Exercise 2 Meaning Mechanics Lecture 4 – Overview
advertisement

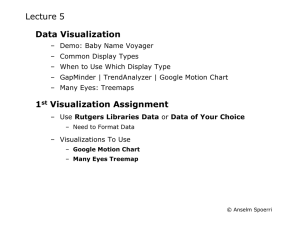
Lecture 4 – Overview Exercise 2 Meaning – Web Design Recap and Handout – Writing for the Web – Redesign Examples Mechanics – Questions: Typography & Web Graphics Recap – Dreamweaver – Recap – Table Games © Anselm Spoerri Exercises 2 Create a draft of "Why be a Librarian in the 21st Century?" in outline form. Describe your Vision of "Librarian in the 21st Century" (value / skills etc.) Provide an outline of your relevant Interests and Passions. Break down your site into categories. Create organization and associated file hierarchy. Each web page contains primary navigation structure. © Anselm Spoerri Exercises 2 (cont.) Each web page has a clear layout and visual hierarchy and reflecting what have learned so far (margins, typography etc.) Each page has a brief sentence describing its goal and an outline of ideas to be covered or linked to. – If possible create hyperlinks to other pages that expand an idea. Create page that contains links to site whose layout / design you would like to emulate. Create at least one web page that contains a table, where at least three cells contain an image Suggestions: Create folder = “project_draft” or … different folder than folder for “Final Project” Submit exercise URL with “http://scils.rutgers.edu/~abcde” etc. © Anselm Spoerri Recap – Web Guiding Principles Diversity of Users & Rapid Change – Diverse users, diverse computers, diverse skills, diverse … – Rapid evolution of technology and expectations – Short attention span Common Sense – No right way to design Make it short – More likely to be used and remembered – Cut in ½ and cut in ½ again Don't make me think – Get rid of question marks - each item has clear purpose Make it work at a glance – People have little time Support intented task - manage expectations © Anselm Spoerri User Behavior Design Implications Design Specifics Scan pages - don't read them • Design for Scanning Make text short - cut words • Make page work at a glance Sufficient left margin, 640x480 = main message • Create Visual Hierarchy Look for anything = Search Interest Decide quickly Choose first “reasonable item” • Make obvious what you can do • Make obvious what is clickable Muddle through Don't figure out how things work Resist forming models • Don't make users think Get rid of question marks Each item = clear purpose 1 Use Grid System • Maintain Consistency Helps you decide: location of primary & secondary navigation; location and sizes of images; location of headlines, main text, annotations etc. • Create Visual Hierarchy & Rhythm • Present Information Clearly & Logically Users can read info more quickly. Facilitates understanding and recall. • Invisible Hand guiding users and creating sense of place Stick to what works • Repetition & Consistency Grid Layout, Easy Navigation, Graphics, Color Coding, Typography © Anselm Spoerri User Behavior Design Implications Design Specifics Scan pages - don't read them • Design for Scanning Make text short - cut words • Make page work at a glance Sufficient left margin, 640x480 = main message • Create Visual Hierarchy Look for anything = Search Interest Decide quickly Choose first “reasonable item” • Make obvious what you can do • Make obvious what is clickable Muddle through Don't figure out how things work Resist forming models • Don't make users think Get rid of question marks Each item = clear purpose Stick to what works • Repetition & Consistency Grid Layout, Easy Navigation, Graphics, Color Coding, Typography 2 Create Visual Hierarchy & Guide Eye • Important Things = Visually Prominent (More Important = Larger / Sharp Contrast) Use headlines to guide the eye • Visual Contrast Use sharp changes in size (headline), light intensity (bold), color, texture, motion to create contrast. • Proximity: related things spatially close Spatial separation = conceptual separation. Don't mix alignment styles. • Use Grouping & Nesting to Increase Information Density (Short-term Memory = 3-7) Use bounding shapes. © Anselm Spoerri User Behavior Design Implications Design Specifics Scan pages - don't read them • Design for Scanning Make text short - cut words • Make page work at a glance Sufficient left margin, 640x480 = main message • Create Visual Hierarchy Look for anything = Search Interest Decide quickly Choose first “reasonable item” • Make obvious what you can do • Make obvious what is clickable Muddle through Don't figure out how things work Resist forming