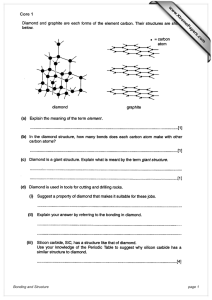
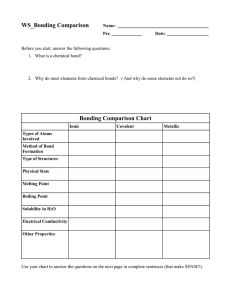
Atoms and Bonding
advertisement

Atoms and Bonding Composition of the Sun Composition of the Sun • Abundance of Light Elements • Rarity of Lithium, Beryllium, Boron • Preference for Even Numbers • Abundance peak at Iron, trailing off after How Elements Form in Stars • • • • • • • Sun: 4 H He He + particle Mass 5 – Unstable He + He Mass 8 – Unstable He + He + He C Add more He to make heavier elements End of the line is iron for energy production Atoms beyond Iron made in massive stars What are Planets Made of? • Same material as Sun • Minus the elements that remain mostly in gases • We find this pattern in a certain class of meteorites (Carbonaceous Chondrites) Chondrites The Earth’s Crust looks Very Different Composition of the Crust Minerals are the Chemicals that make up the Earth • Naturally-occurring • Inorganic • Chemical Compounds • About 3000 Known • 200 Common • 20 Rock-forming Atomic Bonding 1. Ions Atomic Bonding 2. Electrical Neutrality • (+) and (-) Cancel Out 3. Bonding (Satisfy 1 & 2) • Ionic (NaCl) • Covalent (O2) • Metallic (Cu, Al, Fe) • Hydrogen (in water) Ionic and Covalent Bonding Metallic Bonding Hydrogen Bonding Summary of Bonding • Ionic bonding holds rocks and minerals together • Covalent bonding holds people and other organisms together • Metallic bonding holds civilization together • Hydrogen bonding gives water its heatretaining and solvent properties 4. Lattices • Atoms in crystals form a repeating pattern called a Lattice 5. Complex Anions • Many minerals contain groups of atoms that behave as single units What Do Atoms “Really” Look Like? Standing Waves Standing Waves • The wave is everywhere in the tank, all the time • The negative portions are just as real as the positive portions • Other waves could be present in the same space at the same time s-orbitals (Lithium and Beryllium) p-orbitals Boron, Carbon, Nitrogen 1s2s2p3s Sodium, Calcium Carbon and Silicon 1s2s2p3s3p Phosphorus through Argon Hybrid Orbitals: Carbon