Ch 5 Skeletal System Study Guide (Part 1-Axial Skeleton)
advertisement

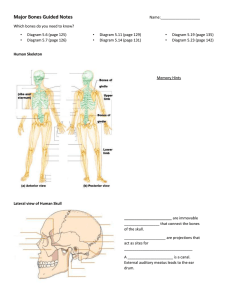
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE – THE AXIAL SKELETON 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. List the 3 major portions of the axial skeleton. Name the two sets of bones that make up the skull. Tell what each of the two sets of bones in the skull accomplishes. What are sutures? Which is the only moveable joint in the skull? How many bones are in the cranium? How many are paired? How many are single? Tell the significance of each of the following: external auditory meatus, styloid process, zygomatic process, mastoid process, jugular foramen. Why is an infection in the mastoid sinuses dangerous? What is the function of the foramen magnum? What is the function of the sella turicica or “Turk’s saddle”? What is the function of the foramen ovale? How do nerve fibers carrying impulses from the olfactory receptors get through the skull and to the brain? How many bones compose the face? Which ones of these are single bones? What is the common name for the maxillae? Name the two functions of the paranasal sinuses. What causes sinusitis? What abnormality results if the palatine bones fail to fuse during development? What is the common name of the zygomatic bones? What bone forms the bridge of your nose? Of what material is the tip of your nose composed? What bone forms the septum in your nose? What it the common name of the mandible? What makes the hyoid bone unique? What is the function of the hyoid bone? List three ways that an infant’s skull is different from that of an adult. What are fontanels? What is their common name? What are the two purposes of the baby’s skull have fontanels? What happens to the fontanels as the baby grows? Name three functions of the vertebral column. How many bones are in the vertebral column? Which type of bones are these? How many bones are in the spine before birth? What happens to the extra nine bones that are not separate bones after birth? Name the two composite bones formed by the fusing of these 9 bones. How many bones are in each of the following sections of the spine? cervical, thoracic, lumbar What separates the vertebrae? What type of tissue are these made of? What is the purpose of these discs? What happens to the water content of these discs with age? What is a herniated disc? What causes this condition? Which curvatures of the spine are primary curvatures? Why are they named this? Which curvature appears when a baby can raise its head? Which curvature appears when a baby begins to walk? Define each of these conditions: scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis Give the names of the C1 and C2 vertebrae. Which joint allows you to nod “yes”. Which allows you to move your head side to side to indicate “no”? What is the significance of the thoracic vertebrae? Describe the shape of lumbar vertebrae. How is their shape related to their function? Which fused bone forms the posterior wall of the pelvis? Which fused bone is the remnant of the human “tailbone”? Which vertebrae contain foramina in the transverse processes, through which the vertebral arteries ascend to reach the brain? Which type of vertebra(e) have transverse processes that have facets for articulation with the ribs? Which bone is a composite bone that articulates with the hip bone laterally? Which bones make up the bony thorax? Where are sample of blood-forming tissues taken for the diagnosis of suspected blood diseases? How many ribs does EVERYONE have? To what structure are all ribs attached? Which ribs are true ribs? false ribs? floating ribs? What is the space between ribs called? With what are these spaces filled? ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE – THE AXIAL SKELETON 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. List the 3 major portions of the axial skeleton. Name the two sets of bones that make up the skull. Tell what each of the two sets of bones in the skull accomplishes. What are sutures? Which is the only moveable joint in the skull? How many bones are in the cranium? How many are paired? How many are single? Tell the significance of each of the following: external auditory meatus, styloid process, zygomatic process, mastoid process, jugular foramen. Why is an infection in the mastoid sinuses dangerous? What is the function of the foramen magnum? What is the function of the sella turicica or “Turk’s saddle”? What is the function of the foramen ovale? How do nerve fibers carrying impulses from the olfactory receptors get through the skull and to the brain? How many bones compose the face? Which ones of these are single bones? What is the common name for the maxillae? Name the two functions of the paranasal sinuses. What causes sinusitis? What abnormality results if the palatine bones fail to fuse during development? What is the common name of the zygomatic bones? What bone forms the bridge of your nose? Of what material is the tip of your nose composed? What bone forms the septum in your nose? What it the common name of the mandible? What makes the hyoid bone unique? What is the function of the hyoid bone? List three ways that an infant’s skull is different from that of an adult. What are fontanels? What is their common name? What are the two purposes of the baby’s skull have fontanels? What happens to the fontanels as the baby grows? Name three functions of the vertebral column. How many bones are in the vertebral column? Which type of bones are these? How many bones are in the spine before birth? What happens to the extra nine bones that are not separate bones after birth? Name the two composite bones formed by the fusing of these 9 bones. How many bones are in each of the following sections of the spine? cervical, thoracic, lumbar What separates the vertebrae? What type of tissue are these made of? What is the purpose of these discs? What happens to the water content of these discs with age? What is a herniated disc? What causes this condition? Which curvatures of the spine are primary curvatures? Why are they named this? Which curvature appears when a baby can raise its head? Which curvature appears when a baby begins to walk? Define each of these conditions: scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis Give the names of the C1 and C2 vertebrae. Which joint allows you to nod “yes”. Which allows you to move your head side to side to indicate “no”? What is the significance of the thoracic vertebrae? Describe the shape of lumbar vertebrae. How is their shape related to their function? Which fused bone forms the posterior wall of the pelvis? Which fused bone is the remnant of the human “tailbone”? Which vertebrae contain foramina in the transverse processes, through which the vertebral arteries ascend to reach the brain? Which type of vertebra(e) have transverse processes that have facets for articulation with the ribs? Which bone is a composite bone that articulates with the hip bone laterally? Which bones make up the bony thorax? Where are sample of blood-forming tissues taken for the diagnosis of suspected blood diseases? How many ribs does EVERYONE have? To what structure are all ribs attached? Which ribs are true ribs? false ribs? floating ribs? What is the space between ribs called? With what are these spaces filled?