Planning and Implementing 20130123
advertisement

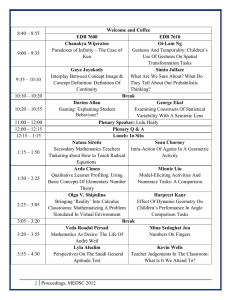
Holistic Planning of the Primary Language Curriculum Language Learning Support Section 23 January 2013 Contents The future is now – challenges faced in language learning and teaching Learning from the past – lessons from the implementation of the NSSC Planning for now and the future – planning the language curricula at senior primary level Taking action now – role of school leaders The future is now What are the challenges of the 21st century? Changed mode of economic activities Changed patterns of work Changed ways of living Changed relations between people and nations Fast pace and permanence of change Key features of 21st century labour market Increasingly difficult to secure a job Pure manual blue-collar jobs diminishing Occupational identities are being blurred Local, national and global work opportunities but fortune favours the ‘educated and skilled mind’ More intensive human interactions Self-confidence, self-management, selflearning, self-reflections increasingly important 21st century demands on frontline workers Ability and willingness to: adapt to new and changing contexts take risks manage self learn on-the-job, on-demand, just-in-time look at the big picture design solutions with creativity improvise fit for purpose activities use multiple skills to solve problems Customer service orientation Good interpersonal skills knowledge worker 21st century learners are expected to be able to… communicate be innovative and creative learn on-demand, query, challenge be responsible and selfdisciplined think and solve problems be conversant with technology work and serve together respect differences and diversity demonstrate integrity lead a healthy life and … 7 Our shared mission : To nurture a new generation of learners who can rise with and to the challenges of the 21st century (from basic education reform in 2000 to NAS since 2009) 8 The Learning Reform for whole person development and life-long learning Recognize roles and responsibilities…and show concern for the society, nation and the world Develop a sense of national identity and multiple identities Basic Education Specialised Teaching Curriculum Guide TSA SBA Develop self-directed learning, independent learning capabilities and personal aspirations New Senior Curriculum & Acquire a solid foundation over a broad school curriculum Small Class Teaching Assessment Guide Student Focused Curriculum & Learning Reform MOI Refinement Chinese Language Curriculum Funding resources Develop trilingual and biliterate language proficiency English Develop a habit of reading and engaging actively in purpose reading across the curriculum Lead an active and healthy lifestyle Professional Development Language Curriculum School-based support What challenges do students & teachers face in language learning and teaching? Relentless advancement in communication technology Gap between the different key stages of the enacted curriculum Positioning of teaching to the target group Exam-oriented culture and practices Early planning is the key to preparing our students for the future 21st Century Demands Challenges faced in learning & teaching Learning from the past The New Senior Secondary Curriculum English Language Purposes authentic holistic rich and varied To extend students’ knowledge & experiences of other people’s What kind of cultures learning To help students build a firm English foundation (to interpret, use & experience produce) for the future for does this imply? further study and work pleasure active purposeful interactive