Geog WTO notestoteachers eng 4982
advertisement

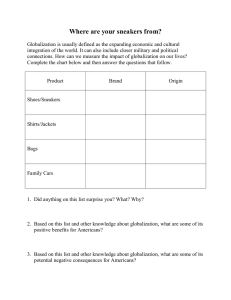
World Trade Organization Geography Worksheets and Learning Activities Notes to Teachers This learning package contains a series of graded worksheets and learning activities. It aims at helping students acquire geographical knowledge and concepts in relation to globalization 1 , the characteristics of rich and poor countries, agricultural and industrial development, population mobility and sustainable development. With adjustment and adaptation to meet the needs and interests of the students, this package can be used in S1 to S7 geography lessons. What are the learning objectives of the worksheets? After completing the learning activities in the worksheets, students should be able to: Knowledge 1. identify the spatial distribution of the rich and the poor countries; 2. understand the key characteristics of the rich and the poor countries, how and to what extent they are interdependent on each other; 3. understand the impact of globalization on industrial location, agricultural development, population mobility, employment structure and the environment; 4. evaluate the cost and benefits brought by globalization to the more and the less developed countries; 5. understand the importance of sustainable development in an age of globalization. Skills 1. observe and collect evidence relating to our lives; 2. collect, extract and generalise information from the Internet; 3. interpret maps and draw sketches; 4. make decisions by analysing information from different sources; 5. develop generic and higher-order thinking skills, including collaboration, decision making and critical thinking skills. Values and Attitudes 1. appreciate the positive influence of globalization on the rich and the poor countries; 2. show concern for others, especially the less fortunate, that are affected by the negative influence of globalization; 3. develop a sense of responsibility towards the building of a better world. The definition of the term ‘globalization’ in the worksheets is restricted to its economic and trade aspect, referring to global trade liberalisation. 1 1 What is included in the worksheets? How should the worksheets be used to facilitate student learning? The WTO worksheets and learning activities consist of two levels. The first level (‘Welcome Our Friends from all over the World!’) is mainly designed for S1 to S3 students and the second level (‘How does Globalization affect Rich and Poor Countries?’) is suitable for S4 to S7 students. In order to cater for the wide range of learners’ differences, teachers should modify the activities where necessary. Objectives and Suggested Learning/Teaching Strategies Level S1 to S32: ‘Welcome Our Friends from all over the World!’ To introduce briefly the basic concepts S1 relating to WTO, globalization as well Where are our factories moving as the rich and the poor. to? To develop map reading and information S3 technology skills in learning. 2 Related Curriculum Area of Geography Students observe and collect data to understand that globalization is closely related to their daily lives By searching for information from the Internet, students find out more about globalization and learn to look at globalization from different perspectives Students are requested to identify the spatial locations of the MDCs and the LDCs on maps and provide reasons for such regional disparities The Rich and the Poor Industrial Miracle This part is designed mainly for S1 to S3 students, but with some adjustment and adaptation, it can be served as the introduction for S4 to S7 students. 2 Objectives and Suggested Level Learning/Teaching Strategies Related Curriculum Area of Geography To investigate the locational change of S4 to S5 industry and its associated impact from Changing locational ‘How does factors of different perspectives. Globalization To help students to develop reading to information Affect Rich technology industry learn, map interpretation, critical and Poor thinking and information technology Food and Hunger Countries?’ skills. Sustainable City Making use of the case studies and maps provided, teachers guide students to S6 to S7 understand the temporal and spatial changes Location of in the information technology and toy industries manufacturing industry Through a series of web-learning activities, S4 to S7 students can assess the impact of globalization on industrial and agricultural development, population mobility, employment structure and the environment of MDCs and LDCs The development of information technology skills and creativity. Extended Activity 3 By means of role-play3, teachers can provide opportunities for students to understand more deeply the importance of sustainable development in an age of globalization, and to see that the world is becoming more and more interrelated and interdependent. This part also helps students to develop their critical thinking skills Through the use of the computer presentation or the webpage design, students can develop their creativity and a deeper understanding of the importance of sustainable development in an age of globalization Appendix 1 lists out the run-down of the role-play activity. 