DNA Replication.ppt
advertisement

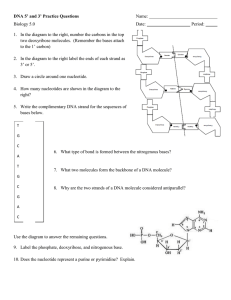
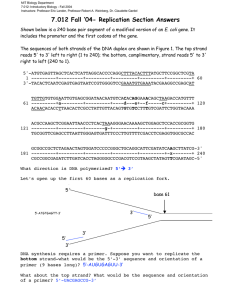
DNA Replication What is DNA? Stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid Has three main parts: 1. Sugar molecules (deoxyribose) 2. Phosphate 3. Nitrogen bases **the deoxyribose and the phosphate make up the backbone while the nitrogen bases join the two backbones in the middle (looks like a ladder!) The structure of DNA is called a double helix, because of the way in which the two backbones wrap around one another What are nitrogen bases? Four different nitrogen bases exist in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), Guanine (G) and cytosine (C) Adenine always pairs with thymine and guanine always pairs with cytosine Why are nitrogen bases important? The sequence of nitrogen bases makes up what we call GENES Each gene controls the production of a protein This in turn controls all of the traits and characteristics that make each of us an individual How is DNA duplicated? Before cells divide, they must duplicate their genetic material This process is called DNA replication The first step in this process involves an enzyme that “unzips” the two strands in the original DNA molecule DNA replication (continued) As the original DNA strand unzips, another enzyme moves along each strand, attaching complimentary nitrogen bases to replace those that were separated When all of the new bases have been placed, two new molecules of DNA have been formed, each one identical to the original strand What happens when DNA is not replicated properly? We all make mistakes in our daily lives! Mistakes can also happen in DNA replication Such mistakes are called MUTATIONS Mutations fall into one of three categories: 1. 2. 3. POSITIVE – one that benefits the organism NEUTRAL – one that has no effect on the organism NEGATIVE – one that is harmful to the organism