The Curriculum for English Language S6 S5 Compulsory Part (75%) S4 Elective Part (25%) Elective Modules Learning English through … Poems & Songs Popular Culture Debating Sports Communication Short Stories Social Issues Drama Workplace Communication Hong Kong Diploma of Education Examination English Language DSE Exam Framework Component Duration Weighting Public exam Paper 1 Paper 2 Paper 3 Paper 4 Reading 1.5 hrs 20% To encourage Writing 2 hrs 25% more exposure to English outside the classroom (extensive Listening & 30% 2 hrs reading/viewing English texts) & integrated skills reading to learn (formation of a 10% 20 base) mins Speaking wider knowledge SBA (for school candidates only) 15% To do well in the examination, students need to….. • understand the features of a wide range of texts (including literary texts) • identify and evaluate information, views and attitudes, both explicitly stated and inferred • gather information from a variety of sources and use it to create a new text • understand the purpose, audience and context of a written task • articulate and communicate their own views and opinions on various issues To do these things they will need…. • • • • a wide repertoire of vocabulary sound mastery of the language system knowledge of different styles of writing well-developed thinking and problemsolving skills • knowledge of various situations and purposes represented in writing or speaking tasks HKDSE English Language Level Statistics No. sat 5** 5*+ 5+ Day school Candidates 69 713 0.8 3.1 7.7 23.7 50.1 79.2 90.0 10.0 All Candidates 71 617 0.7 3.1 7.6 23.3 49.3 78.6 89.6 10.4 4+ 3+ 2+ 1+ U How did they perform? •Identify explicitly stated information •Identify key words •Work with familiar contexts •Give their own views and opinions •Understand main ideas •Infer information, views and attitudes •Support their opinions with evidence •Write with a sense of purpose, audience and context •Work with more academic /literary texts or unfamiliar situations Some food for thought on our current practices Are these practices still good enough for our students? – Teaching them to produce accurate sentences in isolation – Teaching them meaning of new words in textbooks & giving them vocabulary lists & dictations – Having them complete reading/listening exercises & checking the answers with them Some food for thought on our current practices Are these practices still good enough for our students? – Focusing on different skills separately – Targeting at basic comprehension & recall – Covering all the texts in textbooks – Providing step by step guidance to help them complete a task sufficiently Planning for now and the future Curriculum planning Holistic planning of the primary language curriculum Senior primary Junior secondary Vertical curriculum planning 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Develop basic language skills & higher-order thinking skills in English KLA Further develop language skills & higher-order thinking skills with other KLAs S3 S2 P6 P4 Strengthen language skills & higher-order thinking skills within & across KLAs S1 Smooth interface between senior primary P5 & junior secondary Horizontal curriculum planning 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Vocabulary & forms Skills Tasks Texttypes Materials Assessment Curriculum planning Holistic planning of the primary language curriculum Senior primary Implementation of learning & teaching practices Junior secondary Implementation of learning and teaching practices 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Drama Songs & poems Social issues Popular cultures