3 Impact of Urbanization and Industrialization on farming Impact of Urbanization and Industrialization on the quality of the environment S4 to S5 Sustainable City S6 to S7 Impact of Urbanization and Industrialization on the quality of the environment Appendix 1 T HE RUN - DOWN OF THE ROLE - PLAY ACTIVITY Aims Role-play is an interactive teaching strategy. It aims at helping students to analyse issues from multiple perspectives and to develop their critical thinking skills for values judgment. During the role-play activity, teachers should make good use of discussion and encourage students to listen to each other carefully, to consider different viewpoints, to analyse information thoroughly, and where possible, to reach a consensus through group discussion. When the teachers implement the role-play activity on p.19-22, they should note the following points: Pre-requisites 1. To have a brief introduction on the basic concepts of globalization, sustainable development and the issue of e-waste; 2. Arrange students to gather various types of resources. Ask them to complete the worksheets on p.19 so they can appreciate different opinions of the stakeholders; 3. Ask students to read the information provided on p.20 -21 to have a general understanding of the different opinions of various stakeholders; 4. It is important that teachers should not give their own views at this stage, so as to let students develop their own. During the role-play 1. Put the students into groups of 6; 2. Students are free to choose their roles; 3. Ask students to read thoroughly p.20-21, in order to have an in-depth understanding of the views, situations, attitudes and standpoints of the various roles; 4. Arrange the role-play activity, ensuring that each student can express the opinions of his/her selected role, so as to simulate a real life situation; 5. After listening to all the viewpoints in the group, students should try to reach a consensus if they can with honesty; 4 6. Arrange a short presentation from each group. Ask every student in class to listen carefully to the viewpoints of each group; 7. Ensure that each student pays attention to others’ opinions and viewpoints, by getting them to write them down succinctly; 8. It is important that teachers should not give their own views at this stage, so as to let students develop their own. Debriefing session 1. Teachers are recommended to make an overall conclusion for each group, and to provide different viewpoints, so as to allow students to have reflection; 2. Teachers can provide their own views and standpoints for students’ reference; 3. Ask students to complete the worksheets on p.22. 5 Books: 1. Dicken, P. (2003). Global Shift: Reshaping the global economic map in the 21st century. London: Sage Publications. 2. Guinness, P. (2003). Globalsation. London: Hodder & Stoughton. 3. Knox, P. et al (2003). The Geography of the World Economy (4th Edition). London: Arnold Press. 4. Ments, V.M. (1994). The Effective Use of Role-Play: A Handbook for Teachers and Trainers. New York: Nichols Publishing. 5. 鄒崇銘 (2000)。《千禧年、全球化、新思維》。香港:明報出版社。 Websites: 1. 10 Benefits of the WTO Trading System http://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/whatis_e/10ben_e/10b00_e.htm 2. Global Exchange http://www.globalexchange.org/campaigns/wto/ 3. Globalisation http://www.globalisation.com 4. Hazardous E-waste Seized, the Information Services Department of the Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, 22 July 2004 http://www.news.gov.hk/en/category/lawandorder/040722/html/040722en08010. htm 5. The Economist: IT Industry’s Location Shifts, 17 July 2003 http://www.ebusinessforum.com/index.asp?layout=rich_story&doc_id=6582 6. The World Trade Organization (WTO) http://www.ifg.org/wto.html 6 7. Toxic Technology Contaminates E-waste Recycling Yards in China and India, the Green Peace, 17 August 2005 http://www.greenpeace.org/china/en/press/releases/20050817_exeter_report 8. UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs Division of Sustainable Development www.un.org/esa/sustdev/index.html 9. 工業貿易處 http://www.tid.gov.hk/tc_chi/trade_relations/tradefora/wto_bkgd.html 10. 樂施會專題文章:不公平的勞工待遇 http://www.cyberschool.oxfam.org.hk/articles.php?id=72&page=8 11. 世界貿易組織「香港部長級會議」主辦政府的網站 http://www.wtomc6.gov.hk/tc/home/welcome.html 12. 立法會十三題:處理電子廢物的措施,香港政府新聞網,2005 年 8 月 9 日 http://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/200503/09/03090214.htm 13. 全球化監察 http://www.globalmon.org.hk/ 14. 香港特別行政區持續發展組 www.susdev.gov.hk 15. 綠色和平:電子廢物 http://www.greenpeace.org/china/ch/campaigns/toxics/e-waste 16. 「「產品責任制」勢在必行:數碼生活催生電子廢物」 , 《成報》 ,2005 年 2 月 26 日 http://www.singpao.com/20050226/local/679725.html 17. 「1000 激進韓農襲港 年底世貿部長會議」,《明報》,2005 年 7 月 11 日 http://hk.news.yahoo.com/050710/12/1edds.html 18. 「女子非法進口舊顯示屏罰四萬」,香港政府新聞網,2005 年 7 月 15 日 http://www.news.gov.hk/tc/category/environment/050715/html/050715tc04005.htm 19. 「工貿署長:世貿沒製造貧窮 指有關國家沒為農民轉型」,《明報》,2005 年8月9日 http://hk.news.yahoo.com/050808/12/1fcy8.html 20. 「自由貿易好處多 著名藝人話你知」,香港政府新聞網,2005 年 8 月 26 日 http://www.news.gov.hk/tc/category/businessandfinance/050826/html/050825tc0300 1.htm 21. 「南韓團體發公開信 交代反對世貿理由」,《明報》,2005 年 8 月 10 日 7 http://hk.news.yahoo.com/050809/12/1fedt.html 22. 「政府有效管制電子廢物跨境轉移」,香港政府新聞網,2003 年 8 月 15 日 http://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/200308/15/0815249.htm 23. 「世貿組織:中國的未來、香港的機會」 ,香港特別行政區:新聞公布,2000 年9月4日 http://www.info.gov.hk/gia/general/200009/04/0904193.htm 24. 「港下月世貿會議 兩岸擬商農產品」,《明報》,2005 年 6 月 13 日 http://hk.news.yahoo.com/050612/12/1dfr3.html 25. 「憂貿易自由化損利益 韓農 03 年死諫世貿會議」 , 《明報》 ,2005 年 7 月 11 日 http://hk.news.yahoo.com/050710/12/1eddt.html 8