About The Course
advertisement

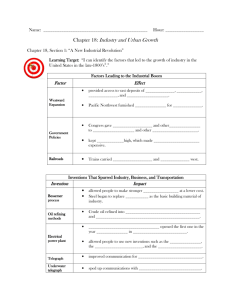
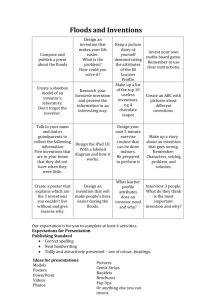
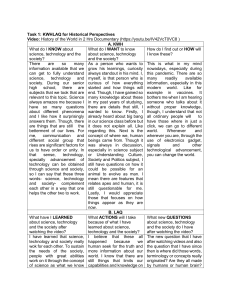
About The Course What the Course is Not • Not designed to teach specific technological skills • Not a refuge from history What is Technology? • Objects people create to extend their capabilities (tools) • Methods people devise to solve problems • Materials people discover or invent to create objects • Human modifications of the environment Broad View of Technology • Inventions (things, materials, methods) • Scientific discoveries behind inventions • Changes in world-view that make inventions possible • Social institutions spawned by technology • Values changes induced by technology • Unanticipated effects of technology History Happened to Real People • They didn’t know how it was going to turn out • They felt pain and fear just like us Technology is a real intellectual triumph Why were key inventions often discovered so late? • • • • Stethoscope Measurement of blood pressure Antiseptics Printing press If you came to Earth from another planet in 1100 A.D., where would you expect Technology to develop? • • • • • • China? Japan? India? Islamic World? Meso-America? Peru? The Goldilocks Factor • Isolation: enough for independent evolution, but not enough to prevent external stimuli • Fragmentation: Neither total central authority nor total anarchy • Diversity: Distinct cultures but with means of interchange • Challenge and Stress: enough to stimulate, not enough to traumatize Western Culture is a Serial Culture • • • • • • Ancient Near East Greek Etruscan Roman Irish Arabic • Western Europe • Britain • America The “What If” Factor Autonomy • People invent things because they see themselves as agents of change • People invent things because they can benefit from the results • Technology loosens social bonds, creates new social niches and roles • Increases expectations