models • Don't make users think Get rid of question marks Each item = clear purpose Stick to what works • Repetition & Consistency Grid Layout, Easy Navigation, Graphics, Color Coding, Typography 3 Typography Heuristics • Sans Serif type is easier to read on screen • Type size 10 -14 points • 7 - 10 words per line • Column width proportional to type size • Bold and italic for small blocks of text • Enough contrast between type & background © Anselm Spoerri User Behavior Design Implications Design Specifics Scan pages - don't read them • Design for Scanning 1 Use Grid System • Make page work at a glance • Create Visual Hierarchy Choose first “reasonable item” • Make obvious what you can do Muddle through 2 Create Visual Hierarchy and Guide Eye • Don't make users think Stick to what works • Repetition & Consistency 3 Typography Heuristics © Anselm Spoerri Recap – Requirements for Web Pages Web Page needs to easily answer • What can I do here? Layout Presents Info Clearly & Logically Facilitates Understanding & Recall • Where do I start? Visual Hierarchy Guides Eye to Important Things Web Navigation needs to easily answer • What site is this? Site ID – logo, image, text • What page am I on? Page name • Major sections of site? Primary Navigation Top Row or Left Column Simple text hyperlinks, icons, rollovers, image-maps, pull-downs • Options at this level? Secondary Navigation Below Top Line or Left Column Expanding / Nesting Hierarchies Static or Dynamic Outlines • Where I am? Go higher or home? Color Coding, Breadcrumbs Primary / Secondary Navigation © Anselm Spoerri Recap – Web Page Needs to Answer What can I do here? – Create Layout to Present Info Clearly & Logically – Use Grid System to Facilitate Understanding & Recall Where do I start? – Create Visual Hierarchy to Guide Eye How can I navigate? – Create Primary & Secondary Navigation – Provide Site ID, Page Name © Anselm Spoerri Layout Visual Hierarchy & Navigation Site ID Primary Navigation Secondary Navigation Page Name Intro Text aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa bbbbbbbbbbb bbbbbbbbbbb Text or Thumbnails © Anselm Spoerri Layout Visual Hierarchy & Navigation Site ID Primary Navigation Secondary Navigation Page Name Intro Text Text or Thumbnails © Anselm Spoerri Design Strategy Tools Create Layout Grid – Create Master Table with Cells of varying sizes – Cell can be a table with cells … – Use Dreamweaver to create layout/grid tables – Use Fireworks to crop images to desired size Create Visual Hierarchy – More Important = Larger / Sharp Contrast – Use Fireworks to create and edit distinct imagery Create Navigation Structure – Designate specific areas for Primary / Secondary Navigation – Use Fireworks to create visual navigations elements – Use Dreamweaver to create interactive navigation © Anselm Spoerri Basic Design Principles Alignment – Don't Mix Alignment Styles - Simplicity – Create Sufficient Left Margin – Constrain Total Width of Page Proximity – Related Things Close Together – Spatial Separation = Conceptual Separation Repetition & Consistency – Grid Layout, Navigation, Graphics Color Coding, Typeface – Creates Ease of Use Contrast – Bigger, Bolder, Color, Spatial Distance – Guide the Eye and Create Visual Hierarchy © Anselm Spoerri Writing for the Web Concise, SCANABLE and Objective By Jacob Nielsen People scan page – Study: 79% always scanned + only 16 % read word-by-word. Make pages “scanable” – – – – – – Start with conclusion One idea per paragraph Half the word count (or less) than conventional writing Highlighted keywords Meaningful sub-headings (not "clever" ones) Bulleted lists Credibility important and increased by: – High-quality graphics – Good writing – Use of outbound hyperlinks © Anselm Spoerri Web Site – Trunk Test © Anselm Spoerri Redesign 1 Source – Steve Krug “Don’t Make Me Think” © Anselm Spoerri Redesign 2 © Anselm Spoerri Redesign 3 © Anselm Spoerri Which Web Graphics Format to Choose? © Anselm Spoerri Recap – Web Graphics Bitmapped vs. Vector-based Graphics Web Graphics File Formats – GIF – – – – – Cross Platform & Lossless Compression Indexed Colors Transparency Create Animations Best for: Solid Color, Simple Illustrations Small Photos – JPEG – – – – Cross Platform & LOSSY Compression No transparency No Animation Best for: Photos with Subtle Changes Save Image for Web – – – – – RGB Mode 72 ppi Indexed Color Mode Reduced Color Palette (e.g. Adaptive Palette) Interlaced Good Form: Alt-labels for Images © Anselm Spoerri Which Web Graphics Format to Choose? Many