Provide chances for Broaden students’ students to read knowledge extensivelybase Able to think Develop critical& thinking skills solve problems Promote Able to assessment as face challenges, learning & beindependent responsible & self-disciplined learning Able to communicate, Provide cross-curricular work &opportunities serve in teams, learning respect differences & be conversant with technology Able to think creativity creatively Develop Curriculum planning Holistic planning of the Alignment primary between language learning, teaching curriculum & assessment (evaluation) Senior primary Implementation of learning & teaching practices Junior secondary 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Alignment between learning, teaching and assessment Learning Teaching Assessment WHAT WE EXPECT STUDENTS TO LEARN WHAT WE TEACH & ASSESS 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Etc. Learning tasks & activities Oral presentations Homework Assessments in schools Conferencing Shared writing & Process writing Projects Portfolios 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Curriculum planning Holistic planning of the primary Alignment language Implementation between curriculum of learning learning, teaching & teaching & assessment practices (evaluation) Continuity of knowledge & skills across subjects & key stages Assessment of knowledge & skills using various meaningful modes 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Holistic planning of the primary language curriculum Development & enrichment of knowledge & skills through careful scaffolding Three-year curriculum plan: Key emphases Broaden students’ knowledge of the world, and enhance their sensitivity to roles and situations through reading extensively Develop students’ higher-order thinking skills through completing tasks (e.g. selection, synthesis & evaluation) Enhance students’ ability to look at the issues from multiple perspectives through designing tasks that require taking on different roles in different social situations Using integrated skills development as an entry point 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Listening Reading Writing Speaking 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Progression: Integrated skills at KS2 synthesise paragraphing 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Progression: Critical thinking skills at KS2 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Progression: Creativity at KS2 Progression : Cater for learner diversity at KS2 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Progression : Cross-curricular learning at KS2 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Progression : Wide reading at KS2 Progression : Assessment as learning at KS2 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Progression : Independent learning at KS2 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Sharing a unit plan Level P4 Topic Old Hong Kong Blogs, conversations, letters, self-directed reading materials Items on homes, shops, games, transports Text type Vocabulary • Ask & answer questions with ‘Was’ or ‘Were’ Language item Task • Talk about past with ‘There was’ or ‘There were’ • Use indefinite pronouns ‘Nobody’ or ‘Everybody’ to talk about what people had and did in the past • Talk about like and dislike with reasons using ‘like/ dislike because’ Write a reply letter to John to describe life of Hong Kong in the past Responding to the challenges of the 21st century: Strategic planning of the senior primary English curriculum 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Use a wider variety