SyllabusMechatronics3
advertisement

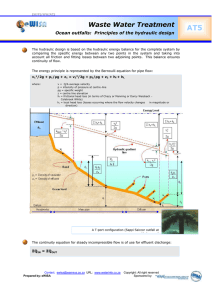
Course Syllabus Mechatronics Level 3 Instructor: Richard Burton Email: richardlburton@anderson5.net Office: 302 Phone: 864-260-5160 ext.149 Planning Time: 3rd Block Course Description: MIT 3 Mechatronics (1Semester). Mechatronics is a new interdisciplinary field involving mechanical, instrumentation, electronics, robotics/automation, computer components, and control systems. The program prepares students who like to work with their hands as well as their minds. Mechatronics is a dynamic field that changes daily with the rapid improvements in technology and computer systems. Systems are networked to meet the demands of automated manufacturing processes, and technicians are trained to meet necessary entry-level industrial skills and entry into a postsecondary program at a technical college. Objectives: Given the necessary equipment ,supplies, and facilities , the student , upon completion of the course instructional hours, will be able demonstrate the following core competencies. Credit: 1 units Requirements: No Prerequisites Clothing: Prior to operating any of the Machinery: Must have closed toe shoes, no loose long sleeves or baggy clothing that could become wrapped up in moving parts of machinery, and all jewelry must be removed from fingers and around wrist. Materials: Students are required to provide the following materials for classroom use: Notebook paper, pens, and pencils. These items need to be brought everyday. Grading, procedures and scale 25% Projects (completion, accuracy, finish quality) 25% Safety & Shop management (tool care, clean up, use of time) 25% Written work (textbook, workbook, quiz) 25% Test (unit, project, final exam) A: 100-93 B:92-85 C:84-77 D:76-70 F:69 and below Attendance Attendance is extremely important in skilled classes. It is students responsibility to make up any work that may have been missed. Units of study 1. Demonstrate hydraulic system safety. 2. Explain the principles of hydraulics and hydraulic fluids. 3. Identify hydraulic components (supply elements, control valves, and actuators). 4. Explain hydraulic systems (forces, speed, friction, flow, and pressure). 5. Identify types of hydraulic pumps. 6. Identify types of hydraulic motors. 7. Demonstrate pneumatic safety. 8. Calculate the physical characteristics and compressibility of gases (Pascal’s law and Boyle’s law). 9. Describe the pneumatic transmission of energy. 10. Identify types of compressors. 11. Analyze the principles of compressor operation and compressed-air treatment. 12. Construct pneumatic systems from components and symbols. 13. Demonstrate the ability to read, construct, and interpret fluid power symbols as well as fluid power diagrams. 14. Demonstrate correct installation and maintenance as well as preventive maintenance techniques for fluid power systems using service manuals. 15. Troubleshoot and repair fluid power systems using service manuals and gauges. Class rules and Expectations 1. Be in class and seated when the bell rings. 2. Bring appropriate materials to class. 3. Always use respectful language and behavior in the classroom. 4. Leave the shop area neat and clean at the end of class. 5. If you borrow it return it. 6. No cell phone use during class time. 7. One person leaves the class at a time with a pass. 8. Transition from shop to computer lab quietly. 9. Do not touch equipment unless you are instructed on its proper usage. 10. All proper safety rules are to be followed at all times. Consequences for violating rules: 1.Reminder of rules through a verbal warning. 2.Private conference with student. 3.Letter and call to parents. 4.Referral to school Administration. Lecture: 1.Raise your hand to ask a question or speak out loud. 2.Pay attention to the lesson and keep your head up. Working in Groups: 1.Stay in your assigned group and work as a team on the assignment. 2.All must contribute to obtain credit for the assignment. Test taking: 1.Keep your eyes on your on test paper. 2.If you have a question raise your hand and I will come to you. 3.Do not leave any books or papers out during test time. 4.No Talking between students will test is going on. Substitute teacher: Worksheet or computer exercise will be given to all students and must work toward or complete during class time. Behavior should follow the same guidelines as if the teacher is present. Actions will be rewarded or punished accordingly. Final Exam: Will be taken from study guide and a hands on demonstration of skills in the shop.