except C1 participate in dermatomes • Most dermatomes overlap, so destruction of a single spinal nerve will not cause complete numbness Innervation of Joints • Hilton’s law: Any nerve serving a muscle that produces movement at a joint also innervates the joint and the skin over the joint