of reading and listening materials Teach reading and listening skills explicitly Help students identify audience and writing purpose Require students to evaluate, synthesis and apply Provide chances for students to integrate skills Steps involved Skills developed Critical thinking & integrated skills – identify the problem & follow instructions 2. Read the blog Critical thinking & integrated skills – (Pre-task 1) locate, extract & transfer details 1. Explain the main task 3. Listen to the dialogue (Pre-task 2) Implications Analyse the task; identify audience & writing purpose Teach reading skills explicitly; broaden knowledge base (reading) Critical thinking & Teach listening integrated skills – skills explicitly; locate, extract, classify broaden & organise details knowledge base (listening) Steps involved Skills developed Implications 4. Search Critical thinking, Broaden knowledge details wide reading, base (self-directed from print independent reading & speaking) & non-print learning, cater for materials learner diversity & Develop skills to (Pre-task 3) integrated skills – communicate with extract, organise & different groups of synthesise details people from Pre-task 1 & Pre-task 2, search Provide chances for extra details by students to integrate setting own research different skills goals & conducting purposeful interviews 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Steps involved 5. Write & present details (Writing & speaking task) 6. Draw about future Hong Kong Skills developed Implications Integrated skills, assessment as learning & cater for learner diversity – present synthesised details using suitable text type features & structures in spoken & written forms, use peer evaluation to reflect own performance Enhance ability to use different skills in an integrated manner Raise sensitivity to play different roles appropriately in different situations Be reflective Creativity & cross Develop creativity curricular learning – give expression to Extend learning of experiences & link with English in other KLAs the Arts subject Writing + Reading + Listening + Speaking 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU R THREE STEPS to bring good changes to your curriculum Step 1: Review school development plan and include 8 issues in 2013-2014 plan 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LOLo&Stephanie WL CHU 23Jan13_Eng_Pri_LLSS_EDB_PY & WL Chu Cecilia Step 2: Write 8 issues in the 3-year plan (KS2) to give a progressive map for development, starting with the English subject 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU Step 3: Promote the development of different skills in an integrated manner 230113_EDB_LLSS_PY LO & WL CHU BY LLSS/EDB/CChu&SLo_2013 21世紀的學生更要學好母語 為學習及工作需要,他們要: 掌握書面語及口語,以便與內地交流 和連繫; 擁有良好的語文基礎,讓他們能學會 學習; 通過學習語文,培養思維等能力; 體認中國文化。 中、小學中國語文科學習目標 小一至中三 增進語文基礎知識及其他生活知識 培養讀寫聽說的基本能力 培養自學語文和創新思考的能力 培養審美情趣,陶冶性情 培養品德及對社群的責任感 中四至中六 / 為學生奠定良好的語文 基礎: (1)提高讀寫聽說及思維 能力; (2)培養學生自主學習; (3)培養正面的價值觀 中學文憑考試考核重點 卷別 考核重點 考核重點 21世紀學生 21世紀學生 特質 特質 卷一 主要考核考生閱讀能力,包括:理解、分析、感受、 掌握書面語及 主要考核考生閱讀能力,包括:理解、分析、感受、鑑 掌握書面語及 口語 鑑賞、運用不同策略等能力;重視思維和分析能力, 賞、運用不同策略等能力;重視思維和分析能力,並考 口語 並考核學生對中國文化、文學的認知和素養。 核學生對中國文化、文學的認知和素養。 卷二 卷二 主要考核學生構思、表達、創作力。 主要考核學生構思、表達、創作力。 具備思維能力 卷三 卷三 主要考核學生辨明說話者立場、觀點、論據、說話技 主要考核學生辨明說話者立場、觀點、論據、說話技巧、認識中國文化 巧、語氣等聆聽能力。 語氣等聆聽能力。 卷四 卷四 主要考核考生的 主要考核考生的口語表達、溝通與應對能力 口語表達、溝通與應對能力。 。 甲部 甲部 朗讀 朗讀 乙部 乙部 口語溝通 口語溝通 卷五 卷五 主要考核理解、思考、組織、 主要考核理解、思考、組織、文字表達 文字表達等能力。學生須 等能力。學生須聆 聆聽 聽 錄音、 閱讀 文字圖表後,再 寫作 。此卷試題多與 生活事有 錄音、 閱讀 文字圖表後,再 寫作 。此卷試題多與 生活事務 務 有關。 關。 在生活情境下, 在生活情境下, 綜合運用語文 綜合運用語文 能力 能力 具備思維能力 從了解學生 學習表現開始‥‥‥ 2012中學文憑考試學生表現 如何協助學生進一步提升語文能力? 