Honors Objectives 14
advertisement

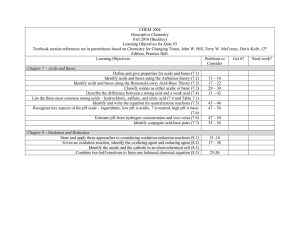
Chapter 14 Acids and Bases- Honors 1.List five general properties of acids. 2.Define and give an example of a traditional acid (Arrhenius), a Bronsted acid and a Lewis acid. 3.Explain the difference in a strong and a weak acid and give an example. 4.Explain and use the naming system for binary acids. 5.Explain and use the naming system for oxyacids (ternary). 6.Explain and use the naming system for organic acids. 7.Name and deiscribe five acids commonly used in industry. 8.List the six strong acids. 9.List five general properties of bases. 10.Define and give an example of a traditional base (Arrhenius), Bronsted base, and a Lewis base. 11.Explain and use the naming system for bases. 12Explain the difference in a strong and a weak base and give an example of each. 13. List the strong bases. 14. List several weak bases. 15.Discuss acid base neutralization rxns. Honors—Chapter 14 Acids and Bases 16. Write B/L acid/base rxns. 17. Select the conjugate pairs when given the B/L acid or base. 18. Define amphoteric and give an example. 19. Write a typical Lewis acid/base rxn 20.Define acid anhydride and give an example. 21. Define basic anhydride and give an example. 22. Write reactions for acid/base anhydrides. 23. Discuss the relative location on the Periodic table and discuss whether they will form acids, bases, or be amphoteric. 24. Name the properties that determine whether an OH will be basic. 25. Discuss the reaction of metals with aqueous acids. 26. Discuss the rxn of acids with metal oxides. 27. Discuss the rxn of acids with carbonates. 28. Discuss the rxn of hydroxides with nonmetal oxides. 29. Discuss the rxn of metal oxides with nonmetal oxides`.