go to market channels
advertisement

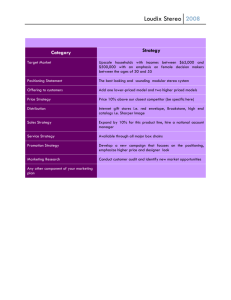
51 SELECTING YOUR MARKET CHANNELS INTRODUCTION In the not so distant past, companies designed their marketing channels (or go-tomarket networks and mechanisms) in a very simple and straightforward way. They sold their products directly to all customers in the one way. Such a ‘one size fits all’ channel strategy is no longer tenable in today’s fragmented markets and customer multi-segments. MARKETING CHANNELS Marketing channels perform a number of key tasks for a company. These can be generically categorized as: 1. Demand Generation The mechanisms by which a company or possibly a collaborator / partner generates a lead , qualifies that lead ( suspect to prospect) and undertakes pre-sale , persuasion of prospective customers. Mechanisms may be advertising, sales force or a retail partner. 2. Demand Fulfilment How an order for the product is taken. How the product is delivered. How the product is installed or used. There may be a third party delivery partner, for example. 3. After-Sale Service The ongoing service. 4. Account Management Future or additional product sales to the customer. CHANNEL SELECTION For each of the four ‘channel’ tasks, there are a number of options to be considered by a company, having regard to (1) customer needs and requirements (2) the way the industry operates in a market and (3) the company’s own objectives for competitiveness and effectiveness. In the start up and emerging stages, the entrepreneur has limited (time, personnel and financial) resources and it is often best to select a limited number of channels that offer: Greatest ease of market segment entry, against the competition Distribution methods and dynamics that are understood/previously experienced by your management Lowest cost of entry, compared to the competition Best fit with brand and product positioning, for example “complex” products will need dedicated sellers or re-sellers Least financial risk Strategic commitment to distribution of your product Likely to be permanent Sufficient volume potential to reach immediate and short-term revenue and profit goals Alternative routes to market, should one lapse or cease producing business Significant level of control in at least one channel to ensure you can communicate fully your product positioning (USP) and can keep the end customer knowledgeable at all times to evolve and develop that positioning. Channel Model Illustration LARGE Account Opportunity MEDIUM FIELD SALES FORCE Call centre WEB DISTRIBUTORS Re-sellers SMALL COMPLEX SIMPLE Transaction Type