Outcomes and Activities and Styles, Oh My! Developing Learning Outcomes to
advertisement

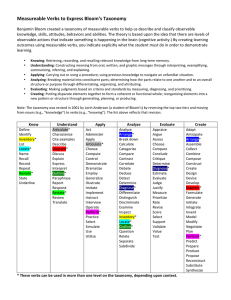
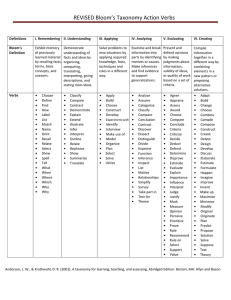
Outcomes and Activities and Styles, Oh My! Developing Learning Outcomes to Create Learning Activities that Address Different Learning Styles Carla List-Handley TCLC Workshop Rosemont College 6 January 2011 The Workshop A question Learning outcomes Another question Active learning & learning styles The rest of the questions First: Learning Outcomes Talking the Talk: Objectives or Outcomes? Learning objectives are “specific, observable, and measurable statement[s] that describe what a student will be able to do at the end of the course.” Learning outcomes are “statements that specify what learners will know or be able to do as a result of a learning activity ... usually expressed as knowledge, skills, or attitudes.” What Do Outcomes DO? For teacher ◦ Provide opportunity to see what you NEED to teach “Please teach ____ database” (something you hear & do often) What are you teaching? ◦ Break classroom approaches down ◦ Help you select methods & materials What Do Outcomes DO? For students ◦ Student-focused ◦ Designed to meet identified skill or comprehension needs ◦ Can provide a means for self-assessment How Do You Create Outcomes? Condition(s): What is needed for the student to demonstrate the performance? “Given three topics and our list of databases ...” Verb: What measurable or observable action will the student perform? “... the student will identify one database appropriate to the research topic...” Accuracy (performance standard): How often does a good choice indicate understanding? “... for two out of three topics.” Mechanics of the Mechanics Condition Include any equipment needed, e.g., computer, database(s), citation site(s) Verb Use action verbs, i.e., Bloom’s Taxonomy Accuracy or Degree Decide what quantity is needed to indicate success, i.e., comprehension Bloom’s Taxonomy “Goals of the educational process” Bloom,1948 Provides a list of verbs and what to use them for ◦ ACTION VERBS, e.g., arrange, differentiate, select, label, evaluate Makes outcomes simple to write www.wisha.org/CE/Writing20%Learning20%Outcomes20%and20%Assessments20%of.pdf Bloom’s Taxonomy - Examples Knowledge Arranges elements of a citation Comprehension Identifies subject-appropriate database(s) Application Uses MLA Manual to assist w/citation problem Analysis Compares bias in two websites Synthesis Organizes gathered information into paper Evaluation Assesses value of website(s) to research topic Using Outcomes for Assessment Because specified actions are ◦ Observable ◦ Measurable Forms of assessment can include ◦ Completion of a project ◦ Written report, e.g., how will student use what s/he learned? Using Outcomes in the Classroom Use outcomes to help you decide on your teaching method TELL students what your goal is at the beginning of the session Let students know how they can measure their success Your Assignment (should you choose to accept it) Write an outcome And ONLY one! You will (and should) come up with more than one. Reporter should report the best one, but also indicate others (no more than 2) that might be worth addressing. Your Outcomes HED311: Given a country to track, the student will identify and locate one authoritative general international source and one authoritative country-specific source from all available sources. Given specific websites, students working in groups will analyze these for currency, authority, and objectivity. ANT380: Given three librarian-recommended databases, students will identify one scholarly article relevant to the topic. Given an APA citation, students will recognize the elements of a citation in order to identify other resources of value. Example of Outcomes http://www.plattsburgh.edu/files/15/files/LIB105Objectives.pdf