Unit 01 - Inverse function and log laws - Lesson element - Learner task (DOC, 807KB)
advertisement
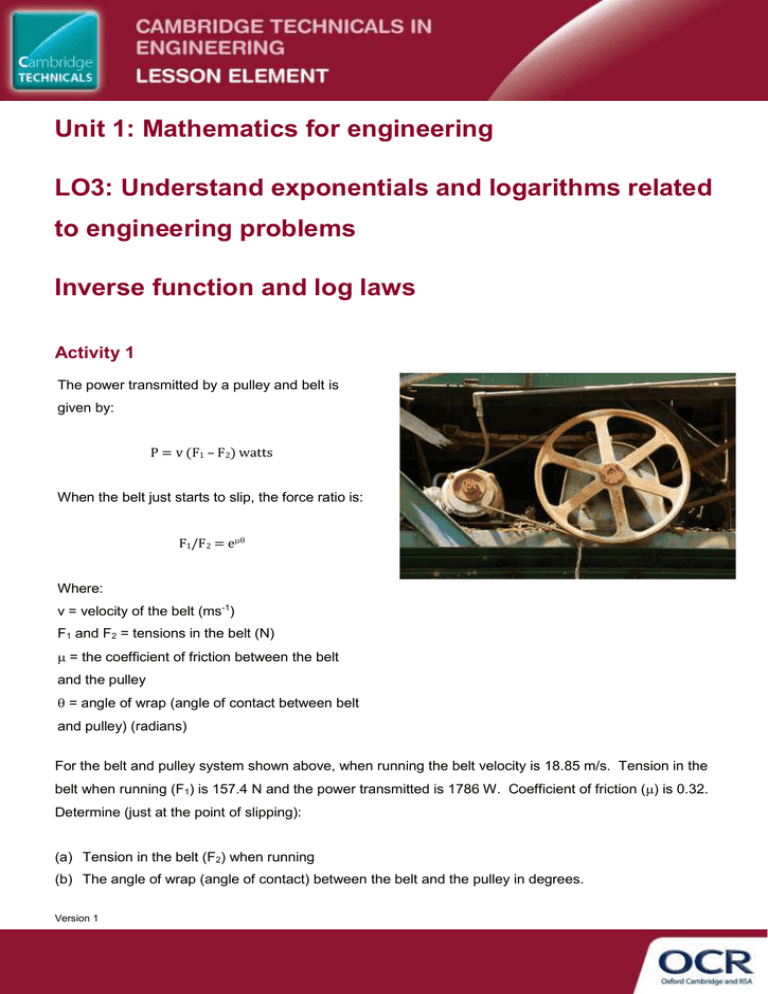
Unit 1: Mathematics for engineering LO3: Understand exponentials and logarithms related to engineering problems Inverse function and log laws Activity 1 The power transmitted by a pulley and belt is given by: P = v (F1 – F2) watts When the belt just starts to slip, the force ratio is: F1/F2 = e Where: v = velocity of the belt (ms-1) F1 and F2 = tensions in the belt (N) = the coefficient of friction between the belt and the pulley = angle of wrap (angle of contact between belt and pulley) (radians) For the belt and pulley system shown above, when running the belt velocity is 18.85 m/s. Tension in the belt when running (F1) is 157.4 N and the power transmitted is 1786 W. Coefficient of friction () is 0.32. Determine (just at the point of slipping): (a) Tension in the belt (F2) when running (b) The angle of wrap (angle of contact) between the belt and the pulley in degrees. Version 1 Activity 2 Charging the voltage across a capacitor (at any time (t)) is given by the formula: VC = VS (1 – e-t/RC) Where: VC = voltage across the capacitor (volts) VS = supply voltage (volts) t = time (seconds) R = value of resistor (ohms) C = value of capacitor (farads) In a circuit consisting of a series resistor and capacitor, the supply voltage is 9 V. The value of the resistor is 470 k, and when charging at t = 100 s the voltage across the capacitor is 7.93 V. Determine the value of the capacitor in the circuit. Version 1