Competitor Research: Positioning
advertisement

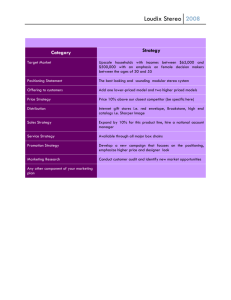
Competitor Research: Positioning Competitor Research-Positioning • Positioning is something you do to the mind of the prospect • It is not enough to invent something. You must get into the subject’s mind • Positioning is designing an offering that target segment members both perceive as different and value more than competitive offerings Positioning • 3 common ways to position 1. Our product is unique 2. Our product is different 3. Our product is similar • To position, managers must understand customers perception of competitive structure of market Positioning • These managerial questions are 1. How do customers view our brand 2. Which brands are perceived to be our closest competitors 3. What product/company attributes are most responsible for these perceived differences Positioning • Requirements of effective positioning 1. Uniqueness 2. Desirability 3. Believability Positioning • Before making claim, company should ask 1. Does any other co. already occupy this position 2. Is the feature /benefit really important to people 3. What objective evidence do we have to support our claim 4. Can we deliver against this claim 5. How much promotion effort will be required to get this position in people’s minds Positioning • Methods of positioning research 1. Product /service profiles 2. Quadrant analysis 3. Importance and uniqueness ratings 4. Perceptual maps Positioning • Perceptual maps are spatial representations with alternatives plotted in a Euclidean space • Features of perceptual maps 1. Pairwise distances between alternatives indicate perceived similarities 2. Vectors on map show both magnitude and direction. Vectors are product attributes 3. Axes of map are underlying dimensions of consumer perceptions of differences between alternatives