colors Few solid colors Solid black / white Few colors © Anselm Spoerri Please Answer these Questions (answers provided at end of lecture) 1. What is the best way to create columns on a web page? a) b) c) d) Draw guidelines across the page. Create tables Type the text in short lines, hitting the Spacebar between columns. Use graphics to contain the text on either side. 2. The difference between a Paragraph and a Line Break is: a) A Paragraph contains a complete thought; a Line Break doesn’t. b) You must have more than one line in a Paragraph; a Line Break can have only one line. c) A Paragraph cannot change color. d) A paragraph has space following it; a Line Break have no space following it. 3. How can you tell where a link is going before you click it? a) You can’t. b) Ask your mother. c) Position the pointer over the link and read the status bar at the bottom of the browser window. d) Type “link=?” in the location box, then hit Return or Enter. © Anselm Spoerri Questions (cont.) 4. Which one is not a “legal” file name, and why not: a) b) c) d) designers.htm tall_tales.html honey bunny.gif gargoyles.jpg 5. Why must you title your web page: a) b) c) d) The title is what appears in the title bar in the browser. The title is what spears in a visitor’s bookmark or favorite list. The title is used by many search engines to add the site to their address. All of above. 6. If you make graphics, what reason could there be for saving the original, high-resolution files that won’t be used in the web site? a) b) c) d) You might need them for print media. You might need to go back and make changes or corrections. You might need to make more of the same, such as buttons. All of the above. © Anselm Spoerri Questions (cont.) 7. If you added a new photo to an existing page on your site, how many files would you have to upload? a) One graphic file. b) One web page file. c) One graphic file and one web page. 8. If you remove 3 pages from your site, what else do you have to do to the site? a) Change your address. b) Remove the links from remaining pages and upload those changes. 9. Which of the following is not an advantage of a GIF file? a) b) c) d) Unlimited color Lossless compression Transparency Interlacing 10. Which of the following is not an advantage of a JPEG file? a) b) c) d) Millions of colors Lossless compression Variety of compression levels Maintains subtle color changes © Anselm Spoerri Questions (cont.) Never True or Sometimes? a) Choose any typeface on your hard disk and set headlines (not graphic ones) with it. b) Let the text stretch the entire width of the web page. c) SET LOTS OF TEXT IN ALL CAPS SO PEOPLE WILL BE SURE TO SEE IT. d) Put red text on an orange background because the subtle yet “dazzling” color combination looks good. e) Make some text very small, but set it in all caps to compensate for the small size. © Anselm Spoerri Dreamweaver – Create Visual Hierarchy You can use 1 Standard Table Standard Mode Regular Columns and Rows 2 Layout Tables and Layout Cells Layout View “Irregular” Columns and Rows to create Layout and Visual Hierarchy © Anselm Spoerri Dreamweaver – Standard Mode View > Table Mode > select “Standard Mode” Certain changes must be completed in Standard mode Format & Edit Table and its Cells – Format Table and Cells – Cut, Copy or Paste Table Cell Specify Width = Pixels or % of Browser Width – “Accordion Effect” if specified as % of Browser Width – If Table “Width” unspecified, then column widths unconstrained! Layers (future lecture) © Anselm Spoerri Dreamweaver – Layout Mode Layout Table can contain contains Layout Table Layout Cell Text Image Media © Anselm Spoerri Format Table – in “Standard Mode” W and H fields – Specify width & height of table as pixels or % of browser window – If “Width” unspecified, then column widths are unconstrained! – Usually don't need to set table height CellPad – Amount of space between content of a cell and cell boundary CellSpace – Amount of space between each layout cell Align – Default = “Left” Border – Specify in pixels thickness of border © Anselm Spoerri Format Table – Layout Table in “Layout Mode” 1 2 3 1 Clear Row Heights 2 Make Widths Consistent 3 – Resets widths of each cell to match the content within that cell. – If width set to 400 pixels, then add content with width of 450, top bar of table in Layout view will display: “400" (450). Clicking "Make Widths Consistent" removes the 400-pixel setting and keeps 450. Remove All Spacers – 4 Remove spacer images inserted when “autostretch” is