2012中學文憑考試學生表現 學習重點 學生表現 能擷取資訊、分門別類 理解內容大意 理解 重視發音 能揣摩作品情感 大抵能辨識寫作和修辭手法 能按實用文題目要求的「情境」 確定目的、 寫作,包括:對象、格式、用語 內容、 表達方式 表達尚算清楚 組織結構 大致能掌握文章的結構和分段 運用聲調以表情達意; 按需要調節音量和語速 辨識不同性質的表達方法 按寫作需要確定寫作內容 用準確語言、禮貌用語說話 按重點分段及有條理表達 2012中學文憑考試學生表現 學習重點 學生表現 未能掌握文章的深層意義 理解 有考生缺乏基本文化常識, 致未能掌握作者的觀點 未能理解文言字詞或句式 確定目的、 內容、 表達方式 組織結構 立意平凡 內容單薄、空洞 聽出故事中的寓意 •不同題材的讀物:生活、 科普、 歷史、文化、藝術等 •涉獵不同題材的讀物/話語 •連繫生活經驗及已有知識 構思話語 用詞造句欠準確 應對一般 機械式的語言表達, 如:「我贊同‥‥‥」 按情境選擇得體的用語表達 取材蕪雜,未能切合主題 選取合適素材 2012中學文憑考試學生表現 學習重點 學生表現 分析和綜合 比較說明或發揮題,思維 能力不足 評價 (感受和鑒賞) 個人見解的題目時,表現 較弱 文學、文化基礎知識不足, 難理解題目或閱讀材料的 意思 其他 小學 •評價內容,如人物的性格行為 •運用聯想想像,產生新的意念 •不同題材的讀物:生活、 科普、 歷史、文化、藝術等 •涉獵不同題材的讀物/話語 •連繫生活經驗及已有知識 構思話語 錯別字較多 認讀常用字 (參《香港小學學習字詞表》) 不同學習階段,學習/評估要求高低有別 TSA 小三 TSA 小六 TSA 中三 DSE 中六 不同學習階段,閱讀材料的複雜性及深度不同 語文課程的學習/評估要求,超出基本能力 基本能力 白話 文言 不同性質的閱讀材料 相同學習重點,在不同學習段階反覆出現 理解 理解內容要點 TSA P6 風俗習慣 理解句子的意義和 在段落中的作用 理解 TSA S3 歷史故事 原文: 那柳堤本應桃花如雲,可惜我們來得不是時候,看不到一片豔豔的勝景,留下一 點遺憾,沿那曲岸枕水的長廊走去。蠡園絕少遊人,令人有一種悠然的心境,可 以慢慢地走,慢慢地品味。水氣從湖裏瀰漫而來,清涼清涼的。穿過空間的鈴聲, 是不是已經抵達彼岸?我玲玲瓏瓏地聽到心跳,於是,我放眼蠡湖,追蹤范蠡、 西施的足跡,但煙水茫茫,一片空濛,只有那不衰的笑聲,隱隱約約在湖中飄盪。 體會作者表達的思想感情 (闡釋內容與文章主旨的關係) 理解 人倫關係 DSE S6 龍應台《目送》 內容 主旨/作用 想一想 設計校本課程時,大家會考慮哪些 原則? ◦ 學習材料的深度(深層理解)?廣度 (多元化閱讀材料)? ◦ 重視基本能力的訓練?重視思維能 力訓練? ◦ 以評「促」教?以評「代」教? 小結 面對的挑戰 對策 • 閱讀材料題材/體裁單一 •拓寬閱讀面 • 偏重理解內容大意,忽略 •提高閱讀深度 引導學生思考文本中心 • 傾向單項能力訓練,缺少 綜合語文運用 • 應試操練的文化,影響課 程規劃與實踐 •全面規劃課程 (1)整體規劃:考慮學校整體課程的 發展 (2)訂定範圍:因應課程特點、學生 需要等,訂定三年的學習範圍 (3)布置評估:因應學校的情況和學 生的學習,訂定預期學生可達到 的學習成果,透過學與教的回饋, 提高學習 把握機遇.做好準備 把握機遇.做好準備 面對的挑戰 • 閱讀材料題材/體裁單一 對 策 •拓寬閱讀面 • 偏重理解內容大意,忽略 •提高深層理解能力 引導學生思考文本中心 •加強自學能力 • 傾向單項能力訓練,缺少 •全面規劃課程 綜合語文運用 • 應試操練的文化,影響課 程規劃與實踐 •善用課時,重學輕練 三年校本課程規劃示例 • 拓寬閱讀面 • 提高深層閱讀能力 • 提升思維能力 • 培養語文內涵與人文素質 • 培養自學能力 三年校本課程規劃示例 鞏固語文基礎能力 全面 規劃 課程 加強自學能力 閱讀 的廣 度和 深度 工作重點 全面規劃課程 鞏固 語文 基礎 能力 閱讀的廣度和 深度 加強自學能力 高小古典詩文的規劃與實踐現況 •依賴教材提供的選文 •閱讀廣度不足、量少 (體裁以古典寓言為主) •主題分散 •偏重文言字詞的解釋 •略教、少評 •未能貼近生活經驗 校本單元規劃示例 (以古典詩文單元為例) • 均衡培養聽、說、讀、寫能力 • 拓寬閱讀面 • 加強中華文化及品德情意的培育 • 跨學習領域和跨學科的元素 全面規劃課程 三年校本課程規劃示例 • 拓寬閱讀面 • 提高深層閱讀能力 • 提升思維能力 • 培養語文內涵與人文素質 • 培養自學能力 單元規劃示例 (以古典詩文單元為例) 全面規劃課程 年級 單元主題 學習材料 單元特色 小四 個人成長 (個人) 弟子規 培養品德、自理能力 小五 個人成長 (個人) 古典寓言 加強課程連繫 小六 友情有義 (群體) 小六 戰爭與和平 (世界) 文言、議論文 加強文化、品德元素 古詩、繪本 加強跨學科元素 三年校本課程規劃示例 • 拓寬閱讀面 • 提高深層閱讀能力 • 提升思維能力 • 培養語文內涵與人文素質 • 培養自學能力 鞏固語文基礎能力 如何提高對文本的深層理解能力? (1) 分析和綜合: • 分析、綜合內容; • 分析組織結構、寫作目的。 (2) 評價: • 評價內容,如人物的性格和行為。 (3) 探究和創新: • 在理解的基礎上,推斷閱讀材料以外 的內容和理解; • 運用聯想和想像,產生新的意念。 閱讀的深層理解:分析、綜合內容 人物 伯牙 鍾子期 擅長 伯牙善鼓琴 鍾子期善聽 他們是什麼關係? 何以見得? 有何例子? 課文中如何顯示伯 牙珍惜這段友誼? 知音人(知己好友) 伯牙所念,鍾子期必得之。 志在高山 峨峨兮若泰山 志在流水 洋洋兮若江河 子期死,伯牙謂世再無知音, 乃破琴絕弦,終身不復鼓。 閱讀的深層理解:分析、綜合內容 管寧 好朋友 華歆 事件(一): 管揮鋤與瓦石 共園中鋤菜, 華捉而擲去之 不異 見地有片金。 事件(二): 寧讀如故 歆廢書出看 同席讀書,有 乘軒冕過門者 結果:割席絕交 寧割席分坐,曰:「子非吾友也!」 三年校本課程規劃示例 • 拓寬閱讀面 • 提高深層閱讀能力 • 提升思維能力 • 培養語文內涵與人文素質 • 培養自學能力 閱讀的深層理解:評價和比較內容 (1) 為什麼伯牙要「絕弦」和管寧要「割席」? 從這兩件事中,你認為他們二人的「擇友」 原則是什麼? 伯牙 管寧 為什麼要「絕弦」/「割席」? 「擇友」的原則是什麼? (2) 伯牙和管寧二人有什麼優點值得我們學習? 人物 優點 伯牙 管寧 學習成果 因為伯牙認為世上再 無知音。 因為他認為華歆不是 他求學問道的朋友。 學習成果 志同道合 他交益友,不交損友。 學習成果 意志堅定,不受外界 的事容易影響自己 非常珍惜朋友 三年校本課程規劃示例 • 拓寬閱讀面 • 提高深層閱讀能力 • 提升思維能力 • 培養語文內涵與人文素質 • 培養自學能力 閱讀的深層理解:文本的主題思想 (1) 從《伯牙絕弦》這個故事中,你獲得了什麼 啟示? 我可以知道友誼永固,即使自己 的朋友死了,但仍然不忘記他對 自己的情誼。 我獲得了要珍惜好友的啟示。 珍惜眼前人和珍惜現在的朋友。 閱讀的深層理解:代入情境,發揮創意 (2) 如果你是伯牙,你又會如何紀念這位好朋友? 我會拿自己的琴在鍾子期的墳前 彈奏,然後把它永久放在墳前來 紀念這位好朋友。 我會為子期同自己的這段友誼作 一首詩來紀念子期。 我會幫他立個碑和在書桌上放了 我和他的拍照的相。 三年校本課程規劃示例 • 拓寬閱讀面 • 提高深層閱讀能力 • 提升思維能力 • 培養語文內涵與人文素質 • 培養自學能力 加強自學能力 忘年之交 私交甚篤 酒肉朋友 刎頸之交 金蘭之契 陳雷膠漆 金石之交 羊左之誼 珍惜 知己 刎頸之交 桃源結義 患難之交 友誼萬歲 莫逆之交 義氣 刎頸之交 珍貴 寶貴 義無反顧 加強自學能力 思維能力 現時,「上網」已是青少年消閒活動之一。 你贊成青少年在互聯網上的交友網站中結識 朋友嗎?為什麼? 立場 觀點 個人角度 家長角度 社會角度 贊成 理由 例證 反對 理由 例證 從語文教育到全人教育 均衡發展讀寫聽說能力。 誘發語文自學,加強語文積累。 藉著品德情意,發展思維能力。 滲入古典文學、中華文化元素,豐富 學習單元的語文內涵。 增加課程的語文內涵,提升學生的人 文素養。 