Inquiry Workshop slides.ppt: uploaded 28 January 2016 at 11:21 am
advertisement

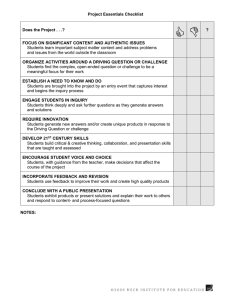
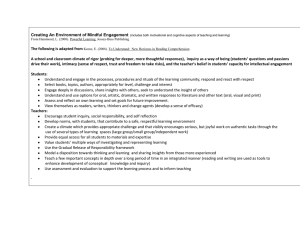
Inquiry Based Learning Donna Barrett Center for Education Integrating Science, Mathematics and Computing Objective – to learn about apples Observe an apple and list all of the observations you can make the apple Why or how does each observation contribute to our knowledge about apples? Observe the artificial apple. Cross out the observations no longer valid. apple pomum Inquiry Cube Activity What are the characteristics of inquiry learning? Adapted from material presented by Dr. Malcolm Butler at the Georgia Science Teachers Association in February of 2003. His presentation was based on activities described in the National Academy of Sciences book titled Evolution and the Nature of Science. 5 Essential Features of Inquiry 1. Learners are engaged by scientifically oriented questions why how 2. Learners give priority to evidence which allows them to develop and evaluate scientifically oriented questions 3. Learners formulate explanations from evidence to address scientifically oriented questions 4. Learners evaluate their explanations 5. Learners communicate and justify their proposed explanations. Adapted from "Inquiry and the National Standards" by the National Research Council. Characteristics of Inquiry Inquiry taps into the natural curiosity of children Students conceptualize a question Student seek possible explanations that respond to that question Students design and conduct investigations, manipulate variables With technical facts and vocabulary students often fail to see how this knowledge is useful in the future Adapted from "Inquiry and the National Standards" by the National Research Council. Types of Inquiry Structured Inquiry – teacher provides the students a hand-on activity; procedures, materials, but NOT the expected outcomes Guided Inquiry – teacher provides materials and the problem to investigate; students devise their own procedure to solve the problem Open Inquiry – similar to guided inquiry with the students formulating their own problem to investigate 5 E Inquiry Model Engage Activity which focuses the students attention; hook Explore Activity which gives students time to think and investigate/test/make decisions/problem solve and collect information Activity which allows students to analyze their exploration; time to reflect and clarify misconceptions Activity which expands and solidifies student thinking and/or apply to real world setting Explain Extend Evaluate Activity which allows the teacher for assess student performance and understandings Cookbook to Inquiry Are we addressing the 5 essential questions of inquiry in the labs we currently use with students? What is a cookbook lab? How can we transform a lab to be more inquiry oriented? Cookbook to Inquiry “Rethinking Laboratories.” The Science Teacher, September 2003 Adaptation Principles - Questions Change the purpose statement of the activity into a question Involve students in activities where they generate questions to investigate Make the question relevant to students “Rethinking Laboratories.” The Science Teacher, September 2003 Cookbook to Inquiry Adaptation Principles – Evidence Throw away the “recipe” (or parts of it) and/or give students, groups or the class opportunities to define variables, develop procedures, set up data tables and make predictions “Rethinking Laboratories.” The Science Teacher, September 2003 Cookbook to Inquiry Adaptation Principles – Explanation Postponing the teacher’s explanation until after the lab and shifting the responsibility of explanation to students Expect students to develop evidence-based explanations as a central step of all lab work Provide students opportunities to work and talk to together Engage students in the analysis of data by looking for patterns, evidence and logic to support it “Rethinking Laboratories.” The Science Teacher, September 2003 Cookbook to Inquiry Adaptation Principles – Communication Provide opportunities to present explanations to other audiences through discussion, writing and drawing Ask students to evaluate the logic of their explanations in terms of evidence “Rethinking Laboratories.” The Science Teacher, September 2003 Inquiry Analysis Tool – does the material…. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Engage the learners in scientifically oriented questions? Ask learners to give priority to evidence? Encourage learners to formulate explanation from evidence? Ask learners to evaluate their explanations in light of alternative explanations? Expect learners to communicate and justify their proposed explanations? “Rethinking Laboratories.” The Science Teacher, September 2003