selected (see next slide) Remove Nesting – e.g. tables within tables Layout cells will become part of parent table © Anselm Spoerri 4 Format Table – Layout Cell in “Layout Mode” Fixed Width – Specify width in pixels, where cell width is constrained by table width page display Autostretch – Resizes width automatically to fill browser window – Displayed as wavy line in page display – With Autostretch, transparent spacer images are inserted in fixed width columns to control the layout. Without spacer images, columns will change size or even visually disappear completely if they do not contain content. – Only one column in a layout can be Autostretch. © Anselm Spoerri Format Table – Layout Cell in “Layout Mode” (cont.) Bg – Set Background Color of layout cell Horz and Vert Alignment – Specify width in pixels, where cell width is constrained by table width No Wrap – If checked, then Text is not allowed to wrap © Anselm Spoerri Table Management Tag Bar (bottom border of selected file) Use it to select specific layout elements Clicking on <table> selects table Clicking on <tr> selects row Clicking on <td> selects cell Expanded Mode Temporarily adds cell padding and spacing to tables and increases the tables’ borders to make editing easier. Select View > Table Mode > Expanded Tables Mode or In Layout category of the Insert bar, click Expanded Tables button © Anselm Spoerri Editing Table – in “Standard Mode” Cut / Copy / Paste preserving the cells’ formatting Single table cell Multiple cells at once – Contents of the Clipboard must be compatible with structure of table or selection in the table in which the cells will be pasted. Insert Row / Column – Modify > Table > “Insert Row” or “Insert Column” or “Insert Row or Column” (latter gives you most control) Merge Cells – Modify > Table > Merge Cells Remove cell content but leave cells intact: – Select one or more cells. (Make sure the selection does not consist entirely of complete rows or columns.) – Choose “Edit > Clear” or press Delete. Delete rows or columns that contain merged cells: – – Select the row or column to be deleted. Modify > Table > Delete Row / Column © Anselm Spoerri Formatting Precedence – “Table Rules” Cell Format overwrites Column / Row Format overwrites Table Format BUT Table Width / Height Column or Row or constrains Cell Width / Height If Table “Width” unspecified, then column widths unconstrained! © Anselm Spoerri Dreamweaver – Table Troubleshooting Make sure Table Width in Layout and Standard Mode Agree – Layout Mode: Table Width = 500 pixels – Standard Mode: Table Width = % Dreamweaver can “suddenly” change widths specified in “pixels” to “%” Good practice to double check (especially when layout behaves strange) © Anselm Spoerri Text + Misc Format Text – Select Text – “Properties” Window changes to “Format” – Style, Font, Size, Color etc. – More Control of Appearance of Text Remember to use Sans Serif Typeface – Preferably set Page Font using Modify > Page Properties Useful Features – Visual Grid – View > Grid > select “Show Grid” and “Snap-to-grid” – View > Grid > Edit Grid (to edit grid) – Tracing Image – Modify > Page Properties: “Tracing Image” category © Anselm Spoerri Dreamweaver “Table Games” Demo – Standard Mode See Video Capture File New File Select “Standard Mode” – View > Table Mode > select “Standard Mode” or Select “Layout” in Insert bar and click “Standard” icon Insert Table – Insert > Table: in dialog box specify number of columns and rows Format Columns / Rows / Cells – – Select columns / rows / cells using dragging Edit entries in Property Inspector for selected items Table: CellPad, CellSpace, Align, Border (which will apply for all cells) Merge Cells – – Select cells to be merged Modify > Table > Merge Cells Insert Row / Column – Modify > Table > “Insert Row or Column” © Anselm Spoerri Dreamweaver “Table Games” Demo – Layout Mode See Video Capture File Create New File Select “Layout Mode” – View > Table Mode > select “Layout Mode” or Select “Layout” in Insert window and click “Layout” icon Create Layout Table with Layout Cells – Create Layout Table and inside two “columns” with two Layout Cells each Format Layout Table and Cells – Select Layout Table or Cells – Edit entries in Property Inspector for selected items Group Layout Cells using Layout Table – Select Layout Table icon – Trace outline of “right column” of layout cells – Specify CellPad = 10 and Bg color = light gray for just created Layout Table © Anselm Spoerri Download files and Initialize Create folder “mplec4” in “My Documents” folder Download Files and Images http://www.scils.rutgers.edu/~aspoerri/Teaching/MPOnline/Lectures/Lecture4/stepbystep/ – Select ZIP file = “stepbystep.zip” – File Download Dialog: select “Open” – Extract into “My Documents/mplec4” and make sure to extract all files (Being able to use WinZip is prerequisite for this course) © Anselm Spoerri “Cell Management” – Cut, Copy, Paste Cells You can cut, copy, or paste a single table cell or multiple cells at once, preserving the cells’ formatting. You can paste cells at insertion point or in place of a selection in an existing table. Pasting Multiple Table Cells – Clipboard content must be compatible with structure of table or the selection in table in which the cells will be pasted. example 1 Open files “CopyPasteSource” and “CopyPasteDestination” Select “CopyPasteDestination” 2 Layout Mode: create similar cell structure in interior Layout Table as in “Source” Select “CopyPasteSource” 3 Standard Mode: copy cells with images and paste in interior Layout Table in “Destination” Delete Layout Table or Cell – Select Layout Table or Cell – Press “Backspace” or “Delete” Key or select “Edit > Clear” © Anselm Spoerri Tracing Image Tracing Image Example – Open new file in Dreamweaver – Modify > Page Properties : select sans serif typeface – Modify > Page Properties : select “Tracing Image” category – Browse for tracing image = “i-R_Opening_Page” and set transparency = 50% – Layout Mode: – Create Layout Table (covering the tracing image) – Create four Layout Cells (along earth contour) – Enter text in each cell – Experiment with type size and bolding to create “visual flow” Step-by-Step files: tracingimage1, tracingimage2, tracingimage3 © Anselm Spoerri Answers to Questions 1. What is the best way to create columns on a web page? a) b) c) d) Draw guidelines across the page. Create tables Type the text in short lines, hitting the Spacebar between columns. Use graphics to contain the text on either side. 2. The difference between a Paragraph and a Line Break is: a) A Paragraph contains a complete thought; a Line Break doesn’t. b) You must have more than one line in a Paragraph; a Line Break can have only one line. c) A Paragraph cannot change color. d) A paragraph has space following it; a Line Break have no space following it. 3. How can you tell where a link is going before you click it? a) You can’t. b) Ask your mother. c) Position the pointer over the link and read the status bar at the bottom of the browser window. d) Type “link=?” in the location box, then hit Return or Enter. © Anselm Spoerri Questions (cont.) 4. Which one is not a “legal” file name, and why not: a) b) c) d) designers.htm tall_tales.html honey bunny.gif gargoyles.jpg 5. Why must you title your web page: a) b) c) d) The title is what appears in the title bar in the browser. The title is what spears in a visitor’s bookmark or favorite list. The title is used by many search engines to add the site to their address. All of above. 6. If you make graphics, what reason could there be for saving the original, high-resolution files that won’t be used in the web site? a) b) c) d) You might need them for print media. You might need to go back and make changes or corrections. You might need to make more of the same, such as buttons. All of the above. © Anselm Spoerri Questions (cont.) 7. If you added a new photo to an existing page on your site, how many files would you have to upload? a) One graphic file. b) One web page file. c) One graphic file and one web page. 8. If you remove 3 pages from your site, what else do you have to do to the site? a) Change your address. b) Remove the links from remaining pages and upload those changes. 9. Which of the following is not an advantage of a GIF file? a) b) c) d) Unlimited color Lossless compression Transparency Interlacing 10. Which of the following is not an advantage of a JPEG file? a) b) c) d) Millions of colors Lossless compression Variety of compression levels Maintains subtle color changes © Anselm Spoerri Questions (cont.) Never True or Sometimes? Never a) Choose any typeface on your hard disk and set headlines (not graphic ones) with it. Never b) Let the text stretch the entire width of the web page. Never c) SET LOTS OF TEXT IN ALL CAPS SO PEOPLE WILL BE SURE TO SEE IT. Never d) Put red text on an orange background because the subtle yet “dazzling” color combination looks good. Never e) Make some text very small, but set it in all caps to compensate for the small size. © Anselm Spoerri