The future is now Tips on planning the senior primary language curricula Set high but achievable expectations Increase learning load progressively Scaffold the learning process carefully Use stimulating and meaningful context for purposeful use of the target language Make coherence between the learning of language and other subjects/disciplines Tips on planning the senior primary language curriculum Professional development Support Holistic planning and effective implementation of the language curriculum School culture Curriculum Leadership Role of the school leaders Lead the teachers to develop the school curriculum holistically (across key stages and between subjects) Involve them in the EPIE process of curriculum development Create space for them to learn, collaborate, try out, reflect and celebrate A word of caution We are not advocating a ‘teach-to-the-test’ approach to curriculum planning & teaching The current assessment requirements are a reflection of the increasing complexity of the world our students will grow up in The NSSC and the assessment mirror the requirements for further study, work and life It’s important to plan the school-based curriculum early to equip our students with the knowledge, skills and attitudes needed to cope with those requirements and the 21st Century challenges http://cd1.edb.hkedcity.net/cd/languagesupport/ Where you can get further information … LLSS homepage Contact persons: Ms Amy POON E-mail: ayypoon@edb.gov.hk Mr. Sergio MEDEIROS E-mail: sergiomedeiros@edb.gov.hk Ms Christine CHOI E-mail: cylchoi@edb.gov.hk Mr.YT Lai E-mail: ytlai@edb.gov.hk LLSS publications Tel.: 3698 4093 Tel.: 3698 4024 Tel.: 3698 3981 Tel.: 3698 3994 References The Curriculum Development Council. (2002). Basic Education Curriculum Guide - Building on Strengths (Primary 1-Secondary 3). HKSAR: The Education Department. The Curriculum Development Council. (2002). English Language Education - Key Learning Area Curriculum Guide (Primary 1Secondary 3). HKSAR: The Education Department. The Curriculum Development Council. (2004). English Language Education Key Learning Area - English Language Curriculum Guide (Primary 1-6). HKSAR: The Education and Manpower Bureau. The Curriculum Development Council & The Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority. (2007). English Language Education KLA - English Language Curriculum and Assessment Guide (Secondary 4-6). HKSAR: The Education and Manpower Bureau. References The Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority. (2012). Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education Examination – English Language 2012 Examination Report & Question Papers. The Hong Kong Examinations and Assessment Authority. (2012). Hong Kong Diploma of Secondary Education Examination: English Language 2012 Practice Papers. The Curriculum Development Council. (2009). Senior Secondary Curriculum Guide - The Future is Now: from Vision to Realisation (Secondary 4-6). HKSAR: The Education and Manpower Bureau. OECD. (2012). Preparing Teachers and Developing School Leaders for the 21st Century – Lessons from Around the World. Retrieved 1 January, 2013, fromhttp://www.oecd.org/site/eduistp2012/49850576.pdf Presentation by Mmantsetsa Marope & Kai-ming Cheng on 21st Century Development Challenges and Opportunities: Demands on Education Systems 參考資料 課程發展議會編訂(2002)。《中國語文教育學習領域 課程指引》。 課程發展議會編訂(2007)。《中學中國語文建議學習 重點(試用)》 課程發展議。會編訂(2008)。《小學中國語文建議學 習重點(試用)》。 課程發展議會與香港考試及評核局聯合編訂(2007)。 《中國語文課程及評估指引(中四至中六)》。 香港文憑考試成績,見 http://www.hkeaa.edu.hk/DocLibrary/Media/PR/20120719 _HKDSE_Results_CHI_FULL.pdf 2011全港性系統評估閱讀卷題目,見 http://www.bca.hkeaa.edu.hk/web/TSA/zh/Introduction.ht ml Thank You!