*** The life of a cell from its origin in the... of a parent cell until its own division into two.
advertisement

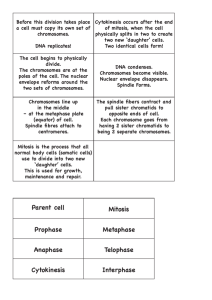
THE CELL CYCLE *** The life of a cell from its origin in the division of a parent cell until its own division into two. The major roles (functions) of cell division • 1. The continuity of life from one cell to another is based on the reproduction of cells via cell division. • 2. Cell division is also central to the development of a multicellular organism that begins as a fertilized egg or zygote. 3. Multicellular organisms also use cell division to repair and renew cells that die normally or by accidents. *** This division process occurs as part of the cell cycle. Cell division distributes the genetic material (DNA) to two daughter cells. Division is differ among cells: -Skin cells divide frequently. -Liver cells divide when needed (damage repair). -Nerve cells and muscle cells do not divide at all. How does Cell division distribute identical sets of chromosomes to daughter cells? • A cell’s genetic information (genome )البنك الـﭽينىis packaged as DNA. • DNA molecules are packaged into chromosomes. • A human cell must duplicate chromosomes so each daughter cell ends up with a complete genome. – Every eukaryotic species has a characteristic chromosomes in the nucleus. – Human somatic cells (body cells) have chromosomes. – Human gametes ( أمشاجsperm or eggs) have chromosomes, half the number in a somatic cell الخلية الجسدية. number of 46 23 *** • Each DNA molecule has hundreds or thousands of genes. • This DNA-protein complex (chromatin) is organized into a long thin fiber. • After the DNA duplication, chromatin coiling and folding to make chromosome smaller package • Each duplicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids which contain identical copies of the chromosome’s DNA. • The narrow region where the chromatids connect is called centromere. • Later, the sister chromatids are pulled apart and repackaged into two new nuclei. • Cytokinesis (division of cytoplasm) It occurs in somatic cells الخاليا الجسدية condenses, a Definitions Genes: *** The units that specify the inherited characters. Chromatin: A DNA-protein complex which is organized into a long thin fiber Chromosome: The package that formed of a condensed, coiled and folded chromatin (chromatids). Chromatids: Two sister chromatids are formed of duplicated chromosome. They contain identical copies of the chromosome’s DNA Centromere: The narrow region at which the two chromatids are connected together. Mitosis (somatic cells): Is the division process which forms two daughter cells , each with the same number of parent cell. Meiosis (In the gonads): is the division process which forms four daughter cells , each with half the chromosomes of the parent. Cytokinesis: is the division stage of the cytoplasm which usually follow mitosis The Mitotic Cell Cycle (division) • • A. *** The mitotic (M) phase of the cell cycle alternates تتبادلwith the much longer interphase المرحلة البينية. – The M phase includes mitosis and cytokinesis إنشطار السيتوبالزم. – Interphase accounts for 90% of the cell cycle. During interphase the cell prepares for division by producing cytoplasmic organelles and copying its chromosomes. Interphase has three subphases: 1. The G1 phase (“first gap”): the cell grows. B. 2. The S phase (“synthesis”): the chromosomes are copied. 3. The G2 phase (“second gap”): the cell completes preparations for cell division. Division phase (M). The cell starts the division process. *** Cell Cycle Interphase Division process (M phase) Cytokinesis Mitosis G1 S Prophase التمهيدية G2 Prometaphase قبل اإلستوائية Metaphase اإلستوائية Anaphase اإلنفصالية Telophase اإلنتهائية *** A. Mitosis: is usually include five sub-phases مراحل فرعية: Prophase, التمهيدية Prometaphase, قبل اإلستوائية Metaphase, اإلستوائية Anaphase, اإلنفصالية Telophase. اإلنتهائية • By late interphase (G2), the chromosomes have been duplicated تضاعفتbut are loosely packed. • The centrosomes have been duplicated and begin to organize microtubules into an aster (“star”). *** 1) Prophase - the chromosomes or joined sister chromatids are tightly coiled. - The mitotic spindle begins to form appears to push the centrosomes away from each other towards opposite ends (poles) of the cell. 2) Prometaphase - the nuclear envelope fragments. - spindle fibers from each pole attach to centromeres. 3) Metaphase the spindle fibers push the sister chromatids until they are all arranged at the imaginary equator plane between the poles. 10 • Anaphase *** - the centromeres divide, result in separating the sister chromatids into 2 chromosomes. - each chromosome is then pulled toward the pole by spindle fibers. - by the end, the two poles have equivalent chromosomes. • Telophase the cell continues to elongate however each centrosome pushs off each other. 1) 2) 3) Two nuclei begin to form, surrounded by the fragments of the parent’s nuclear envelope. Chromatin becomes slightly uncoiled. Cytokinesis, begins as the division of the cytoplasm occurs. 11 B. The cytokinesis: إنشطار السيتوبالزمdivides the cytoplasm: • Cytokinesis (division of the cytoplasm) typically follows mitosis. • In animals, the first sign of cytokinesis (cleavage )إنغماد is the appearance of a cleavage furrow in the cell surface near the old metaphase plate. • Contraction إنقباضof the ring pinches the cell into two 13 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL LIFE CYCLES The Role of Meiosis in Sexual Life Cycles *** Meiosis reduces chromosome number from diploid to haploid *** (Reduction Division) It occurs mainly in sex gonads to form Gametes (sperms and ova) Many steps of meiosis resemble steps in mitosis. Meiosis reduces chromosome number by copying the chromosomes once, but dividing twice (meiosis I and meiosis II). The first division (meiosis I) separates homologous chromosomes. The second (meiosis II) separates sister chromatids. Each final daughter cell has only half chromosomes number (haploid (فردى. 15 Meiosis *** A)- Meiosis I interphase the chromosomes replicated to form sister chromatids. are 1) Prophase I, - the chromosomes condense and homologous chromosomes pair up to form tetrads. Homologous (synapsis )التشابك. chromosomes attached together - (internal) Chromatids of homologous chromosomes are crossed (chiasmata) and segments of the chromosomes are exchanged (Crossing Over). 2) Metaphase I - the tetrads are all arranged at the metaphase plate. - Microtubules (spindle) from one pole are attached to the centromere of one *** chromosome of each tetrad, while those from the other pole are attached to the other centromere. 3) Anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate and are pulled toward opposite poles. *** 4) Telophase I movement of homologous chromosomes continues to each pole. – Each chromosome consists of linked sister chromatids. Cytokinesis • by the same mechanisms as mitosis usually occurs simultaneously. B)- Meiosis II *** . 1) Prophase II: spindle fibers attaches to centromers of each sister chromatids, and moves them around. • 2) Metaphase II: the sister chromatids are arranged at the metaphase plate. • 3) Anaphase II: the sister chromatids separate into 2 chromosomes each one travels toward opposite poles. and *** 4) Telophase II separated sister chromatids arrive at opposite poles. – Nuclear envelop forms around the chromatids. • Cytokinesis • Divide of the cytoplasm. • At the end of meiosis, there are four haploid daughter cells.