Unit 09 - Tolerance, limits and fits - Lesson element - Learner task (DOCX, 178KB) 24/02/2016
advertisement

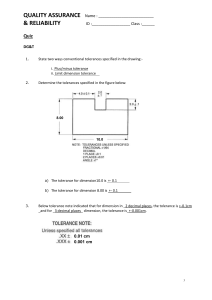
Unit 9: Mechanical design LO1: Be able to use graphical and engineering drawing techniques to communicate design solutions Tolerances, Limits and Fits Learner activity sheet Activity 1: Tolerances, Limits and Fits – Application Depending on the mode of operation, assemblies will require different types of fits. Look at the examples below and circle the appropriate type of fit (you may need to do a little investigation first to check the application): Application Fit Pin in a bicycle chain Clearance Interference Key in a lock Clearance Interference Coin in a coin slot Clearance Interference Gudgeon pin in a piston Clearance Interference Cap on a marker pen Clearance Interference Version 1 Activity 2: Tolerances, Limits and Fits – Symbols The figure below presents a standard notation used to specify a hole/shaft fit: Identify each of the following features (A to E) in the notation above: Shaft tolerance Zone: Fundamental Deviation: Hole tolerance Zone: International tolerance grade number: Basic Size: Version 1 Activity 3: Tolerances, Limits and Fits – Calculation Using the tables shown below, determine the type of fit as well as maximum and minimum values of clearance or interference for the following shaft-hole assemblies: a) 132 H9/d9 b) 60 H7/n6 c) 49 H7/p6 Nominal Size (mm) From To 18 30 30 50 50 80 80 120 120 180 Nominal Size (mm) From To 18 30 30 50 80 120 Version 1 50 80 120 180 H7 H8 H9 H10 Deviations (µm) 21 33 52 84 0 0 0 0 25 39 62 100 0 0 0 0 30 46 74 120 0 0 0 0 35 54 87 140 0 0 0 0 40 63 100 160 0 0 0 0 d9 n6 p6 h7 Deviations (µm) -65 28 35 0 -117 15 22 -21 -80 33 42 0 -142 17 26 -25 -100 39 51 0 -174 20 32 -30 -120 45 59 0 -207 23 37 -35 -145 52 68 0 -245 27 43 -40