Presented by Ye Yu @ CS685 Fall 2015
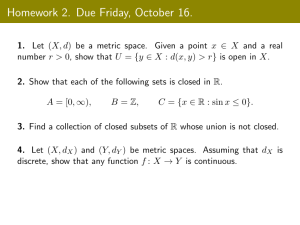
advertisement

Presented by Ye Yu @ CS685 Fall 2015
Overview
Goal: Rapid/Efficient design cycle for Data
Center Topo
Approach:
• Topology Description Language (TDL):
• Loose Requirements of the Topo
• TDL “Translator” + Optimizer = Synthesizer
• Find a Topo that satisfies TDL
• Topology Analysis Tools
Core?
FatTree?
Layer 3
Layer 2
Layer 1
Layer 0
20
Break The Symmetry
21
Break The Symmetry
22
AB FatTree: F10
Sub Trees in Type A and B
23
Observation:
• TDL is not a ‘programming language’.
• TDL is a Python package (Not Open Source)
• A list of Objects ( OOP concept)
• The attributes of ‘Topology’ describes the
connection/constraints/Service Level Objectives.
Look into the code
Another Example : Dcell
Dcell :Hierarchy Graph! FatTree: Hierarchy Tree!
Another Example : Dcell
• Class Dcell(i):
• If i>0:
• Sub-Dcells[0] = new Dcell(i-1)
• Sub-Dcells[1] = new Dcell(i-1)
• Sub-Dcells[2] = new Dcell(i-1)
• Sub-Dcells[n-1]= …
• Connect All Sub-Dcells
• If i==0:
• Connect switch/hosts.
Synthesizer: Roadmap
• 1. Expand Hierarchy Graph
• 2. Arrange Connections.
Synthesizing Recursive Graph
• Easy & Simple Recursive
• Start from highest-rank (logical) node
The Connections.
• Connection Example:
• Connection(Agg, Spine)
C1(Agg_in_pod1,Spine),C2(Agg_in_pod2,Spine)
• Scope: When dealing with a connection i, only
consider links between Agg_in_pod_i and Spine.
• Candidate Connections for C1:
All edge (x,y): x is Agg_in_pod1, y is Spine.
• Select link from candidates: CSP problem.
Constraint satisfaction problem
• Example:
• Find x,y,z : [variables]
• 1<=x,y,z<=3, integer. [domains]
• (x,y) is one of {(1,2),(2,3),(3,1)}
[constraints]
• (y,z) is one of {(2,3),(1,1),(1,2)}
• NP-hard.
The Connections.
• Select link from candidates: CSP problem.
• Decision: (agg_1_1,spine_1),(agg_1_1,spine_1)….
• Decision variable: decision[agg_1_1][1] = 1,
decision[agg_1_1][2] = 2….
• Acceleration: order by rank. [Tiebreakers]
(Enumrate possible topologies that satisfies TDL)
Note: This is just for Fat-Tree-like topologies….
Metric?
• Cost: Easy to compute
• Proxy metrics: “Bisection Bandwidth?” “Hop
Count”
• Mainly reflects the worst case.
• Given traffic matrix?
• Real traffic is related to protocols/queueing mechanisms
…
Metric for Real Network Traffic?
• use an approximate bandwidth metric to illustrate
how changes in the TDL for a network (or its
expansion plan) affect several metrics of interest.
• Given Traffic matrix, compute throughput.
• ABM = throughput under given traffic + network
changes.
•
Reliability Metric?
• Simplified Reliability Metric [Next Slides]: Measure
the probability that the topo is able to satisfy SLO
under failure.
• Routing Convergence Metric
• first, the number of components C that can react when
any component F fails.
• the maximum distance between C and F over all such
pairs
a tiebreaker that
prefers connecting
to spine switches
that have fewer
connections